|
Oracle® Application Server Administrator's Guide
10g Release 2 (10.1.2) B13995-06 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
|
Oracle® Application Server Administrator's Guide
10g Release 2 (10.1.2) B13995-06 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
This appendix describes how to view Oracle Application Server release numbers.
It contains the following topics:
|
Note: Oracle recommends you keep a log of all interim patches applied to your Oracle Application Server installations. |
To understand the release level nomenclature used by Oracle, examine the example of an Oracle release number shown in Figure I-1.
Figure I-1 Example of an Oracle Release Number
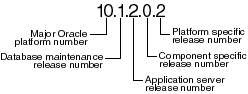
In Figure I-1, each digit is labeled:
Major Oracle Platform Number
This is the most general identifier. It represents a major new edition (or version) of an application, such as Oracle database server or Oracle Application Server, and indicates that the release contains significant new functionality.
Database Maintenance Release Number
This digit represents a maintenance release level. Some new features may also be included.
Application Server Release Number
This digit reflects the release level of Oracle Application Server.
Component Specific Release Number
This digit identifies a release level specific to a component. Different components can have different numbers in this position depending upon, for example, component patch sets or interim releases.
Platform Specific Release Number
This digit identifies a platform-specific release.
All Oracle Application Server installations have a release number. This number is updated when you apply a patch set release or upgrade the installation.
You can view the release number of an Oracle Application Server installation using Oracle Universal Installer, as follows:
Launch Oracle Universal Installer:
(UNIX) ORACLE_HOME/oui/bin/runInstaller.sh (Windows) ORACLE_HOME\oui\bin\runInstaller.bat
Click Installed Products to open the Inventory Page.
In the Inventory Page, expand Oracle Homes. You will see entries for all installations on your host.
Expand the Oracle home entry for the installation you are interested in.
You will see an entry with the release number for your original installation, followed by entries for any patch sets that have been applied.
All Oracle Application Server components have a release number and many contain services that have release numbers. These numbers may be updated when you apply a patch set release or upgrade the installation.
You can view the release number of components and their services in the following ways:
On the Filesystem
You can view component release numbers as follows on UNIX:
cd ORACLE_HOME/inventory
ls -d Components*/*/*
Using Oracle Universal Installer
If you installed Oracle Application Server using Oracle Universal Installer, you can view component release numbers as follows:
Launch Oracle Universal Installer:
(UNIX) ORACLE_HOME/oui/bin/runInstaller.sh (Windows) ORACLE_HOME\oui\bin\runInstaller.bat
Click Installed Products to open the Inventory Page.
In the Inventory Page, expand Oracle Homes. You will see entries for all installations on your host.
Expand the Oracle home entry for the installation you are interested in.
You will see an entry with the release number for your original installation, followed by entries for any patch sets that have been applied.
Expand the initial entry to view the component release numbers at installation time. If you have subsequent patch set entries, expand them to see the component release numbers updated for each patch set.
Oracle Internet Directory has a server release number, which is the version of the binaries. It also has schema and context versions. All of these numbers correspond to the Oracle Application Server installation release number through the third digit. These numbers may be updated when you apply a patch set release or upgrade the installation.
Viewing the Oracle Internet Directory Server Release Number
The Oracle Internet Directory server release number is the version of the binaries. You can view the Oracle Internet Directory server release number as follows:
Make sure the ORACLE_HOME environment variable is set.
Run the following command:
(UNIX) ORACLE_HOME/bin/oidldapd -version (Windows) ORACLE_HOME\bin\oidldapd -version
Viewing the Oracle Internet Directory Schema and Context Versions
You can view the Oracle Internet Directory schema and context versions in this file:
(UNIX) ORACLE_HOME/ldap/schema/versions.txt (Windows) ORACLE_HOME\ldap\schema\versions.txt
The contents of this file are kept up-to-date, however, you can also query the schema and context release from Oracle Internet Directory, just to be sure.
To view the schema version:
Make sure the ORACLE_HOME environment variable is set.
