| Constituent | Effect | Critical concentration ( mg / L ) |
| Suspended solids | May cause sludge deposits or interfere with receiving water clarity | Variable |
| Biodegradable organics | May deplete oxygen resources | Variable |
| Priority pollutants |
- Toxic to humans and carcinogenic - Toxic to aquatic environment |
- Varies by individual constituent - Varies based on presence in water column, biota, or sediment |
| Volatile organic compounds | Toxic to humans, carcinogenic, form photochemical oxidants ( smog ) | Varies by individual constituent |
| Ammonia |
- Increases chlorine demand, can be converted to nitrates and, in the process, can deplete oxygen resources, with
phosphorus, can lead to the development of undesirable aquatic growths - Toxic to fish |
- Any amount - Variable |
| Nitrate |
- Stimulates algal and aquatic growth - Can cause methemoglobinemia in infants ( blue babies ) |
- 0.3 - 45 |
| Phosphorus |
- Stimulates algal and aquatic growth - Interferes with coagulation - Interferes with lime - soda softening |
- 0.015 - 0.2 - 0.4 - 0.3 |
| Calcium and magnesium | Increase hardness and total dissolved solids | Variable |
| Chloride |
- Imparts salty taste - Interferes with agricultural and industrial processes |
- 250 - 75 - 200 |
| Sulfate | Cathartic action | 600 - 1,000 |
| Surfactants | Cause foaming and may interfere with coagulation | 1.0 - 3.0 |
| Principal removal function | Description of operation or process | Type of wastewater treated |
| Suspended solids removal | - Filtration - Microstrainers |
- EPT, EST - EST |
| Ammonia oxidation | Biological nitrification | EPT, EBT, EST |
| Nitrogen removal | Biological nitrification / denitrification | EPT, EST |
| Nitrate removal | Separate stage biological denitrification | EST + nitrification |
| Biological phosphorus removal |
- Mainstream phosphorus removal - Sidestream phosphorus removal |
- RW, EPT - RAS |
| Combined nitrogen and phosphorus removal by biological methods | Biological nitrification / denitrification and phosphorus removal | RW, EPT |
| Nitrogen removal by physical or chemical methods |
- Air stripping - Breakpoint chlorination - Ion exchange |
- EST - EST + filtration - EST + filtration |
| Phosphorus removal by chemical addition |
- Chemical precipitation with metal salts - Chemical precipitation with lime |
- RW, EPT, EBT, EST - RW, EPT, EBT, EST |
