|
Oracle® Application Server Administrator's Guide
10g Release 2 (10.1.2) B13995-06 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
|
Oracle® Application Server Administrator's Guide
10g Release 2 (10.1.2) B13995-06 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
This chapter provides instructions for enabling SSL in Infrastructure installations.
It contains these topics:
This section identifies all SSL communication paths used in the Oracle Application Server Infrastructure, and provides cross-references to the configuration instructions in component guides in the Oracle Application Server documentation library.
|
Note: When you install Identity Management, you are prompted to select a mode for Oracle Internet Directory. The default mode is dual mode, which allows some components to access Oracle Internet Directory using non-SSL connections. If SSL mode was chosen during installation, then all installed components must use SSL when connecting to the directory.Before you begin SSL configuration, determine the Oracle Internet Directory mode. Start the |
The following are the communication paths through the Oracle Application Server Infrastructure, and their related SSL configuration instructions:
Oracle HTTP Server to the OC4J_SECURITY instance
To configure the AJP communication over SSL, you must configure mod_oc4j's communication with the iaspt daemon. To do this, follow the instructions in the Oracle HTTP Server Administrator's Guide, section titled "Configuring mod_oc4j to Use SSL."
Oracle HTTP Server to iaspt (Port Tunneling) and then to the OC4J_SECURITY instance
To configure this connection path for SSL, follow the instructions in the Oracle HTTP Server Administrator's Guide, section titled "Understanding Port Tunneling."
The OC4J_SECURITY instance to Oracle Internet Directory
To configure this connection path for SSL, follow the instructions in the Oracle Application Server Single Sign-On Administrator's Guide. It explains how to configure SSL communication between the browser and the OracleAS Single Sign-On server (section titled "Enable SSL on the Single Sign-On Middle Tier".
Oracle Delegated Administration Services is SSL-enabled after you configure the Oracle HTTP Server for SSL. The Oracle Delegated Administration Services communication to Oracle Internet Directory is always SSL-enabled; you do not have to perform any configuration tasks to accomplish this. (OracleAS Single Sign-On, Oracle Application Server Certificate Authority, and Oracle Delegated Administration Services communicate with Oracle Internet Directory in SSL mode by default.)
Oracle Directory Integration and Provisioning to Oracle Internet Directory and Oracle Internet Directory replication server to Oracle Internet Directory
As shown in Figure 16-1, a variety of components and communication paths may be configured for SSL. The following lists references to the instructions for each:
Communication between the Oracle Internet Directory Replication server and the Oracle Internet Directory server: Oracle Application Server High Availability Guide, section titled "Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Oracle Internet Directory Replication"
Communication between Oracle Directory Integration and Provisioning and the Oracle Internet Directory server: Oracle Identity Management Integration Guide, chapter titled "Oracle Directory Integration and Provisioning Server Administration"
The OC4J_SECURITY instance to the Metadata Repository database and Oracle Internet Directory to the Metadata Repository database
If Oracle Internet Directory configured to accept SSL connections on the SSL port specified, you need only specify the SSL protocol and SSL port in the JDBC URL requesting an application, as follows:
ldaps://host:sslport/...
Note that when you are using a secure connection, you must add an s to the name of the protocol. For example, use ldaps instead of ldap.
If Oracle Internet Directory is not configured to accept SSL connections on the SSL port, you must modify the configuration. See Oracle Internet Directory Administrator's Guide, section titled "Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and the Directory."
Figure 16-1 Identity Management Components and SSL Connection Paths
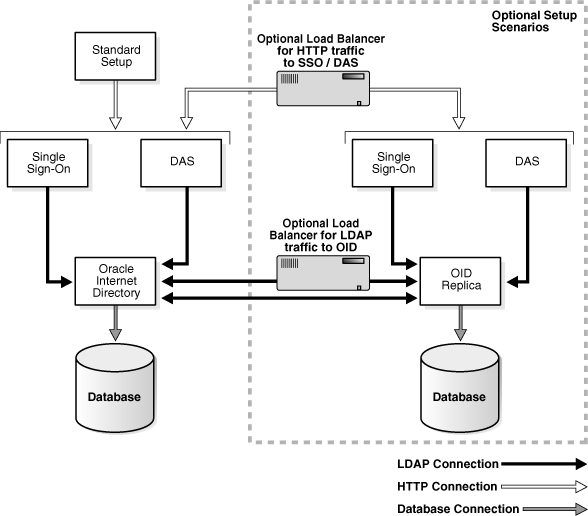
The Oracle Application Server Security Guide discusses security concepts in detail and provides recommendations for configuring security in various configurations. The "Recommended Deployment Topologies" chapter presents sample architectures for Oracle Application Server 10g Release 2 (10.1.2) installation types. After you have identified the components on which you need to enable SSL, use the instructions in this chapter and Chapter 17, "Enabling SSL in the Middle Tier" to configure the components.
Configuring SSL in OracleAS Single Sign-On and Oracle Delegated Administration Services is typical in the recommended deployment topologies (as described in Section 16.3.1, "Configuring SSL for OracleAS Single Sign-On and Oracle Delegated Administration Services"). Configuring SSL in all Infrastructure communication paths is described in Section 16.1, "SSL Communication Paths in the Infrastructure".
