Design, Construction, and Operation of the Small Wastewater Systems - 05...
Chapter 05 - Treatment Design Considerations...
5-1. General...
This chapter identifies treatment design considerations for wastewater treatment facilities and/or plants with relatively
small capacities, those constructed in recreational areas with wastewater flows less than 379,000 L/d (100,000 gal/d).
(Note: these considerations generally apply to large treatment facility planning as well.) Factors to be considered in the
preparation of a design for small wastewater facilities include site selection, treatment system selection, and design
steps. Site selection considerations are presented in Chapter 2, and certain design steps and process selection criteria
are to be found throughout Chapter 7. For proper design it is mandatory to know the quantity of wastewater to be expected
(see paragraph 3-4), the monthly and daily flow distributions (see paragraph 3-5), as well as the wastewater composition,
constituents, and strength (see paragraph 3-6).
5-2. Small Individual Units...
( a ) Pit privy.
( 1 ) Historically the pit privy has been the simplest and most commonly used wastewater treatment device. It is a
non-water carrying unit which has been developed to store human waste from a single building or several small buildings
without other sanitary facilities. In brief, a pit privy is a dug hole over which an outhouse has been built. Privy
construction should be limited to low use or highly remote areas, as for all intents and purposes, privies have been
replaced by "Port-a-Johns" or chemical toilets which may be easily transported by truck from one location to another during
periods of high use. To be effective, pit privys must be pumped out from time to time and the septage trucked to a larger
holding tank or wastewater treatment plant (see paragraph 4-3). The privy waste, consisting primarily of human excreta,
is generally referred to as "blackwater", as opposed to the "graywater" generated by water-using fixtures such as showers
and lavatories.
( 2 ) Design considerations for pit privies include additional requirements such as animal- or rodentproofing. Privy
contents should not be permitted to overflow onto the ground surface, and surface drainage should be directed away from the
privy site. The privy site should be constructed on raised concrete slab, and preferably located well above the underlying
groundwater table. The privy structure should be constructed of durable wood or molded plastic and built to last 10-15
years.
( 3 ) There is no generally accepted standard privy design. Unlined pits of short length, width and depths are simply dug
and covered with a fabricated (plastic or wooden) structure resting on a concrete slab with apertures or holes in wooden or
plastic seats. For general information regarding options and guidelines for pit privies consult USDA-1 and USDA-2.
( b ) Vault toilets.
( 1 ) Simple vault toilets, or outhouses over enclosed chambers, are most often used for remote-site wastewater treatment.
The toilets are located in vented structures under which is a below-ground enclosed and preferably watertight chamber
fabricated to prevent both infiltration and exfiltration. The terms vault toilet and pit privy are often used
interchangeably: both must be periodically pumped out; both have associated odor problems; both are the receptacles for
rags, cans, trash, bottles, plastic, meal containers, and almost any throw-away objects or items carried by users; both attract disease vectors; both have the potential for contaminating the groundwater resources; both require frequent
oversight; both often require addition of chemical additives. Except under unusual circumstances, use of pit privys and
vault toilets should be discouraged when construction of modern wastewater treatment facilities is being considered.
( 2 ) Improved aerated vault toilets have been in operation at a number of Army facilities for over 20 years. Various types
of air compressors and blowers, including diffuser types, have been successfully used at these facilities. The two most
accepted types of aeration system configuration are bubble aeration and mechanical aeration. Bubble aerators are
belt-driven, lubrication-free, carbon-vaned blowers. Blower inlets must be provided and fitted with a replaceable-element
air filter. Blower outlets must be connected to a perforated air distribution pipe mounted along the vault floor. Air must
be continuously supplied to mix wastes and supply oxygen.
( 3 ) The alternative method for aerating a vault toilet is mechanical, i.e., mixing of the wastes using a motor-driven
impeller combined with injection of air below the vault liquid surface. The entire unit is mounted on a float which rides
on the waste surface, thereby maintaining a constant immersion depth for the impeller. When operating, the impeller creates
a vortex which lowers the pressure at the end of the hollow shaft driving the impeller and allows the atmospheric pressure
to draw air down the shaft and into the liquid waste where it is mixed by the vortex. Of the two systems, the bubble
aeration system appears to have fewer design and operating problems.
( 4 ) Both bubble and mechanical type aeration devices require electric power. Unlike composting toilets (see paragraph
5-2c below), these two systems require too much energy on a continuous basis to make solar power practical.
( 5 ) General design information for vault toilets can be found in USACERL 1984, USDA-1, and USDA-4. General information
regarding options and guidelines for the selection of vault toilets can be found in USDA-2 and USDA-4.
( c ) Composting toilets.
( 1 ) Composting is the controlled decomposition of organic material into humus. The organic materials are converted to a
more stable form by either aerobic decomposition or anaerobic fermentation. Most composting toilets are designed for
continuous aerobic decomposition of human waste. As flushing of waste is not provided for, no water is introduced into the
composting chamber, which receives fecal matter, urine, toilet tissue and a bulking agent (sometimes sawdust). Composting
generally decreases the volume of the waste. Electricity must be made available for ventilation. Ventilation consists of a
vent pipe and fan system to remove carbon dioxide, water vapor, and air from the composting chamber. Composting toilets
have capacities for 2 to 25 persons with 2- to 6-person capacities being the most common. Electrical heating elements are
usually provided for cold-weather climates. Where solar energy is available or feasible, it should be used for heating and
ventilation (Clivus Multrum, a patented process). Composting toilets may be used as alternatives to pit privies, vault
toilets, or chemical toilets.
( 2 ) General design information for composting toilets can be found in USACERL 1984, USDA-4, and USDA-5.
( d ) Septic tank systems.
( 1 ) The septic tank has been successfully employed for well over a century, and it is the most widely used on-site
wastewater treatment option. Septic tanks are buried, watertight receptacles designed and constructed to receive wastewater
from the structure to be served. The tank separates solids from the liquid, provides limited digestion of organic matter,
stores solids, and allows the clarified liquid to discharge for further treatment and disposal. Settleable solids and
partially decomposed sludges accumulate at the bottom of the tank. A scum of lightweight material (including fats and
greases) rises to the top of the tank’s liquid level. The partially clarified liquid is allowed to flow through an outlet
opening positioned below the floating scum layer. Proper use of baffles, tees, and elbows protects against scum outflow.
Clarified liquid can be disposed of to soil absorption field systems, soil mounds, lagoons, or other disposal systems.
( 2 ) Factors to be considered in the design of a septic tank include tank geometry, hydraulic loading, inlet and outlet
configurations, number of compartments, temperature, and operation and maintenance practices. If a septic tank is
hydraulically overloaded, retention time may become too short and solids may not settle properly.
( 3 ) Both single-compartment and multi-compartment septic tank designs are acceptable. Baffled or multi-compartment tanks
generally perform better than single-compartment tanks of the same total capacity, as they provide better protection against
solids carryover into discharge pipes during periods of surges or upsets due to rapid sludge digestion. Poorly designed or
placed baffles create turbulence in the tank which impairs the settling efficiency and may promote scum or sludge entry into
the discharge pipes.
( 4 ) Septic tanks, with appropriate effluent disposal systems, are acceptable where permitted by regulatory authority and
when alternative treatment is not practical. When soil and drainage characteristics are well documented for a particular
site, septic tank treatment is eminently feasible for small populations. Septic tanks are effective in treating from one to
several hundred population equivalents of waste, but should generally be used only for 1 to 25 population equivalents,
except when septic tanks are the most economical solution for larger populations within the above range. The minimum tank
size is at least 1,900-L (500-gal) liquid capacity. In designing tanks, the length-to-width range should be between 2:1
and 3:1, and the liquid depth should be between 1.2 and 1.8 m (4 and 6 feet). When effluent is disposed of in subsurface
absorption fields or leaching pits, a minimum detention time in the tank based on average flows is generally required.
Different states have specific detention time requirements. Table B-2 identifies the states which have specific septic tank
design requirements.
( 5 ) The septic tank must be sized to provide the required detention (below the operating liquid level) for the design
daily flow plus an additional 25 percent capacity for sludge storage. If secondary treatment, such as a subsurface sand
filter or oxidation pond or constructed wetland is provided, the detention period may be reduced. Open sand filter treatment
of septic tank effluent can further reduce the required detention time. Absorption field and leaching well disposal should
normally be limited to small facilities (less than 50 population equivalents). If the total population equivalent is over
50, then more than one entirely separate absorption field would be acceptable. For ten or more population equivalents,
discharge of effluent will be through dosing tanks which periodically discharge effluent quantities of up to 80 percent
of the absorption system capacity.
( 6 ) Combined septic tank and recirculating sand filtration systems have been shown to be effective in providing a
closed-loop treatment option for either a single or a large septic tank or a multiple series of small tanks. The septic
effluent is directed to a recirculation tank from which it is discharged by a sump pump to a sand filter contained in a
open concrete box which permits no seepage to the local groundwater table. The recirculation pump discharge enters a
multiple-pipe distribution device of manifold-lateral design overlying the sand bed. The discharge is sprayed, or trickles,
onto a sand bed underlaid by graded gravel through which underdrain piping collects the filtered wastewater and returns to
the same recirculation tank. Ultimately, the wastewater can be discharged to a receiving stream following disinfection, or
to a leaching or absorption field. The design of a septic tank system discharging to surface waters normally includes sand
filtration to lower the concentrations of suspended solids and BOD 5 to acceptable levels. Ammonia-nitrogen
concentration in the effluents may be high, especially during winter months.
( 7 ) Design features for various septic tank systems including leaching or adsorption fields and mound systems can be
found in Burs 1994, Converse 1990, EPA/825/1-80/012, EPA/625/R-92/010, Kaplan 1989, Kaplan 1991, OSU 1992, and Perkins 1989.
( e ) Imhoff tanks.