| Toxic compounds and refractory organics removal |
- Carbon adsorption - Activated sludge + powdered activated carbon - Chemical oxidation |
- EST + filtration - EPT - EST + filtration |
| Dissolved inorganic solids removal |
- Chemical precipitation - Ion exchange - Ultrafiltration - Reverse osmosis - Electrodialysis |
- RW, EPT, EBT, EST - EST + filtration - EST + filtration - EST + filtration - EST + filtration + carbon adsorption |
| Volatile organic compounds | Volatilization and gas stripping | RW, EPT |
|
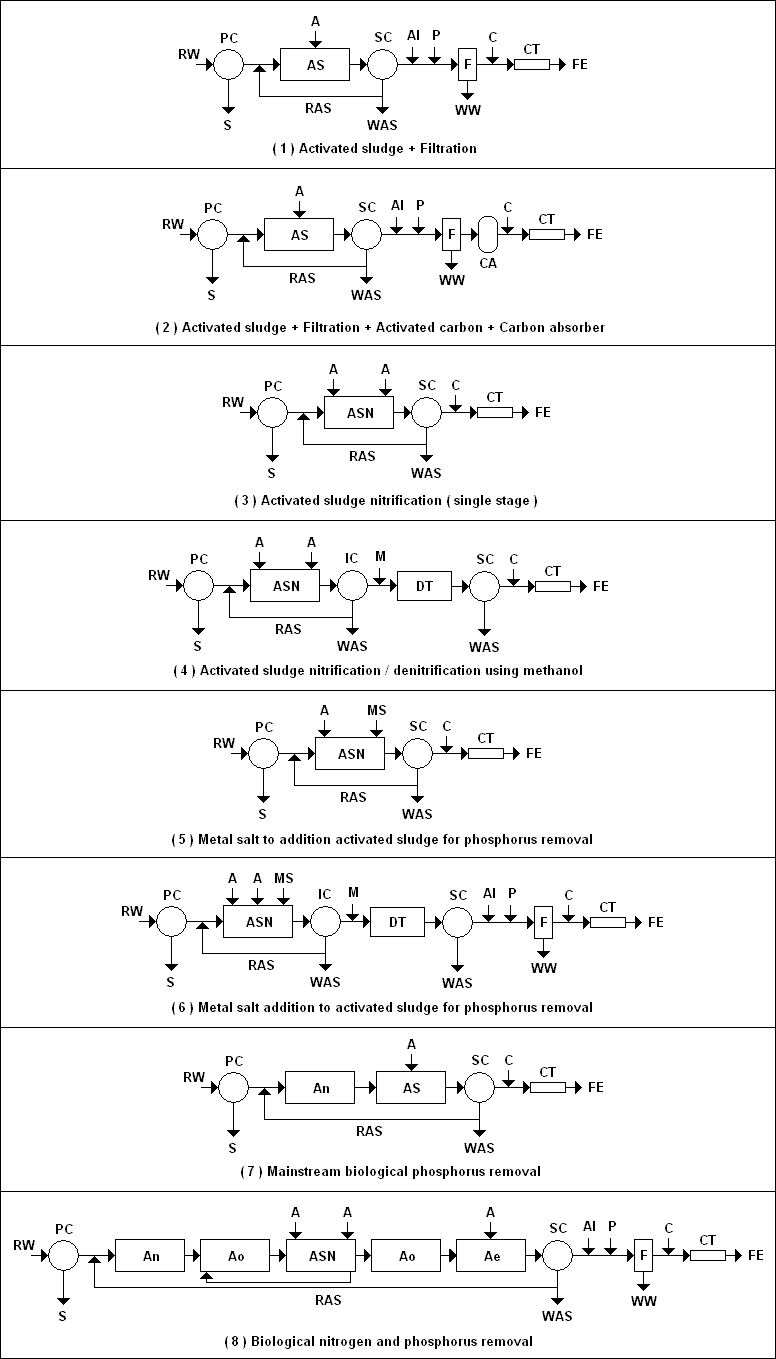
EPT : Effluent from primary treatment EBT : Effluent from biological treatment ( before clarification ) EST : Effluent from secondary treatment ( after clarification ) RW : Raw ( untreated ) wastewater RAS : Return activated sludge |

| A : Air |
| Ae : Aerobic tank |
| Al : Alum |
| An : Anaerobic tank |
| Ao : Anoxic tank |
| AS : Activated sludge |
| ASN : Activated sludge nitrification |
| C : Chlorine |
| CA : Carbon absorver |
| CT : Contact tank |
| DT : Denitrification tank |
| F : Filter |
| FE : Final effluent |
| IC : Intermediate clarifier |
| M : Methanol |
| MS : Metal salt |
| P : Polymer |
| PC : Primary clarifier |
| RAS : Return activated sludge |
| RW : Raw wastewater |
| S : Sludge |
| SC : Secondary clarifier |
| WAS : Waste activated sludge |
| WW : Washwater |
| Treatment operation or process | Organic nitrogen | NH3/NH4+ | NO3- | Removal of total nitrogen entering process ( % ) |
| Conventional treatment | ||||
| Primary | 10 - 20 % removed | No effect | No effect | 5 - 10 |
| Secondary |
15 - 50 % removed urea====>NH3/NH4+ |
< 10 % removed | Slight effect | 10 - 30 |
| Biological processes | ||||
| Bacterial assimilation | No effect | 40 - 70 % removed | Slight effect | 30 - 70 |
| Denitrification | No effect | No effect | 80 - 90 % removed | 70 - 95 |
| Harvesting algae | Partial transformation to NH3/NH4+ | ====>Cells | ====>Cells | 50 - 80 |
| Nitrification | Limited effect | ====>NO3- | No effect | 5 - 20 |
| Oxidation ponds | Partial transformation to NH3/NH4+ | Partial removal by stripping | Partial removal by nitrification - denitrification | 20 - 90 |
| Chemical processes | ||||
| Breakpoint chlorination | Uncertain | 90 - 100 % removed | No effect | 80 - 95 |
| Chemical coagulation | 50 - 70 % removed | Slight effect | Slight effect | 20 - 30 |