Run the following command:
ldapsearch -h oid_host -p oid_port -D "cn=orcladmin" -w orcladmin_password -b "cn=base,cn=oracleschemaversion" -s base "objectclass=*" orclproductversion
The output will be in this form:
cn=BASE,cn=OracleSchemaVersion orclproductversion=90500
To view the context version:
Make sure the ORACLE_HOME environment variable is set.
Run the following command:
ldapsearch -h oid_host -p oid_port -D "cn=orcladmin" -w orcladmin_password -b "cn=oraclecontext" -s base "objectclass=*" orclversion
The output will be in this form:
cn=oraclecontext orclversion=101200
Metadata Repositories have the following release numbers:
Database release number
This is the Oracle Database 10g database release number.
Metadata Repository Container release number
This is the release number for the Metadata Repository. The number is equal to the Oracle Application Server installation release number.
Schema release numbers
The Oracle Application Server schemas in the Metadata Repository have release numbers. These numbers do not necessarily correspond to Oracle Application Server release numbers or database release numbers.
Viewing the Database Release Number
The Metadata Repository is an Oracle Database 10g database that has a release number. This number is updated when you apply a patch set release or upgrade the database.
You can view the Metadata Repository release number using SQL*Plus as follows (you can be connected to the database as any user to issue these commands):
SQL> COL PRODUCT FORMAT A40 SQL> COL VERSION FORMAT A15 SQL> COL STATUS FORMAT A15 SQL> SELECT * FROM PRODUCT_COMPONENT_VERSION; PRODUCT VERSION STATUS ---------------------------------- -------------- ---------------- NLSRTL 10.1.4.0.2 Production Oracle Database 10g Enterprise Edition 10.1.4.0.2 64bi PL/SQL 10.1.4.0.2 Production TNS for Solaris: 10.1.4.0.2 Production
Viewing Metadata Repository Container and Schema Release Numbers
You can view the Metadata Repository Container release number, as well as schema release numbers, using SQL*Plus as follows (you must log in as a user with SYSDBA privileges):
SQL> COL COMPONENT_NAME FORMAT A35 SQL> COL ID FORMAT A15 SQL> COL VERSION FORMAT A15 SQL> SELECT * FROM IAS_VERSIONS; COMPONENT_NAME ID VERSION ----------------------------------- --------------- ------------------- Metadata Repository Container mrc 10.1.0.4.0 Oracle Ultrasearch ultrasearch 10.1.0
IAS_VERSIONS is a public synonym to a view owned by the INTERNET_APPSERVER_REGISTRY user. If the preceding query returns an error, it may be because:
There was an error in seeding one or more components
Not all of the components whose underlying tables are read by the view are present in the database
Either case indicates that the database is not properly seeded to be a Metadata Repository.
To get the same result by querying the underlying table:
SQL> SELECT * FROM INTERNET_APPSERVER_REGISTRY.SCHEMA_VERSIONS;
The OPatch utility is a tool that allows the application and rollback of interim patches to Oracle products, such as Oracle Application Server. For the latest information about the opatch utility, and to check for updates, refer to Oracle MetaLink at
http://www.oracle.com/support/metalink/index.html
The OPatch utility has the following requirements:
Perl environment, included with Oracle Application Server or downloaded with a patch set.
The Oracle home environment variable (ORACLE_HOME) must point to a valid Oracle home directory and match the value used during installation of the Oracle home directory.
If the -invPtrLoc command-line argument was used during installation, then it must be used when using the OPatch utility. Oracle recommends the use of the default central inventory for a platform.
The jar, java, ar, cp, and make commands must be available in the PATH statement. The commands are not available for all platforms.