The Imhoff tank is a primary sedimentation process which performs two functions, the removal of settleable solids and the
anaerobic digestion of those solids. In these respects, the Imhoff tank is similar to a septic tank. The difference is that
the Imhoff tank consists of a two-story tank in which sedimentation occurs in the upper compartment and the settled solids
are deposited in the lower compartment. Solids pass through a horizontal slot at the bottom of sloping sides of the
sedimentation tanks to the unheated lower compartment for digestion. Scum often accumulates in the sedimentation chamber,
where it may be skimmed off manually. Digestion-produced gases rise vertically, and with a properly designed overlapping
sloping wall arrangement, are directed through length-wise vents on either side of the horizontal sedimentation chamber.
Thus, gases and any entrapped sludge particles rise to the upper compartment liquid surface from the bottom sludge and do
not interfere with the sedimentation process in the upper compartment. Accumulated or digested sludges are withdrawn from
the lower compartment by hydrostatic head through a simple vertical piping system. Sludges must be disposed of after being
dried on sand drying beds or other approved systems.
5-3. Conventional Wastewater Treatment Facilities...
Conventional wastewater treatment refers to a complete biological wastewater treatment process that includes flow
measurement and equalization, primary and secondary sedimentation treatment, biological treatment, and effluent
disinfection. The following paragraphs present a discussion of the various unit processes and design considerations for
conventional wastewater treatment processes as well as pretreatment considerations. A description of flow monitoring devices
is presented in Chapter 6.
( a ) Oil and grease interceptors.
( 1 ) When restaurants, laundromats and/or service stations are located within the sewer collection system, but away from
the camping or tenting or recreational areas, the liquid wastes discharged to a treatment facility typically contain oil
and grease, cleaning agents, and organic material from kitchen sink garbage disposal units which interfere with the
treatment process effectiveness. Grease is usually collected in interceptor traps using cooling and/or flotation, while
oils are intercepted by flotation. For effective flotation, a grease interceptor trap or and oil/water separator should be
designed with a minimum detention time of 30 minutes (Metcalf & Eddy 1991).
( 2 ) In remote areas where many small treatment plants have been constructed, oil- and grease-related operations and
maintenance problems sometimes arise once the facilities are in full use. Therefore, the selection of effective
low-maintenance solutions for collecting oils and greases is of paramount importance when designing a wastewater treatment
system for such locations.
( b ) Preliminary treatment.
Preliminary treatment is the conditioning of a waste stream to partially reduce or remove constituents that could otherwise
adversely affect the downstream treatment processes. Preliminary treatment processes include coarse screening, comminutor,
grit removal, and flow equalization.
( 1 ) Coarse screening.
( a ) Coarse screening includes both manually and mechanically cleaned bar racks. Mechanical screens have generally
replaced the hand-cleaned racks. Manual labor is required to reduce rack clogging and clean the bar racks by vertically
pulling the collected debris with rakes or tongs onto a perforated plate on top of the rack and then disposing of the
rakings. Mechanically cleaned racks are divided into four types: chain operated; reciprocating rake; catenary; and cable.
Some mechanically cleaned racks are cleaned from the upstream face and some from the downstream face. Chain, rake,
catenary, or cable cleaning devices usually operate on set timing sequences and are not necessarily flow dependent.
( b ) Screenings are the floating or suspended material collected and retained on bar racks. The quantity of screening
retained increases with smaller openings between bars. Coarse screenings typically retained on racks or bars with spacings
greater than or equal to 13 mm (0.5 in) include plastics, rags or fibrous materials, rocks, floating wood, lawn waste or
plant cuttings, and other miscellaneous materials which find their way into sanitary sewers.
( c ) Typical design information for hand and manually cleaned racks can be found in Droste 1997, Metcalf & Eddy 1991,
Reynolds 1995, and WEF MOP-8.
( 2 ) Comminutors.
( a ) Comminutors are adjuncts to bar racks or screens and sometimes are alternatives to the coarse screening devices. Most
contemporary designs consist of vertical revolving-drum screens. All designs, irrespective of efficiency, are equipped with
high-quality metal cutting disks or teeth which periodically require sharpening.
( b ) Comminutors are continuously operating devices for catching and shredding heavy, solid, and fibrous matter; the
suspended material is cut into smaller, more uniform sizes before it enters the pumps or other unit processes. Some fibrous
material which is shredded or cut may later recombine into ropelike pieces following comminution.
( c ) Typical design information for comminutors can be found in Metcalf & Eddy 1991, Reynolds 1995, and WEF MOP-8.
( 3 ) Grit removal.
( a ) Grit is the heavy suspended mineral matter present in wastewater (sand, gravel, rocks, cinders), which is usually
removed in a rectangular horizontal-flow detention chamber or in the enlargement of a sewer channel. The chamber may be
aerated to assist in keeping the influent wastewaters from becoming septic. Detention reduces the velocity of the influent and permits separation of the heavier material by differential settling. A mechanical grit collection system may be
provided to collect the grit and convey it to a point of collection adjacent to the grit chamber, usually a metal can or
dumpster. Vortex-type grit chambers may also be employed. Manually cleaned, gravity grit chambers are not considered
state-of-theart and generally should not be included in modern wastewater treatment plant design.
( b ) Typical design information for horizontal flow and aerated grit chambers can be found in WEF MOP-8, and in Metcalf
& Eddy 1991 for vortex-type grit chambers.
( 4 ) Flow equalization.
( a ) Flow equalization is a method of retaining wastes in a separately constructed basin such that the basin effluent is
reasonably uniform in flow and wastewater characteristics or strength. The purpose of equalization is to average, dampen,
or attenuate the flow and composition of the waste stream. In effect, the equalizing or holding basin is a balancing
reservoir. Equalization tanks may be either in-line, or single basin, in which the influent flows directly into and is
directly drawn off from the basin; or sideline, which employs two basins, the larger usually serving as the prime
equalization basin and the other as a pump wet well.
( b ) Equalization basins may be placed off-line in the collection system, after headworks, or at a point to following
primary clarification (and before advanced treatment, if any).
( c ) Techniques for sizing equalization basins include the mass-diagram for hydraulic purposes, and statistical techniques
and interactive procedures for hydraulic and organic conditions. Although mixing of basin influent is not always provided,
mixing methods include surface aeration, diffused air aeration, turbine mixing, and inlet flow distribution and baffling.
( d ) Typical design information for equalization can be found in Metcalf & Eddy 1991 and WEF MOP-8.
( c ) Primary sedimentation treatment.
( 1 ) In a conventional wastewater treatment plant, primary sedimentation is employed to remove settleable particulate and
colloidal solid material from raw wastewater. The principal design considerations for primary clarification or sedimentation
basins are horizontal flow cross-sectional areas, detention time, side water depth and overflow rate. Efficiency of the
clarification process is significantly affected by the wastewater characteristics, suspended solids concentration, the
number and arrangements of basins, and variations in the inflow.
( 2 ) Settling basin designs must provide for effective removal of suspended solids from the wastewaters which have already
passed through the preliminary process units (screens, grit chambers, comminutors, equalization basins), and collection and
removal of settled solids (sludge) from the basin. Short-circuiting of flows in sedimentation should be avoided whenever
possible.
( 3 ) Basin design should consider the following factors: basin inlet and outlet velocities; turbulent flow; wind stresses,
if any; temperature gradients; and basin geometry.
( 4 ) Principal design considerations should also ensure evenly distributed inlet flow with minimal inlet velocities to
avoid turbulence and short-circuiting; quiescent conditions for effective particle and suspension settling; sufficient
basin depth for sludge storage to permit sufficient or desired thickening; mechanical sludge scrapers (horizontal or
circular) to collect and remove the sludges; and minimum effluent velocities by limiting weir loadings and by proper weir
leveling and placement. Plain sedimentation horizontal flow basins may be either circular or rectangular. The preferred
minimum diameter of circular clarifiers in small conventional wastewater treatment plants is 3 m (10 ft), and a like
dimension for the sidewater depth.
( 5 ) Typical design information for primary sedimentation basins can be found in Droste 1997, Metcalf & Eddy 1991, Reynolds
1995, and WEF MOP-8.
( d ) Secondary sedimentation treatment.
( 1 ) Secondary sedimentation or final clarification is employed to remove the mixed-liquor suspended solids (MLSS)
following the activated sludge processes and oxidation ditches treatment or to remove growths that may slough off from
trickling filters and rotating biological contactors. Well-designed secondary clarification processes produce high-quality
effluents with low suspended solids. In advanced or tertiary treatment plants (rarely found in remote or recreational
areas), secondary sedimentation is employed to remove flocculated suspended solids and/or chemical precipitates. The same
design considerations for primary sedimentation apply to secondary clarification. Efficient sludge collection and removal
from secondary sedimentation is of prime importance in the design procedure.
( 2 ) Typical design information that applies to secondary sedimentation treatment can be found in Droste 1997, Metcalf &
Eddy 1991, Reynolds 1995, and WEF MOP-8.
( e ) Trickling filters.
( 1 ) The conventional secondary treatment trickling filter process employs an attached-growth biological system based on
passing (trickling) organically loaded wastewater over the surface of a biological growth attached to a solid media which
is firmly supported on a well-ventilated underdrain system. The conventional trickling filter process is best employed in
situations where the organic concentrations in the effluent from the primary sedimentation process are moderate rather than
high.
( 2 ) Trickling filters are generally classified, with respect to the application rate of both organic and hydraulic
loadings, as low rate, high rate, and roughing or super rate. Super-rate or roughing filters are not applicable to
wastewater plants at recreational areas and require special Corps of Engineers approval prior to construction. The process
is further categorized by media type, media depth, number of trickling filter stages, mode of wastewater distribution (fixed
nozzles in smaller units or rotary arm distributors), and/or intermittent dosing cycles or frequency.
( 3 ) Recirculation of trickling filter effluent back through the primary sedimentation basins or directly to the trickling
filter influent, or to the second filter in a two-stage system, is often practiced. The main purpose of recirculation is to
provide continuous flow through the filter media to maintain a continuous organic material feed for the media-attached
microorganisms and to prevent dehydration of the attached growth.
