(i) Screening
(ii) Grit removal
(iii) Flow equalisation
(iv) Primary settling
(v) Secondary settling following biological treatment
(vi) Filtration
(a) Describe the function of each unit operation in turn. Include a description of the equipment used for each unit operation as part of your discussion.
(b) Describe a unit operation that could be used to thicken the waste sludge from the biological treatment unit.
Q - 2 : Compare the disinfectants chlorine, ozone and uv radiation using the criteria listed below :
(a) Toxicity to mircoorganisms (describe how disinfection is achieved)
(b) Solubility
(c) Toxicity to higher life forms
(d) Interaction with extraneous matter
(e) Toxicity at ambient temperature
(f) Penetration
(g) Availability
(h) Environmental impact
(i) Additional benefits / drawbacks
Q - 3 : You have selected a process to recover a valuable metal from a process stream in a printed-circuit-board manufacturing process. Write a summary report for your boss using the following headings :
(a) Process description
(b) Equipment required
(c) Advantages and disadvantages of the process
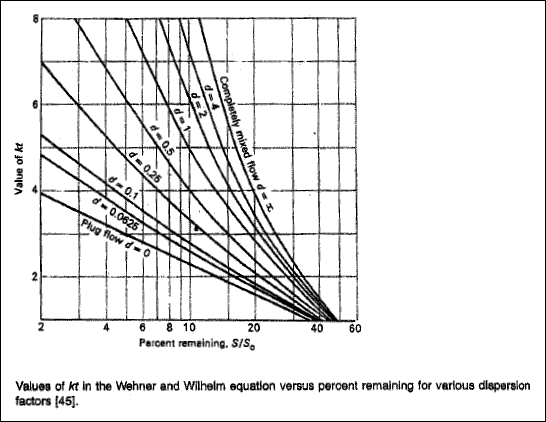
Q - 4 : It has been found that the observed die-off coefficient for E.coli in biological stabilization ponds can be described adequately with first order kinetics. Assuming that the value of the specific reaction-rate constant is 1.0 d-1, determine the concentration of E.coli in the effluent from a series of three ponds, when the initial concentration, N0, is 106 organism / mL and the average flowrate is 1.32 Mgal / day. The ponds are rectangular and have an average depth of 5 ft. The surface areas of the ponds are 2.5, 5.0, and 2.5 acres respectively. The dispersion factor for the small ponds is 0.5 and 0.25 for the large pond. t is the pond retention time (days).
Data Sheet :
7.48 gal = 1 ft3
1 acre = 43,560 ft2
Q - 5 : The design of a complete mix activated sludge process to treat 5.71 Mgal / day of settled wastewater with 250 mg / L of BOD5 is to be considered. The effluent is to have 20 mg / L of BOD5. Calculate :
(i) The concentration of soluble BOD5 in the effluent.
(ii) The reactor volume.
(iii) The quantity of sludge to be wasted each day.
(iv) Compute the sludge wasting rate if wasting is accomplished from the reactor.
(v) Compute the hydraulic retention time for the reactor.
(vi) Compute the oxygen requirements based on BODL. ( Neglect O2 requirements for Nitrification ).
(vii) Calculate the F / M ratio.
(viii) Compute the volume of air required per minute, assuming that the oxygen efficiency for the aeration equipment to be used is 8 %. A safety factor of 2 should be used to determine the actual design volume for blower sizing.
Data Sheet :

Q - 6 : A municipal waste having a BOD5 of 200 mg / L is to be treated by a two stage trickling filter. The desired effluent quality is 25 mg / L of BOD5. If both the filters are to be 6 ft deep and the re-circulation ratio is 2 : 1, find the required filter diameters. Calculate the BOD5 loading to each filter ( lb / ft3 ). Calculate the hydraulic loading to each filter ( gal / ft2 min ). If rotary distributor mechanisms are to be utilised suggest modified filter diameters.
Data Sheet :
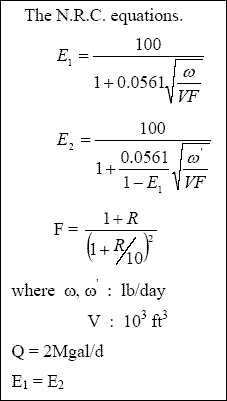
Q - 7 : Questions :
(a) Describe the two fundamental approaches to the control of air pollution at source.
(b) Another control method is to rely on dilution. Discuss the various parameters that will influence how effective this method will be.
(c) Which of the three methods you have outlined above will be the most effective in the prevention of pollution.
Q - 8 : Questions :
(a) List the various ways in which pollutants, both particulate and gaseous, are released into the atmosphere.
(b) Describe the effects both types of pollutant will have on the plants and animals exposed to them.
(c) How is the earth in general affected by these pollutants ?