The library path must be set correctly for Oracle Real Application Clusters environments. Refer to the FAQ document in the opatch/doc directory for additional information.
|
See Also: For the latest information about the OPatch utility, and to check for updates, refer to OracleMetaLink at |
The OPatch utility is located in the ORACLE_HOME/OPatch directory. It is run with options and command-line arguments. The following command shows the syntax for the OPatch utility:
path_to_opatch/opatchoption-command_line_arguments
In the preceding command, the following variables are used:
command_line_arguments: The command-line arguments for the option. Values are described in the following sections.
option: The OPatch option. Values are described in the following table:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| apply | Installs an interim patch. Refer to Section I.6.2.1 for more information. |
| lsinventory | Lists what is currently installed on the system. Refer to Section I.6.2.2 for more information. |
| query | Queries a given patch for specific details. Refer to Section I.6.2.3 for more information. |
| rollback | Removes an interim patch. Refer to Section I.6.2.4 for more information. |
| version | Prints the current version of the patch tool. Refer to Section I.6.2.5 for more information. |
To view additional information for any option, use the following command:
path_to_OPatch/opatchoption-help
If using Perl, then use the following command:
perl opatch.pl option -help
The apply option applies an interim patch to a specified Oracle home. The ORACLE_HOME environment variable must be set to the Oracle home to be patched. The following syntax is used for this option:
path_to_opatch/opatch apply [patch_location] [-delay (value)] [-force] \
[-invPtrLoc (path)] [-jdk (location)] [-jre (location)] [-local] \
[-minimize_downtime] [-no_bug_superset] [-no_inventory] \
[-oh (Oracle home location)] \
[-post (options to be passed into post) [-opatch_post_end]]\
[-pre (options to be passed into pre) [-opatch_pre_end]] \
[-retry (value)] [-silent] [-verbose]
The following table lists the command-line arguments available for use with the apply option:
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
| delay | Specifies how many seconds to wait before attempting to lock the inventory in the case of a previous failure. |
| force | Removes conflicting patches from the system. If a conflict exists which prevents the patch from being applied, then the -force command-line argument can be used to apply the patch.
|
| invPtrLoc | Specifies the location of the oraInst.loc file. This command-line argument is needed when the -invPtrLoc argument was used during installation. Oracle recommends the use of the default central inventory for a platform.
|
| jdk | Specifies the location of a particular JDK (jar) to use instead of the default location under the Oracle home directory. |
| jre | Specifies the location of a particular JRE (Java) to use instead of the default location under the Oracle home directory. |
| local | Specifies that the OPatch utility patch the local node and update the inventory of the local node. It does not propagate the patch or inventory update to other nodes.
This command-line argument can be used on Oracle Real Application Clusters environments and non-clustered environments. If an entire cluster is shutdown before patching, then this argument can be used for non-rolling patches. |
| minimize_downtime | Specifies the order of nodes to be patched by the OPatch utility.
This command-line argument only applies to Oracle Real Application Clusters environments. It cannot be used with the |
| no_bug_superset | Specifies to error out if the current patch bugs-to-fix is a superset or the same as an installed patch bugs-fixed in the Oracle home directory. |
| no_inventory | Bypasses the inventory for reading and updates. This command-line argument cannot be used with the -local command-line argument. This command-line argument puts the installation into an unsupported state.
|
| oh | Specifies the Oracle home directory to use instead of the default. |
| opatch_post_end | Marks the end of the post options. This command-line argument is used with the post command-line argument. If this argument is not used, then everything after post is passed into post.
|
| opatch_pre_end | Marks the end of the pre options. This command-line argument is used with the pre command-line argument. If this argument is not used, then everything after pre is passed into pre.
|
| post | Specifies the parameters to be passed inside the post script besides the standard parameters.
|
| pre | Specifies the parameters to be passed inside the pre script besides the standard parameters.
|
| retry | Specifies how many times the OPatch utility should try when there is an inventory lock failure. |
| patch_location | Specifies the directory of the interim patch. This should be a directory with the same name as the patch. |
| silent | Suppresses user interaction, and defaults any answers to "yes." |
| verbose | Prints output to the screen as well as to the log file. |
|
Note: If a patch consists of SQL changes, then they are only staged. Follow the instructions included with the patch to apply the patch manually on the affected instances. For some products, such as OracleAS Portal, the SQL application may be implemented as a post-staging action by the tool. These patches cannot be rolled back. |
The lsinventory option reports what has been installed on the system for a particular Oracle home directory, or for all installations. The following syntax is used for this option:
path_to_opatch/opatch lsinventory [-all] [-detail] [-invPrtLoc (path)] \
[-jre (location)] [-oh (Oracle home location)]
The following table lists the command-line arguments available for use with the lsinventory option:
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
| all | Reports the name and installation directory for each found Oracle home directory. |
| detail | Reports the installed products and other details. This command-line argument cannot be used with the -all command-line argument.