( 4 ) The most frequently employed trickling filter media is granite rock. Slag has also been used. Plastic media in
various shapes and redwood lath media are also to be found in more recently designed processes. The principal criteria
for media are the specific surface area (area per unit volume) and the percent void space. Organic loading is directly
related to specific surface area available for the media-attached biological growth. Increased void spaces enhance oxygen
transfer to the attached growths, provide adequate ventilation throughout the media bed, and permit significantly higher
hydraulic loadings. Should a dosing system be required (infrequently installed in new designs and limited to low-rate
filters), dosing of wastewater to the media should occur at least every 5 minutes to ensure or provide nearly
continuous liquid applications. Ventilation of the media bed is necessary to ensure effective operation of the trickling
filter. In both cold and warm climates, disinfection of trickling filter plant effluent is required.
( 5 ) Design information for trickling filter systems, media, and rates of application can be found in Metcalf & Eddy 1991,
Reynolds 1995, and WEF MOP-8.
( f ) Extended-aeration activated sludge processes (package plants).
The activated sludge process, in conventional or modified forms, has been shown to meet secondary treatment plant effluent
limits. The three modified categories of activated sludge processes for small wastewater plants are extended-aeration
package plants, oxidation ditches, and sequencing batch reactors. All are primarily based on the food-tomicroorganism
(Food:Mass, or F:M) ratio principle.
( 1 ) Extended-aeration package plant.
( a ) The extended-aeration activated sludge process is commonly used to treat small wastewater flows up to 379,000 L/d
(100,000 gal/d). The aeration process ranges in detention time from 24 to 36 hours and is, along with oxidation ditches
(see below), considered the longest of any activated-sludge process. As BOD 5 loadings are generally low in
recreational areas, the extended aeration system usually operates in the endogenous growth phase. Extended aeration
processes generally accept periodic or intermittent heavy organic loadings without significant plant upsets.
( b ) Process stability is believed to result from the large aeration tank volume as well as the continuous and complete
mixing of tank contents. Long detention times and low overflow rates are effected by final settling tank design. Overflow
rates generally range from about 8150 to 24,450 L / day . m 2 (200 to 600 gal / day . ft 2 ).
Aeration tank volumes ranging from 19,000 to 379,000 liters (5,000 to 100,000 gallons) are not uncommon, although this is
considered unusually large for such small flows. Generally, excess sludge is not removed continuously because the suspended
solids concentration of the mixed liquor is permitted to increase with intermittently periodic dumping of the aeration
tank.
( c ) The popularity of small extended-aeration plants has increased the demand for factory-manufactured and -assembled
units. Most extended-aeration systems are factory built with the mechanical aeration equipment often installed in
cast-in-place reinforced-concrete tanks.
( d ) Components of extended-aeration package plants include a combination built-in bar screen and comminutor aeration basin
or compartment, aeration equipment, air diffuser drop assemblies, a froth spray system, at least two air blower and motor
combinations (rotary positive blowers are usually preferred), and a hoppered clarifier to receive aerated mixed liquor from
the aeration compartment. Airlift educator pipes return hopper-collected sludge to a front-of-system sludge holding tank
through a relatively small sludge waste line. A totalizer meter with a specific flume or weir is required for flow
measurement.
( e ) Seasonal changes are important in extended-aeration package plants as the efficiency of treatment will be determined,
to a great extent, by the ambient temperature. During winter months in colder climates the activity of microorganisms is
reduced, particularly in above-ground tanks. For example, if the organic loading remains constant, more microorganisms are
needed in winter months than in summer months to achieve the same effluent quality. Lower temperatures also affect the
dissolved oxygen concentrations in the aeration chamber; the colder the liquid, the more oxygen the wastewater can
assimilate in solution. As the temperature increases, the ability of the wastewater to assimilate gases in solution
decreases. Sludge production also varies with seasonal changes as the biological life forms are more active in warmer
climates. In both cold and warm climates, disinfection of the plant effluent is required.
( f ) Design information for extended-aeration package plants can be found in Metcalf & Eddy 1991, Reynolds 1995, and WEF
MOP-8.
( 2 ) Oxidation ditches.
( a ) Oxidation ditches, also referred to in the U.S. Army as Closed Loop Reactors (CLRs), are activated sludge treatment
processes of reinforced-concrete or steel tank design and are principally considered a secondary treatment process. Small
prefabricated units of metal tank construction are commercially available. Depending on the anticipated wastewater
composition, some of the preliminary units, particularly primary sedimentation, may be omitted. Oxidation ditches are
extended aeration processes that also operate on a food-to-microorganism ratio principle. Reaction time, based on influent
flow, varies from 18 to 36 hours, but typically averages 24 hours. The reactors are usually circular or "race-track"
shaped. Brush-type aerators (rotating axles with radiating steel bristles) or vertically mounted shaft propeller
aerators aerate the wastewater and provide the constant motion of the wastewater in the reactor. The vertical shaft
aerators are designed to induce either updraft or downdraft. Final clarification or secondary settling is a required
feature with an additional capacity to recycle activated sludge from the clarifier bottom. In both cold and warm climates,
disinfection of the plant effluent is required.
( b ) Design information for CLRs can be found in Metcalf & Eddy 1991, Reynolds 1995, TM 5-814-3, and WEF MOP-8.
( 3 ) Sequencing batch reactors (SBRs).
( a ) SBR systems combine biological treatment and sedimentation in a single basin. The design considerations for SBRs
include the same factors commonly used for a flow-through activated sludge system. The principal operating stages of an
SBR system include :
- Static fill—influent flow is introduced to an idle basin.
- Mixed fill—influent flow continues and mixing by diffused aeration begins.
- React fill—influent flow continues, mixing continues, and mechanical aeration begins.
- React—influent flow is stopped and mixing and aeration continue.
- Settle—mixing and aeration are stopped and clarification begins.
- Decant—clear supernatant is decanted.
- Waste sludge—optional sludge wasting may occur.
- Idle—basin is on standby to restart the process.
( 6 ) SBRs also operate on the Food:Mass (F:M) ratio, which ranges generally from 0.05 to 0.30, and from 0.10 to 0.15 for
domestic waste. At the end of decant the stage, the mixed-liquor suspended solids (MLSS) concentration may vary between
2,000 and 5,000 mg/L. A typical value for municipal waste would be 3,500 mg/L. At least two basins are provided in an SBR
design to provide operational flexibility and improve effluent quality. Design criteria information for SBRs can be found
in EPA-625-R-92/005 and EPA/625/R-92/010.
( g ) Rotating biological contactors (RBC).
( a ) The RBC is an attached growth secondary treatment process. RBC is principally composed of a box-like container, most
frequently a concrete tank or metal vat, through which wastewater flows following preliminary treatment, and a complex of
multiple plastic discs mounted on a horizontal shaft. The shaft is mounted at right angles to the wastewater flow;
approximately 40 percent of the total disc area is submerged. As the shaft rotates, the disc slowly revolves and biological
growths flourish on the disc plates by sorbing organic materials; these growths slough continuously off, thereby eliminating
any excess growth. As the top 60 percent of the disc plate area passes through the air, oxygen is absorbed to keep the
growths in a semiaerobic state. In principle, the mobile sorption and oxidation processes simulate the static trickling
filter media growth conditions.
( b ) Multistage RBC units consist of two or more stages in series. Multistage contactors achieve greater BOD removal than
do single-stage contactors. Recycling of RBC effluent to the head of the plant is usually not practiced. Any sludge
collected in the holding vat, container, or tank, along with secondary clarifier sludge, is usually returned to the primary
clarifier influent stream to aid in thickening of any collected primary sludge.
( c ) In cold climates, discs and operating equipment are generally covered to reduce heat loss and to protect the system
from freezing. In warmer climates, no permanent enclosed structure is required, although open-sided sunroofs may be
provided.
( d ) The principle RBC design consideration is the wastewater flow rate per unit surface of the discs. A properly designed
hydraulic loading rate produces an optimum food-to-microorganism ratio. Peripheral speed of the discs is usually limited to
0.3 m/s (1 ft/s). Disinfection of the plant effluent is required.
( e ) Design information for RBCs can be found in Metcalf & Eddy, Reynolds 1995, and WEF MOP-8.
5-4. Stabilization Ponds...
( a ) Classifications.
Stabilization ponds provide treatment for wastewaters through a combination of sedimentation and biological treatment using
extensive detention times. Stabilization ponds are generally categorized as aerobic, facultative, or anaerobic according to
their dissolved oxygen depth profile. An aerobic pond has varying concentrations of oxygen throughout its entire depth,
while an anaerobic pond is devoid of oxygen at any depth except in the very top few millimeters (inches) at the air-liquid
interface. A facultative pond supports oxygen, or is aerobic, in its top zone and is anaerobic or devoid of oxygen at the
lower depths or bottom zone. Most stabilization ponds fall into the facultative category. The amount of oxygen present
depends on temperature, organic loading, and sunlight intensity (photosynthetic effect), and the dissolved oxygen
concentrations in the top zone will vary with time and conditions. During periods of no direct sunlight (prolonged hazy or
very cloudy conditions) and during the night hours, dissolved oxygen concentrations will decrease as the dense microbe
population and algae, if any, readily consume available oxygen. As the microbes and algae expire, they settle to the pond
bottom and enter the anaerobic state and decompose. Few local odors are experienced in facultative and aerobic ponds; anaerobic ponds produce pronounced odors.
( b ) Design guidance.
Design considerations and guidelines for stabilization ponds and aerated lagoons can be found in Metcalf & Eddy 1991,
Reynolds 1995, and WEF MOP-8.
5-5. Natural Systems for Wastewater Treatment...
( a ) System types and parameters.