This section provides references to the component guides in the Oracle Application Server documentation library that provide instructions for configuring SSL in individual components.
Follow the instructions in the Oracle Application Server Single Sign-On Administrator's Guide to configure SSL communication between:
The browser and the OracleAS Single Sign-On server (section titled "Enable SSL on the Single Sign-On Middle Tier")
The OracleAS Single Sign-On server and the Oracle Internet Directory server (section titled "Configuring SSL Between the Single Sign-On Server and Oracle Internet Directory")
Oracle Delegated Administration Services is SSL-enabled after you configure the Oracle HTTP Server for SSL (as described in "Enable SSL on the Single Sign-On Middle Tier"). The Oracle Delegated Administration Services communication to Oracle Internet Directory is always SSL-enabled; you do not have to perform any configuration tasks to accomplish this.
Instructions for configuring SSL communication in Oracle Internet Directory are provided in the following:
Oracle Internet Directory Administrator's Guide, section titled "Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and the Directory"
Oracle Internet Directory Administrator's Guide, section titled "Configuring SSL Parameters"
Oracle Internet Directory Administrator's Guide, section titled "Limitations of the Use of SSL in 10g (10.1.2)"
As shown in Figure 16-1, a variety of components and communication paths may be configured for SSL. The following lists references to the instructions for each:
Communication between the Oracle Internet Directory Replication server and the Oracle Internet Directory server: Oracle Application Server High Availability Guide, section titled "Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Oracle Internet Directory Replication"
Communication between Oracle Directory Integration and Provisioning and the Oracle Internet Directory server: Oracle Identity Management Integration Guide, chapter titled "Oracle Directory Integration and Provisioning Server Administration"
Follow the instructions in the Oracle Application Server Single Sign-On Administrator's Guide, section titled "Reconfigure the Identity Management Infrastructure Database" to configure SSL communication to the Identity Management database.
This section provides references to SSL configuration information for mod_oc4j and OC4J.
To configure the AJP communication over SSL, you must configure mod_oc4j's communication with the iaspt daemon. To do this, follow the instructions in the Oracle HTTP Server Administrator's Guide, section titled "Enabling SSL between mod_oc4j and OC4J."
To configure this connection path for SSL, follow the instructions in the Oracle HTTP Server Administrator's Guide, section titled "Understanding Port Tunneling."
If Oracle Internet Directory configured to accept SSL connections on the SSL port specified, you need only specify the SSL protocol and SSL port in the JDBC URL requesting an application, as follows:
ldaps://host:sslport/...
Note that when you are using a secure connection, you must add an s to the name of the protocol. For example, use ldaps instead of ldap.
If Oracle Internet Directory is not configured to accept SSL connections on the SSL port, you must modify the configuration. See Oracle Internet Directory Administrator's Guide, section titled "Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and the Directory."
Oracle Application Server Certificate Authority is SSL-enabled by default, so there are no configuration tasks associated with this component.
|
Tip: OracleAS Certificate Authority simplifies the task of certificate provisioning for Identity Management users (certificate are automatically provisioned to OracleAS Single Sign-On-authenticated users).To enable certificate based authentication using OCA OracleAS Single Sign-On, see the Oracle Application Server Certificate Authority Administrator's Guide. To enable certificate-based authentication to OracleAS Single Sign-On, see the Oracle Application Server Single Sign-On Administrator's Guide. |
Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g comprises two components, each of which can be configured for SSL communication: Grid Control Console and Application Server Control Console.
Follow the steps in the "Configuring Security (SSL and HTTPS) for Grid Control" in the Oracle Enterprise Manager Advanced Configuration Guide.
The communication paths of interest in the SSL configuration of Application Server Control Console are shown in Figure 16-2, and are labeled https.
Figure 16-2 SSL Connection Paths in Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g
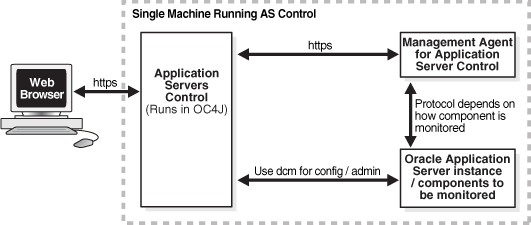
To secure the communications between the Web browser and the Application Server Control Console, and between the Application Server Control Console and the Management Agent, you can use the emctl secure iasconsole command-line utility. See Section A.4, "Configuring Security for Application Server Control Console" for instructions.
The communication (that is, obtaining monitoring information and configuration and administration tasks) between the Management Agent and the application server being monitored, and the Application Server Control and the application server being administered is not affected in any way when you use the emctl secure iasconsole utility. Those communication paths are not secured until you perform the application server security configuration steps for the particular path. Instructions on configuring SSL for application server communication paths are provided in Section 16.1, "SSL Communication Paths in the Infrastructure" and Section 17.1, "SSL Communication Paths in the Middle Tier". In addition to their SSL configuration, some components also require that you perform configuration changes to the application Server Control's Management Agent. The instructions for these changes are included with the instructions for enabling the components for SSL.
For information and instructions on configuring SSL in the Application Server Control Console, see Section A.4, "Configuring Security for Application Server Control Console".