| Carbon adsorption | 30 - 50 % removed | Slight effect | Slight effect | 10 - 20 |
| Selective ion exchange for ammonium | Slight, uncertain | 80 - 97 % removed | No effect | 70 - 95 |
| Selective ion exchange for nitrate | Slight effect | Slight effect | 75 - 90 % removed | 70 - 90 |
| Physical operations | ||||
| Filtration | 30-95 % of suspended organic N removed | Slight effect | Slight effect | 20 - 40 |
| Air stripping | No effect | 60 - 95 % removed | No effect | 50 - 90 |
| Electrodialysis | 100 % of suspended organic N removed | 30 - 50 % removed | 30 - 50 % removed | 40 - 50 |
| Reverse osmosis | 60 - 90 % removed | 60 - 90 % removed | 60 - 90 % removed | 80 - 90 |
| Treatment process | Typical effluent quality | ||||||
| SS (mg/L) | BOD5 (mg/L) | COD (mg/L) | Total N (mg/L) | NH3-N (mg/L) | PO4-P (mg/L) | Turbidity (NTU) | |
| Activated sludge + granular medium filtration | 4-6 | <5-10 | 30-70 | 15-35 | 15-25 | 4-10 | 0.3-5 |
| Activated sludge + granular medium filtration + carbon adsorption | <3 | <1 | 5-15 | 15-30 | 15-25 | 4-10 | 0.3-3 |
| Activated sludge / nitrification, single stage | 10-25 | 5-15 | 20-45 | 20-30 | 1-5 | 6-10 | 5-15 |
| Activated sludge / nitrification - denitrification, separate stages | 10-25 | 5-15 | 20-35 | 5-10 | 1-2 | 6-10 | 5-15 |
| Metal salt addition to activated sludge | 10-20 | 10-20 | 30-70 | 15-30 | 15-25 | <2 | 5-10 |
| Metal salt addition to activated sludge + nitrification - denitrification + filtration | 5-10 | 5-10 | 20-30 | 3-5 | 1-2 | <1 | 0.3-3 |
| Mainstream biological phosphorus removal | 10-20 | 5-15 | 20-35 | 15-25 | 5-10 | <2 | 5-10 |
| Mainstream biological nitrogen and phosphorus removal + filtration | <10 | <5 | 20-30 | <5 | <2 | <1 | 0.3-3 |
| Treatment operation or process | Removal of phosphorus entering system ( % ) |
| Conventional treatment | |
| Primary | 10 - 20 |
| Activated sludge | 10 - 25 |
| Trickling filter | 8 - 12 |
| Rotating biological contactors | 8 - 12 |
| Biological phosphorus only | |
| Mainstream treatment | 70 - 90 |
| Sidestream treatment | 70 - 90 |
| Combined biological nitrogen and phosphorus removal | 70 - 90 |
| Chemical removal | |
| Precipitation with metal salt | 70 - 90 |
| Precipitation with lime | 70 - 90 |
| Physical removal | |
| Filtration | 20 - 50 |
| Reverse osmosis | 90 - 100 |
| Carbon adsorption | 10 - 30 |