( 1 ) Natural systems for land wastewater treatment encompass both soil-based and aquatic methods. These systems consume
less energy and produce less sludge than conventional systems. Soil-based methods include subsurface systems such as septic
tank leach fields to serve occupants of a single structure, limited populations in small communities, or a few visitors to
remote areas. Aquatic methods are those in which wastewater is applied at the surface of the soil and include slow-rate (SR)
land treatment, rapid infiltration (RI) land treatment; and overland flow (OF) land treatment. SR and RI systems rely on
infiltration and percolation in soil matrices for applied wastewater movement. OF systems utilize sheet flow of the applied
wastewater along a gentle slope. Vegetation is important in both SR and OF systems. RI hydraulic loading rates are higher
than those for SR and OF systems, and vegetation is not important. Surface application gives the SR and RI systems a higher
treatment potential than OF; most aerobic microbic activity occurs in the top layer of soil and not merely along the soil
surface treated by the OF system. Figure 5-1 presents a process selection chart for natural systems (MOP FD-16, Natural
Systems for Wastewater Treatment). Figure 5-2 presents a decision diagram for selecting wetland alternatives (MOP FD-16).
Figure 5-3 identifies climatic control and zone considerations for land treatment facility selection (MOP FD-16).
( 2 ) Limiting design parameters for the various natural system types are as follows :
- For on-site septic leach fields—hydraulic capacity of soil.
- For slow-rate land treatment—hydraulic capacity, nitrogen or phosphorous.
- For rapid infiltration land treatment—hydraulic capacity, nitrogen or phosphorous.
- For overland flow land treatment—BOD, TSS removal, infrequently nitrogen.
( 3 ) For flows of 378,500 L/d (100,000 gal/d), SR processes may require 1 to 10 hectares (2.5 to 25 acres), OF processes
from 0.4 to 2 hectares (1 to 5 acres), and RI basins from 0.4 to 1.2 hectares (1 to 3 acres) of suitable land surface.
( b ) Slow rate (SR) land treatment.
( 1 ) SR is a widely used treatment method, and requires the highest level of pretreatment. Secondary clarification and
disinfection are not uncommon prior to using SR. SR systems typically achieve the highest level of performance of the three
natural systems. Site requirements depend on loading rates, site characteristics, and design objectives. Loading rates
generally vary from 1 to 2 m (3 to 7 ft) of applied wastewater per annum, much of which can be lost by evapotranspiration.
Additional area is required for any needed pretreatment systems, roads, odor buffer zones, and structures. Soil type and
depth to groundwater are important considerations. The SR land treatment design procedure is shown in Figure 5-4
(MOP FD-16). A minimum of primary sedimentation or pretreatment is a prerequisite for successful operation; Imhoff tanks
with influent grinder pumps have been successfully employed as pretreatment or preliminary treatment processes. SR design
considerations include loading rate, allowable soil permeability, field surface areas, and wastewater storage requirements.
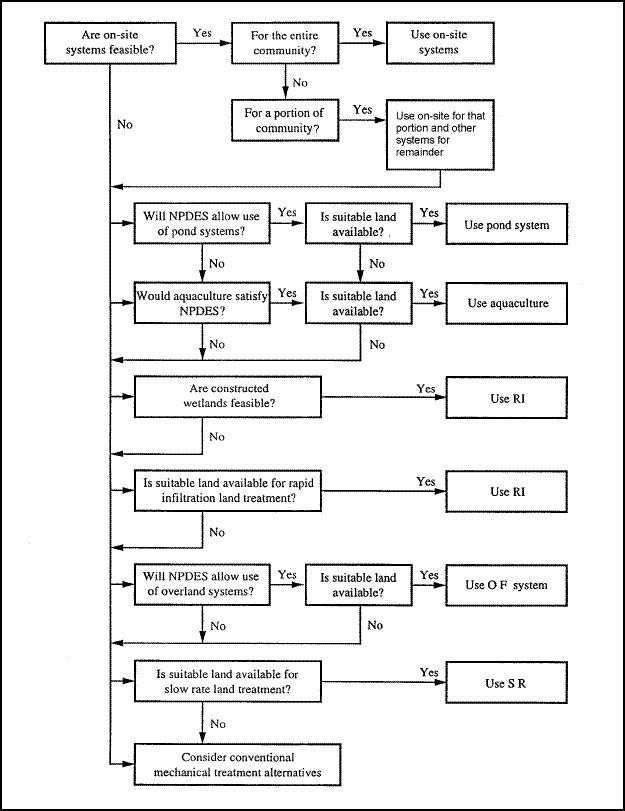
Figure 5-1. Process selection for natural treatment systems.
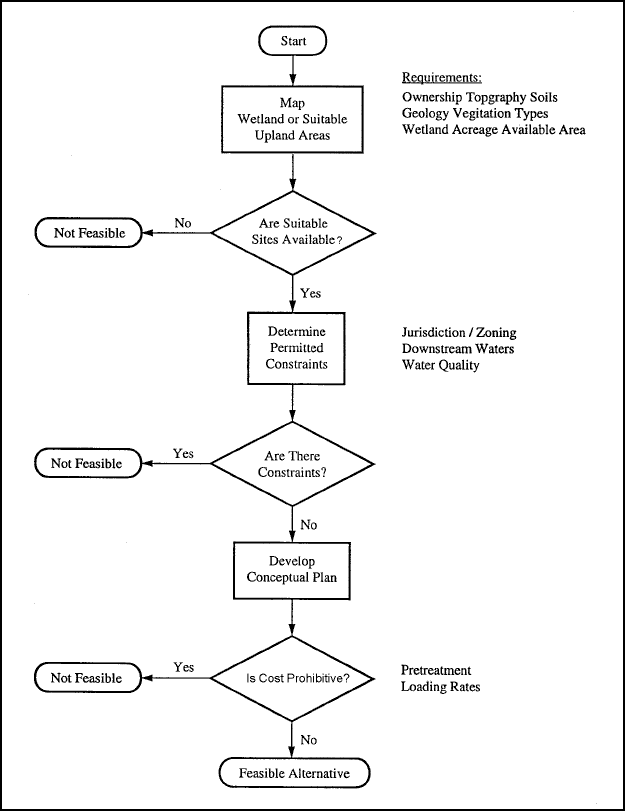
Figure 5-2. Decision diagram for selecting wetland alternatives.
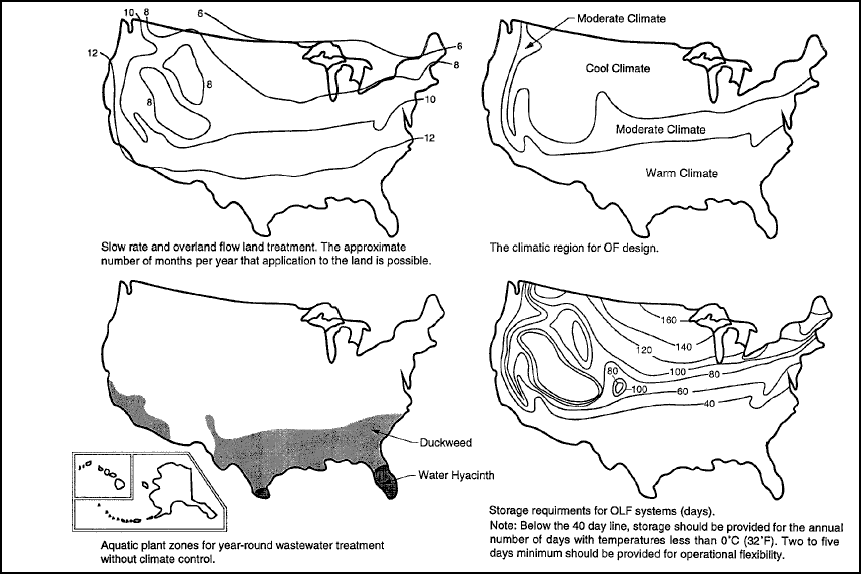
Figure 5-3. Climate control and zone considerations for land treatment facilities.
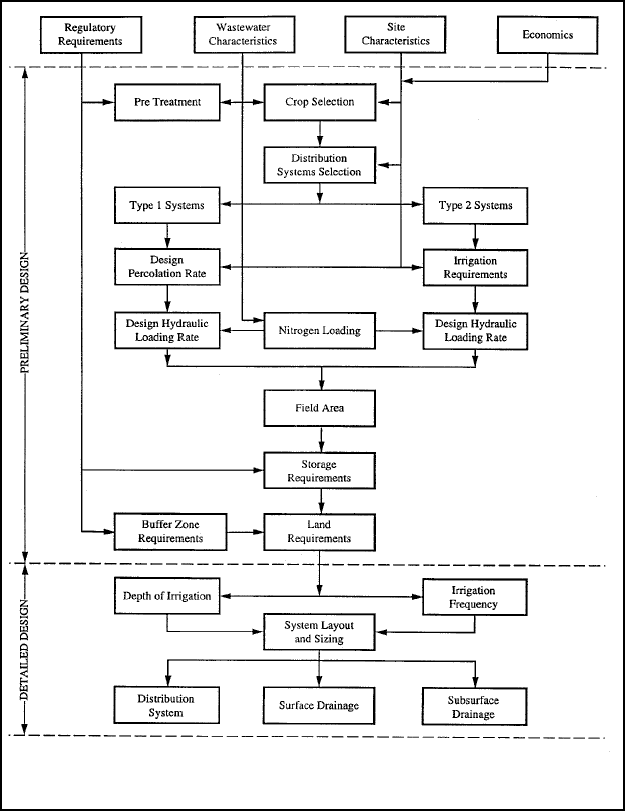
Figure 5-4. Slow rate system design procedure.
( 2 ) BOD removal is accomplished by soil adsorption. Microbe oxidation removal efficiencies invariably range above 90
percent. Total suspended solids are effectively removed by the soil filtration process, with many designs achieving
suspended solids removals to 1 mg/L. Nitrogen is removed by crop uptake, denitrification, volatilization of ammonia, and
soil matrix storage, with removal efficiencies typically varying between 60 and 90 percent. Pathogen removal is generally
excellent. Phosphorous adsorption also readily occurs in soils, and 90 to 99 percent reduction can be expected in both cold
and warm climates.
( 3 ) SR site characteristics, typical design features, and expected water quality can be found in EM 1110-2-504,
EPA/625/1-84/013a, Metcalf & Eddy 1991, MOP FD-16, and WEF MOP-8.
( c ) Rapid infiltration (RI) land treatment systems.
( 1 ) RI, a well established natural system also known as soil-aquifer treatment (SAT), operates yearround utilizing primary
clarification or Imhoff tanks as pretreatment processes. Treatment is achieved mainly by wastewaters percolating vertically
downward through permeable soil columns, making RI the most intensive of the natural systems options. Basically, RI operates
on a "fill and subside" regime in shallow basins. RI basins typically are intermittently dosed on 1- to 7-day cycles and
rested for 6 to 20 days. The rapid infiltration method generally produces a high degree of treatment, although nitrate
concentrations of 10 mg/L have been known to reach underlying groundwaters. More intensive soil investigation is required
for RI than for either the SR or the OF method.
( 2 ) To be successful, an RI system must be constructed at a site with more than sufficient area of both permeable and
well-drained soil to depths that satisfactorily meet treatment objectives. The RI system has the greatest impact on
underlying groundwater quality. Extensive data is required on the hydrogeology of the subsurface to include :
• Geometry of the system.
• Hydraulic loading rate.
• Minimum depth to the fluctuating groundwater table.
• Slope of the groundwater table.
• Depth to the underlying impervious formation.
• Hydraulic conductivity of the aquifer soil.
• Porosity of the soil.
• Elevation of and distance to any stream, river, lake, or wetland water surface.
( 3 ) Loading cycles are seasonally dependent. Hydraulic loading rates with accompanying drying periods for RI systems
greatly exceed those of either SR or OF systems.
( 4 ) BOD removals of 80 to 100 percent can be expected. Nitrogen removal depends on the raw BOD to N ratio, hydraulic
loading rate and wet/dry cycle with percentage removals fluctuation over a wide range, i.e., from 10 to 90 percent.
Phosphorous removal is dependent upon vertical soil column travel distance. Fecal coliform removal of 2 to 6 log correlate
directly with soil composition, vertical soil column travel distance and wastewater application schedules versus bed drying
times. Suspended solids removal is high.
( 5 ) Aerobic and facultative ponds are not recommended as pretreatment processes for RI unless algae effluents therefrom
are controlled; algae can clog the underlying infiltration surfaces.
( 6 ) Typical design features and considerations for RI systems can be found in EM 1110-2-504, EPA/625/1-84/013a, Metcalf &
Eddy 1991, MOP FD-16, and WEF MOP-8.
( d ) Overland flow (OF).
( 1 ) OF is a more recent development than either the RI or the SR process. The system was selected for use in areas with
low-permeability, or poorly drained soils which are slowly permeable such as clays and silts. Such conditions necessitate
low hydraulic loading rates, thereby requiring a larger application area over a network of vegetated sloping terraces.
Wastewater flows down the sloping terraces over the top of the surface with infiltration being limited by the low soil
permeability. Wet-dry cycles produce a batch mode treatment, and the treated liquid experiences a variety of physical,
chemical, and biological conditions. The combination of sloping terraces 30 to 60 m (100 to 200 ft) at two to eight percent
slopes; hydraulic loading rate, wastewater application rate, time of continuous application versus drying periods,
application of wet-dry ratio, and time required for a given application cycle in days or hours usually produces a
high-quality effluent.
( 2 ) BOD, TSS, and nitrogen are significantly removed by the OF process; phosphorous and pathogens are removed to a
lesser degree. BOD effluent concentrations of less than 10 mg/L are often achieved and except for algae, the TSS effluent
concentrations are also less than 10 mg/L. Some algae types are not consistently removed. If large algal blooms occur in
pretreatment or preliminary treatment processes (e.g., facultative ponds or lagoons), then concentrations of algae in OF
algae effluents can be expected to be considerable. Nearly complete nitrification of ammonia can be expected whereas
significant nitrogen removal, (i.e., above 80 percent) is difficult to achieve and is dependent on temperature, application
rate, and wet/dry cycles. The higher the rate of wastewater application, the quicker the runoff with correspondingly lower
treatment efficiency for all parameters.
( 3 ) OF process sheet flow schematics are shown in Figure 5-5 (MOP FD-16 Natural Systems for Wastewater Treatment).
Wastewater treatment is achieved mainly by direct percolation and evapotranspiration. Wastewater is generally applied by
gated piping at pressures of 14 kPa to 35 kPa (2 to 5 psi), by low-pressure fan spray devices at 35 kPa to 138 kPa (5 to 20
psi), or by high-pressure impact sprinklers at 138 kPa to 522 kPa (20 to 80 psi). The OF process is most successfully
operated following a combination of screened wastewater, primary, or pond treatment.
( 4 ) Design considerations for OF can be found in EM 1110-2-504, EPA/625/1-84/013a, EPA/1- 81/013, Metcalf & Eddy 1991,
MOP FD-16, and WEF MOP-8.
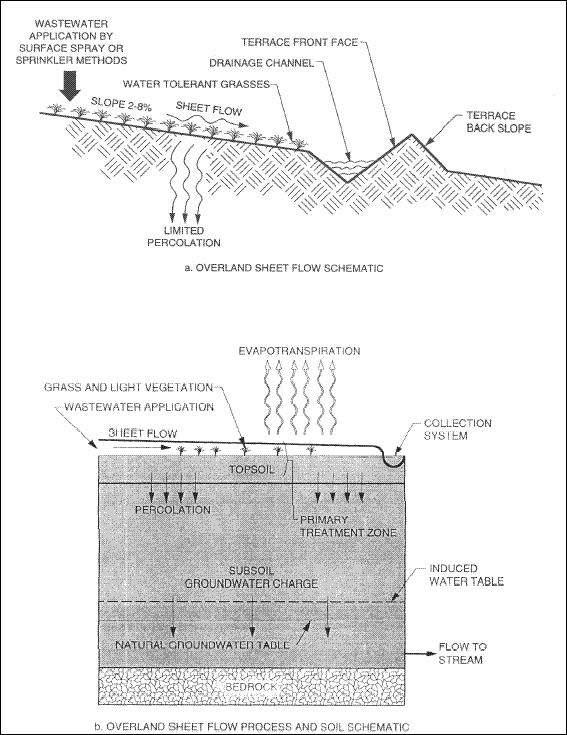
Figure 5-5. Overland flow process schematic.
5-6. Man-Made Wetlands...
The Environmental Protection Agency has developed definitions and interpretations to differentiate between natural wetlands
and man-made systems (CWA, Section 404), as follows :
( a ) Constructed wetlands.
Constructed wetlands are those intentionally created from non-wetland sites for the sole purpose of wastewater and
stormwater treatment. These are not normally considered waters of the U.S. Constructed wetlands are considered treatment
systems (i.e., non waters of the U.S.); these systems must be managed and monitored. Upon abandonment, these systems may
revert to waters of the U.S. Discharges to constructed wetlands are not regulated under the Clean Water Act. Discharges
from constructed wetlands to waters of the U.S. (including natural wetlands) must meet applicable NPDES permit effluent
limits and state water quality standards.
( b ) Created wetlands.
Created wetlands are those intentionally created from non-wetland sites to produce or replace natural habitat (e.g.,
compensatory mitigation projects). These are normally considered waters of the U.S. Created wetlands must be carefully
planned, designed, constructed, and monitored. Plans should be reviewed and approved by appropriate state and federal
agencies with jurisdiction. Plans should include clear goal statements, proposed construction methods, standards for
success, a monitoring program, and a contingency plan in the event success is not achieved within the specified time frame.
Site characteristics should be carefully studied, particularly hydrology and soils, during the design phase.
( c ) Natural wetlands.
Natural wetlands have not been fully defined, but certain guidelines and restrictions on use were emphasized. Natural
wetlands may not be used for in-stream treatment in lieu of source control/advanced treatment, but may be used for
"tertiary" treatment or "polishing" following appropriate source control and/or treatment in a constructed wetland,
consistent with the proceeding guidelines.
( d ) Constructed wetlands and wastewater management.
( 1 ) Constructed wetlands are areas that are periodically inundated at a frequency and depth sufficient to promote the
growth of specific vegetation and are generally categorized as either free water surface systems (FWS) or subsurface flow
systems (SFS). Figure 5-6 identifies the types of constructed wetlands most commonly used for wastewater management (MOP
FD-16 Natural Systems for Wastewater Treatment). Shallow basins or channels comprise the former with an impervious layer to
prevent infiltration plus a supporting vegetative growth medium. Basically, wastewater flows at a low velocity over the
medium which supports the growth and through and around the vegetative stalks. Wastewater application is essentially plug
flow. The subsurface method is composed of a slightly inclined trench or bed underlaid by an impervious layer to prevent
seepage and a permeable medium to support vegetative growth through which the wastewater flows. The root-zone method of
rock-reed-filter is categorized as a subsurface flow system.
( 2 ) The hydrology of wetlands is not significantly different from that of other surface wastewater treatment processes;
however, plant growth and substrate do affect flow. Hydrologic factors to be considered in design are the hydroperiod,
hydraulic loading rate, hydraulic residence time, infiltrative capacity of the underlying hyperoid, evapotranspiration
effects, and the overall water balance. Hydroperiod includes both duration and depth of flooding. Hydraulic residence time
of a treatment wetland is the average time a typical unit of water volume exists within the system. Infiltrative capacity
is the measure of net water transfer through the sediments either infiltration or exfiltration. Evapotranspiration is the
combined water loss from a vegetated surface area via plant transpiration or surface water evaporation. Figure 5-7
identifies the most commonly used effluent distribution methods in wetlands (MOP FD-16 Natural Systems for Wastewater
Treatment).
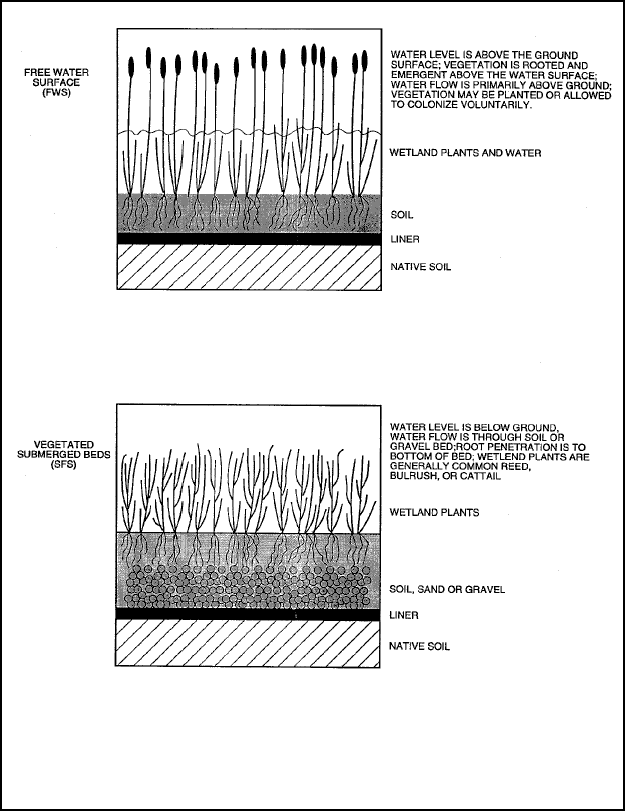
Figure 5-6. Types of constructed wetlands.
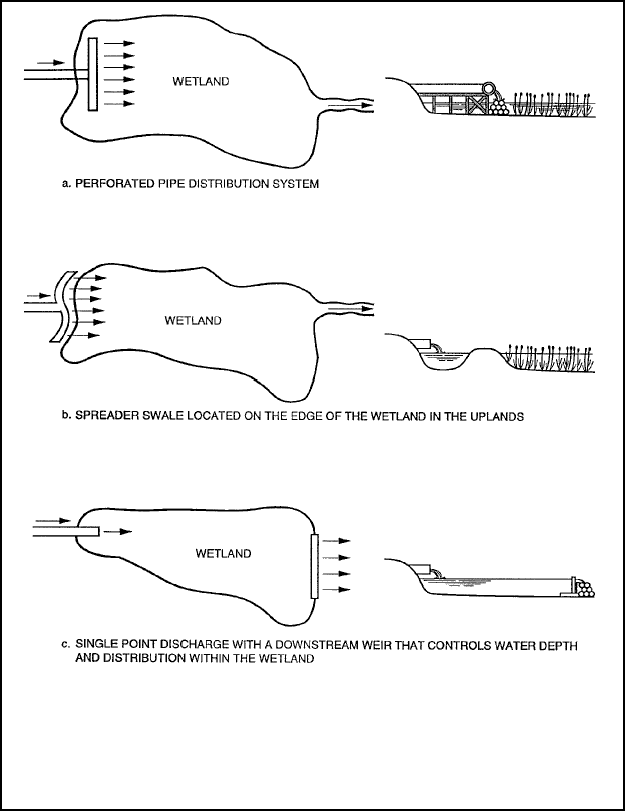
Figure 5-7. Effluent distribution methods in wetlands.
( 3 ) Wetlands have been shown to be excellent assimilators of both BOD and TSS. Decomposition is mostly aerobic. Microbial
populations apparently flourish similar to activated sludge plants and trickling filter attached growths. BOD removal
efficiencies are lowest at low input concentrations (less than 5 to 10 mg/L) but increase to 70 to 90 percent removals at
higher input concentrations. TSS removal efficiencies are also input related, consistently above 50 and up to 90 percent.
Nitrogen removal efficiencies generally are 25 percent or less. Ammonia assimilation by wetlands, while sometimes high,
is reduced by short hydraulic loading rates and low temperatures. When other factors do not interfere, total ammonia may be
reduced 70 to 90 percent. Total nitrogen removal is also directly affected by loading rates with typical expected removal
efficiencies of 75 to 95 percent. Removal efficiencies of phosphorous generally range from 30 to 50 percent. Total
phosphorous removal efficiency increases with higher input concentrations and higher hydraulic residence times.
( 4 ) The four basic flow patterns for constructed wetlands are plug flow, step feed, recirculation, and step feed with
recirculation in a wraparound pond (more commonly known as "jelly roll"). For more details on wetland design considerations,
flow pattern configuration, primary or preliminary treatment requirements, and applicable design data, consult
EPA/625/1-91/024, EPA/625/1-88/022, EPA/832/R-93/008, Hammer 1989, NSFC-2, and NSFC-3.
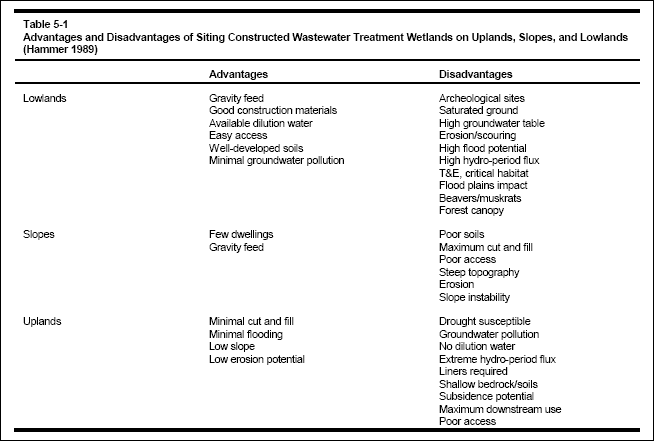
( 5 ) Advantages and disadvantages of siting constructed wastewater treatment wetlands in uplands, on slopes, and in
lowlands are summarized in Table 5-1.
( e ) Aquatic plants.
Aquatic plants employed in one or more of the natural systems are considered under the generic term of vegetation and are
categorized as floating plants or submerged plants. Floating plants (water hyacinths, pennywort, and duckweed) have their
photosynthetic portions at or above the water surface with roots extending down into the water column and serving as
filtration/-adsorption media for suspended solids and bacteria growth.
( 1 ) Hyacinths.
As hyacinths are productive photosynthetic plants, they proliferate and are considered a nuisance in southern U.S. waterways
but are highly effective in natural wastewater treatment systems. Nitrogen and phosphorous uptake by hyacinths decreases in
colder weather. Therefore, hyacinths are generally most effective south of the 30 O parallel in the U.S.
( 2 ) Pennywort.
Pennywort is not free floating but intertwines and usually grows horizontally; at high densities the plants experience
vertical growth. Pennywort nitrogen and phosphorous uptake is relatively steady in both cold and warm climbs and exceeds
the uptake rates of hyacinths in cold weather.
( 3 ) Duckweed.
Duckweeds, small freshwater plants, are the smallest and simplest of flowering plants but have one of the fastest
reproduction rates of those plants suitable for aquaculture. Duckweed design procedures are generally the same as
for facultative lagoons and their effluents often exceed the performance of conventional facultative lagoons for BOD,
total suspended solids, and nitrogen removal. Sometimes the duckweed systems are anaerobic and may require post aeration
treatment.
( 4 ) Submerged plants.
Submerged aquatic plants are either suspended in a water column or rooted in bottom sediments and are susceptible to being
shaded out by algae. They are also sensitive to anaerobic conditions. The full worth of submerged plant systems has yet to
be determined.
( f ) Regulatory concerns.
( 1 ) Most natural wetlands are classified as waters of the United States. They are also considered state waters in many
states. The Clean Water Act prohibits discharges to natural wetlands which do not meet a minimum of secondary treatment or
its equivalent (TM 5-814-3). Before discharge into surface receiving bodies (streams, rivers, lakes, impoundments, and
estuaries), wasteload allocation processes are often required in order to determine the discharge criteria. Entirely
different effluent criteria may be applicable to groundwater discharge. A groundwater monitoring plan will generally be
required for all natural treatment systems. Groundwater regulatory standards must be met during the operating lifetime of
all natural treatment systems.
( 2 ) Design examples of the three alternative wastewater collection systems can be found in EPA/625/1-91/024.
5-7. Nutrient Removal...
( a ) Conventional and natural treatment.
Nutrient removal of both nitrogen and phosphorous by both conventional and natural treatment systems is of concern as
regulatory requirements may impose effluent discharge limits on these two nutrients. In conventional treatment systems both
nutrients are generally removed by chemical precipitation. In certain instances, patented treatment processes (such as,
Orbal Bionutre, A / O TM , A 2 / O TM , Bardenpho TM , Modified Bardenpho
TM , or PhoStrip TM ) must be used where 2 regulatory standards demand. Each case is site specific;
therefore, no trademark nutrient removal processes are included herein.
( b ) Nutrients in wastewater.
In considering nutrient removal from wastewater, nitrogen and phosphorous are of prime consideration. Both must be
considered potential pollutants in any wastewater discharges.
( 1 ) Nitrogen.
( a ) Nitrogen, a ubiquitous element, is a water pollutant in four biochemically interconnectable oxidation states :
organic-N => ammonia-N => nitrite-N => nitrate-N, which taken together compose the total nitrogen in any given sample. As
there is almost no nitrate and nitrite to be found in municipal wastewaters, the nitrogen content is most frequently
determined as Kjeldahl N, which is the sum of the remaining nitrogenous material, i.e., organic-N + ammonia-N. The behavior
of nitrogen in any wastewater system is complex. Organic-N and ammonia-N are oxidized to nitrite and nitrate in wastewater
treatment. Nitrites are somewhat unstable and readily oxidize to nitrates. Further oxidation of nitrates will produce
inert nitrogen gas (N 2 ).
( b ) The conversion of ammonia to nitrate is known as nitrification, a secondary treatment wastewater phenomenon
occurring in the presence of the nitrosomonas and nitrobacter nitrifying bacteria. Conversion of nitrate to nitrogen gas
(N 2 ) is known as denitrification, which requires the presence of denitrifying bacteria.
( c ) Both nitrification and denitrification require ideal conditions for the most favorable results, and may occur in the
same tank, but at different times and in different environments. The principal ingredients required for nitrification and
denitrification are sufficient oxygen levels and adequate bacterial concentrations. Currently, in conventional plants, the
total nitrogen (organic, ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate) is reduced from influent concentrations of about 40 mg/L to 10 mg/L
or less in the discharged effluent. Additional treatment may be required for more stringent effluent quality requirements.
( 2 ) Phosphorous.
( a ) The sources of phosphorus are several: human excreta in water carriage wastes; food residues from households,
commercial and recreational establishments and restaurants; water treatment additives; detergents, both domestic and
commercial; and indirectly from surface treatment fertilizers through sewer or manhole infiltration. The nutrient
phosphorous mainly occurs in solution as particles or waste elements in microorganism forms as : orthophosphates
(PO 4 - 3 , HPO 4 - 2 , H 2 PO 4 - 1 ,
and H 3 PO 4 ); polyphosphates (P 2 O 7 ); and as organically bound
phosphorous, the latter two comprising more than two-thirds of wastewater phosphorous. Phosphorous stimulates the growth
of photosynthetic algae, which may cause eutrophication in receiving bodies of water such as lakes or slow-moving
streams.
( b ) Originally, phosphorous removal in wastewater treatment was achieved by chemical precipitation, principally with
ferric chloride. In today’s design approaches, treatment is accomplished through the more advanced biological processes.
Biological treatment, mainly conventional activated sludge, converts phosphorous to the orthophosphate forms, which are
then removed in a chemical precipitation process by calcium, aluminum, or ferric compounds. Normally, if lime is the
calcium source of choice, precipitation follows biological treatment. Should alum or iron be employed as precipitants,
they may be added in either the primary sedimentation or activated sludge processes.
( c ) Combined nitrification-denitrification system.
A two-stage biological nitrogen removal scheme typically employs primary sedimentation, followed by an anaerobic (anoxic)
tank for denitrification. The anoxic tank effluent then passes to an aerobic tank for oxidation and nitrification and
finally to a secondary sedimentation or clarification tank. Nitrate concentrations are generally returned from the
aerobic tank effluent to the anoxic tank influent. Secondary clarifier sludge is either wasted or returned to the anoxic
tank. Oxidation ditches (CLRs) with single aerobic and anoxic zones are particularly effective as
nitrification-denitrification treatment processes. Nitrogen removals can be significantly reduced further with the addition
of a second anoxic zone (Bardenpho process).
( d ) Biological phosphorous removal.
Primary treatment removes about ten percent of municipal influent phosphorous levels. Conventional secondary wastewater
treatment processes remove approximately 20 percent of the effluent from the primary process. Typical municipal influent
wastewaters have phosphorous concentrations of approximating 10 mg/L, with some regulatory restrictions requiring
effluent limits of 1 mg/L or less. Conventional treatment may be inadequate to accomplish the requisite phosphorous
removal; chemical precipitation originally became the common phosphorous removal technique when limitations were placed on
effluent levels. More recently, certain patented biological phosphorous removal systems have been successfully employed to
meet the stringent effluent requirements. As biological processes can reduce primary sedimentation phosphorous levels of
applied loads by 70 to 80 percent, a plant influent level of 10 mg/L can be reduced to 2 or 3 mg/L. Phosphorous levels can
be further reduced to 0.5 to 1.0 mg/L, if needed, by 3 to 6 mg/L coagulant additions.
( e ) Comparison of nutrient removals by treatment systems.
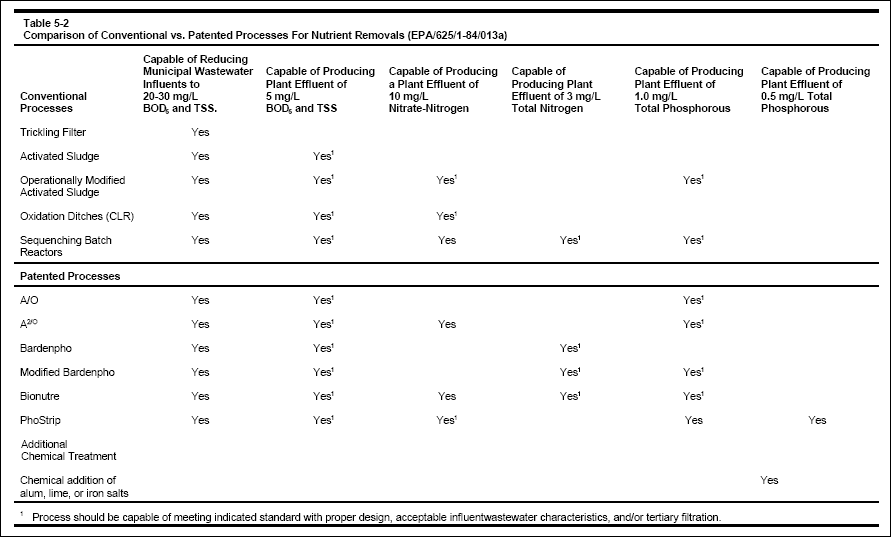
A brief comparison of nutrient removal processes is shown in Table 5-2. Conventional nutrient removals are identified in
the top portion of the table. Certain patented processes are grouped alphabetically in the lower half of the table. The
use of patented approaches generally requires license fees for their installation and use. Any license or royalty fees for
specific applications are negotiated between the user and the patent holder which ultimately affect any economic analysis
of the proposed system.
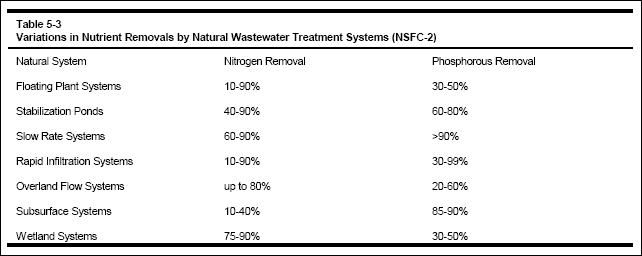
( f ) Wetland systems.
Wetland systems are particularly efficient in removing one or both wastewater nutrients. The wide range of efficiencies or
percent removals is influenced by loading rates, influent constituent strength, soil conditions, plant uptake, and climatic
conditions. Removal efficiencies generally increase with higher input concentrations. Table 5-3 identifies the range of
variation in nitrogen and phosphorous removals for natural wastewater treatment systems.
 5-8. Sludge Treatment and Disposal...
( a ) Treatment selection criteria.
5-8. Sludge Treatment and Disposal...
( a ) Treatment selection criteria.
The selection of sludge treatment methods, if required, is a function of the raw wastewater characteristics, unit processes
employed in the small conventional plant treatment train, efficiencies of those treatment processes in removing suspended
solids, chemical usages if any (not normally expected in facilities solely treating human wastes), and other site-specific
conditions. Sludge disposal is controlled by Federal, state, and local regulations. Chapter 10 summarizes the current
national requirements and standards for the use or disposal of sewage sludge.
( b ) Treatment and disposal.
Sludge treatment and disposal depends upon the wastewater treatment selected, as follows :
- For individual units such as pit privies, vaults, compost systems, and septic tanks, collected sludges should be trucked
off-site for treatment and disposal.
- For small conventional plants, sludge treatment and disposal depends upon the wastewater treatment process selected but
will not necessarily include on-site treatment.
( c ) Transport.
The USDA Forest Service has successfully managed sludges generated at domestic wastewater treatment facilities at remote
sites (USDA-2). These include the use of 210-L (55-gal) drums to store the sludge. When drums are filled, they may be
transported to an offsite treatment facility by truck, helicopter, mule/horse pack, or all terrain vehicle (ATV) (USDA-2).
( d ) Stabilization.
Sludge stabilization is provided to eliminate nuisances and reduce health-related threats. In small plants, stabilization
depends upon whether the sludge is anaerobically or aerobically digested in the treatment train, whether chemical
stabilization is employed, and whether composting of sludge is attempted for disposal purposes. Usually, in small
conventional plants, sludges are not gravitory polymer-thickened, nor are mechanical means (centrifuges, filter presses,
horizontal belt filters, or rotary vacuum filters) applied.
( e ) Lagoons.
Infrequently, at small plants some sludges are lagooned. The limitations on using lagoons as biological digesters are the
availability of appropriate land areas, aesthetic or odor problems, lack of flexibility in operations, and generally poor
performance in humid and rainy climates. Often, several years may be required for lagoon sludge drying to complete a life
cycle. Lagoons must be diked to prevent surface runoff from entering. Lagoons may be used in emergency operations and may
be placed in operation after the plant has been constructed, should the need arise.
( f ) Dewatering and sand drying beds.
Dewatering of anaerobically or aerobically treated sludge reduces the amount of water in the sludge so that it can be
handled and disposed of as a solid rather than a liquid. The simplest dewatering method for small treatment facilities
is the use of uncovered or open sand filtration drying beds. The use of sand drying beds, which may be enclosed for
aesthetic reasons, is applicable for smaller conventional treatment plants if the residues are well stabilized. Design
considerations include: solids concentrations of the applied sludges; proposed depth of sludge to be applied to the bed;
efficiency of the filtered water collection system; degree, type, and sludge conditioning in the treatment processes;
climatically affected evaporation rate; method to remove dried sludge cake from the beds; and ultimate sludge disposal
method contemplated.
( 1 ) Drying beds are usually 6 to 9 m (20 to 30 ft) wide and 7.5 to 38 m (25 to 125 ft) long, and consist of 150 mm to 250
mm (6 in to 10 in) coarse sand layers in rectangular reinforced concrete-walled enclosures over a 150 mm to 300 mm (6 in to
12 in) graded gravel layer. The bottom of the bed should be impervious. A minimum of two beds should be provided for each
plant. The sand media subgrade is sloped and a manifold-lateral system of perforated pipe is installed to collect the
liquid, leaving the solid concentrations on top of the sand layer. Evaporation of surface waters to the atmosphere aids in
the dewatering process. Filtrate from the manifold-lateral collection system should be returned by pumping to the head of
the plant.
( 2 ) Splash blocks at gate locations in the concrete walls and concrete pads for truck or front-end loader wheels should
be provided. Sludge is removed either manually or by careful loader scraping to remove as little of the sand layer as
possible in each emptying action. Sand replacement is inevitable after several years of operation. Trucked sludge is
directed to a local municipal landfill or sludge monofill. Bed-dried sludge is removed by contract at most government plants.
( 3 ) As an operator of over 100 small wastewater plants, the U.S. Army has an interest in efficient and cost-effective
sludge dewatering systems. The majority of currently operating Army plants use conventional sand-drying beds to dewater
sludges. The U.S. Army Engineer Construction Engineering Research Laboratory (USACERL) has recently evaluated the Reed bed
technology for potential Army use (USACERL 1993). Reed bed dewatering is a relatively new modification to sand drying beds
which uses a common reed (genus Phragmites) to treat wastewater sludges. Sludge is applied to an actively growing stand of
reeds. The sludge dries naturally in the sand beds by evaporation and drainage. This technology has been successfully
demonstrated in the northeastern United States, where some 50 sludge drying beds are in operation. Reed beds are easier to
operate and maintain than regular sand drying beds and virtually eliminate the need for regular sludge removal.
( 4 ) Sludge treatment and disposal design information can be found in Table D-3.
5-9. Disinfection of Wastewater Effluents...
( a ) General.
The most common means of wastewater disinfection is by liquefied chlorine gas or in the form of varying chlorine compounds.
Disinfection is defined here as inactivation of all microorganisms. Disinfection in one form or another is almost always
required to meet National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System permit requirements or state-imposed effluent quality
standards. Concerns for sideeffects and/or undesirable chlorine by-product formation, as well as toxic chlorine effect on
humans, aquatic life, and shell-fish growing regimes have increased the need for carefully controlled dechlorination
practices or alternative disinfectant processes for some discharges.
( b ) Non-chlorine techniques.
Recent technology has emphasized other techniques for treating wastewater discharge effluents, particularly ozonation and
ultraviolet light. Other available techniques include several chemical disinfectants and their compounds such as bromine
chloride, iodine, hydrogen peroxide, and potassium permanganate. Thermal and radiation processes have not been actively
pursued. Of the non-chlorine techniques, ozonation and ultraviolet light appear most promising.
( c ) Chlorination.
( 1 ) Chlorination is the most widely used method of disinfection and is accomplished with gaseous chlorine, hypochloites,
or chlorine dioxide. Chlorine demand to inactivate organisms is the difference between applied chlorine and the residual
chlorine and provides a measure of disinfection and all other chlorine-demanding reactions for the contact period between
the disinfectant’s injection into the wastewater and effluent release. There are numerous configurations of chlorine
control systems, all requiring special delivery and control equipment, weighing scales (for accurate measurement of dose
rates), and carefully controlled dosage devices. For small treatment plants, liquified chlorine gas is delivered in
pressurized containers, usually 45.5-kg (100-lb) and 68-kg (150-lb) cylinders. Should dechlorination of effluents be
required to meet effluent quality standards, specific feed rates of sulfur dioxide, sodium sulfite, sodium bisulfite, and
sodium thiosulfate have been developed for use in either in-line or contact mixing to nullify the effluent residual
chlorine concentrations prior to discharge to the receiving body of water.
( 2 ) The design of any attendant chlorination facility at a wastewater plant must provide automatically controlled forced
venting of chlorinator and chlorine tank storage rooms, and a chlorine contact chamber with a detention period of not less
than 30 min following chlorine injection. An inspection window or glass pane door panel must be provided to permit outside
viewing of the chlorinator installation. Both chlorinator and chlorine tank storage rooms must be provided with a means of
heating to at least 16 O C (60 O F).
( 3 ) Chlorinator equipment must have the capacity to provide design dosage requirements at maximum anticipated plant flow.
A solution-feed chlorinator, either pressure feed or vacuum feed, will be required with a suitable make-up water supply.
Scales of sufficient size will be required to meet maximum effluent flow rates; preferably the scales will be self-reading
to record continuous chlorine application. Piping will be that approved by the equipment manufacturer and will be color
coded throughout the treatment facility.
( 4 ) Hypochlorinators, if employed in small flow plants of 75,700 L/d (20,000 gal/d) or less, must be of the
positive-displacement metering type and located in a separate room. The hypochlorinator solution feed is chiefly made from
commercially available calcium and sodium hypochlorite salts in both dry and liquid form, respectively. The most popular
form of hypochlorite is of the sodium type, the liquid form of which can be prepared onsite and commercially delivered at
12 to 15 percent available chlorine. Hypochlorites, in terms of available chlorine, have the same oxidizing potential as
chlorine gas. With the exception of the liquid feeder, storage, and piping, a hypochlorination system is quite similar to
larger chlorine gas systems. However, since the chlorine is not in the gaseous form, there is less concern with chlorine
gas leaks and exposure of personnel.
( 5 ) Design considerations for disinfection by chlorination can be found in Droste 1997 and Metcalf & Eddy 1991.
( d ) Ozonation.
Ozone with its high oxidation potential has been used for many years, particularly in Europe, and has received growing
attention as a chlorine alternative for disinfection. Ozone may be superior in its ability to inactivate viruses and is
equally able to inactivate bacteria. Ozone reduces wastewater odor, produces no dissolved solids, is not affected by pH,
and increases oxygenated effluents. As an unstable gas, ozone quickly breaks down into elemental oxygen. Ozone is generated
on-site by commercially available generator equipment. Design considerations for the equipment installation include
on-site electricity availability, and automatic devices to control voltage, frequency, gas flow, and moisture. The primary
deterrents to the use of ozone at small treatment systems are relatively high capital and operating costs.
( e ) Ultraviolet light.
( 1 ) Disinfection by ultraviolet (UV) light is increasingly used as a wastewater effluent disinfection process at both
military and municipal facilities. UV disinfection is a process by which ultraviolet light is used to destroy pathogenic
organisms. Absorption of UV light by microbes is believed to cause damage of cellular DNA and protein. As cellular damage
is caused by UV light, no residuals are added. Germ-killing (germicidal) UV light can be generated by low-pressure mercury
lamps. The process has been shown to be a viable, reliable, safe, and cost-effective alternative to the
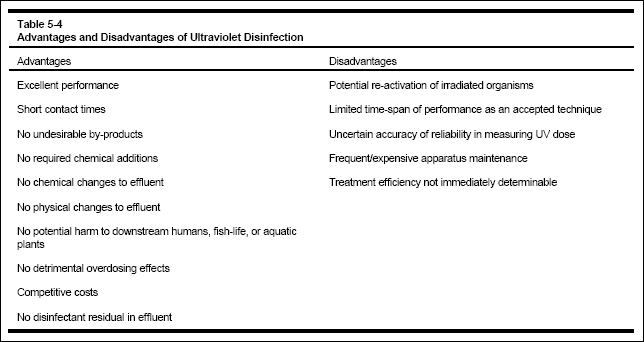
chlorination/dechlorination method. While there are some disadvantages to using UV, the advantages appear to outweigh any
negative implications, as shown in Table 5-4.
( 2 ) A typical UV disinfection unit consists of UV lamp modules placed in an open reactor or a wastewater channel.
Depending on the UV intensity requirements, two or more UV lamps are placed adjacent to each other or at a predetermined
distance to or from individual modules. Lamp modules may be configured horizontally or vertically.
( 3 ) For a bank, two or more lamp modules may be placed adjacent to each other across the width of the channel or a
reactor. UV banks may be placed in series or in parallel depending on space availability and permissible head losses.
Reactors may be made of concrete, metal, or UV-resistant plastic. Reactor dimensions vary depending on the flow and the
size and arrangement of the lamps and the desired retention time. Flow control devices such as weirs or automatic level
control gates are provided to maintain steady state flow and constant water level. UV reactors can contain vertical or
horizontal banks placed in series or in parallel depending upon flow, microbial population, and percent inactivation
required.
( 4 ) UV disinfection units usually include control panels and power distribution panels. Configurations and features of
power distribution panels and control panels vary widely depending on manufacturer specifications and models.
( 5 ) Design considerations for UV disinfection include: delivered UV dose to provide the required inactivation (UV dosage
is a function of UV intensity as well as retention time within the banks of the lamps); hydraulic characteristics of the
reactor which must closely resemble turbulent plug flow; flow pacing which is not a concern in small plants; reactor
hydraulic level control; availability of critical chamber head loss; wastewater characteristics including suspended solids,
BOD, dissolved organics, and color; and redundant UV disinfection units if required by state or local regulations. Also of
importance are individual lamp condition, ultraviolet light intensity, and projected lamp life.
( 6 ) Small wastewater treatment plants are especially adaptable to the UV disinfection process for up to 379,000 L/d
(100,000 gal/d). UV disinfection units may be designed to meet specific disinfection goals, or prefabricated submersible
units may be used and retrofitted at existing plants.
( 7 ) In the design of a UV disinfection system, the following steps must be performed :
Step 1—Collect wastewater data.
Step 2—Establish mathematical model coefficients and parameters.
Step 3—Establish reactor parameters and equipment conditions.
Step 4—Determine reactor UV density.
Step 5—Establish UV radiation intensity.
Step 6—Establish inactivation rates.
Step 7—Set hydraulic rates.
Step 8—Establish UV loading/performance relationship.
Step 9—Establish performance goals.
Step 10—Determine reactor size.
( b ) Design considerations for disinfection by UV light can be found in ETL 1110-3-442.