|
| invPtrLoc | Specifies the location of the oraInst.loc file. This command-line argument is needed when the invPtrLoc command-line argument was used during installation. Oracle recommends the use of the default central inventory for a platform.
|
| jre | Specifies the location of a particular JRE (Java) to use instead of the default location under the Oracle home directory. |
| oh | Specifies the Oracle home directory to use instead of the default directory. |
The following is a sample output of opatch lsinventory -detail:
ORACLE_HOME LOCATION
----------- --------
Home1 /private/phi_local/OraHome1
There is no Interim Patch
Home2 /private/phi_local/OraHome2
There is no Interim Patch
Home3 /private/phi_local/OraHome6
Installed Patch List:
=====================
1) Patch 20 applied on Mon Jul 11 15:53:51 PDT 2005
[ Base Bug(s): 21 ]
2) Patch 80 applied on Fri Jul 01 16:15:52 PDT 2005
[ Base Bug(s): 80 81 ]
The query option queries a specific patch for specific details. It provides information about the patch and the system being patched. The following syntax is used for this option:
path_to_opatch/opatch query [-all] [-get_base_bug] [-get_component] \
[-get_date] [-get_os] [-get_system_change] [-is_rolling]
The following table lists the command-line arguments available for use with the query option:
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
| all | Retrieves all information about a patch. This is equivalent to setting all command-line arguments. |
| get_base_bug | Describes the base bugs fixed by a patch. |
| get_component | Describes the Oracle components, optional or required, for a patch. |
| get_date | Provides the build date of a patch. |
| get_os | Provides the operating system description supported by a patch. |
| get_system_change | Describes the changes that will be made to the system by a patch. This command-line argument is not available. |
| is_rolling | Specifies if the patch is a rolling patch for Oracle Real Application Clusters. The set of patches need not be applied to the whole cluster at the same time. The patches can be applied to a select set of nodes at a time. |
The rollback option removes a specific interim patch from the appropriate Oracle home directory. The following syntax is used for this option:
path_to_opatch/opatch rollback -idpatch_id-ph (patch directory) \ [-delay] (value) [-invPtrLoc (path)] [-jdk (location)] [-jre (location)]\ [-local] [-oh (Oracle home location)] \ [-post (options to be passed into post) [-opatch_post_end]] \ [-pre (options to be passed into pre) [-opatch_pre_end]] [-retry (value)] \ [-silent] [-verbose]
The following table lists the command-line arguments available for use with the rollback option:
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
| delay | Specifies how many seconds the OPatch utility should wait before attempting to lock inventory again, if the -retry command-line argument is used with the apply option.
|
| id | Indicates the patch to be rolled back. Use the -lsinventory option to display all patch identifiers. To successfully rollback a patch, the patch identifier must be supplied.
|
| invPtrLoc | Specifies the location of the oraInst.loc file. This command-line argument is needed when the -invPtrLoc command-line argument was used during installation. Oracle recommends the use of the default central inventory for a platform.
|
| jdk | Specifies the location of a particular JDK (jar) to use instead of the default location under the Oracle home directory. |
| jre | Specifies the location of a particular JRE (Java) to use instead of the default location under the Oracle home directory. |
| local | Specifies that the OPatch utility patch the local node and update the inventory of the local node. It does not propagate the patch or inventory update to other nodes.
This command-line argument can be used on Oracle Real Application Clusters environments and non-clustered environments. If an entire cluster is shutdown before patching, then this argument can be used for non-rolling patches. |
| oh | Specifies the Oracle home directory to use instead of the default directory. |
| opatch_post_end | Marks the end of the post options. This command-line argument is used with the post command-line argument. If this argument is not used, then everything after post is passed into post.
|
| opatch_pre_end | Marks the end of the pre options. This command-line argument is used with the pre command-line argument. If this argument is not used, then everything after pre is passed into pre.
|
| ph | Specifies the valid patch directory area. The utility will use the command types found in the patch directory to identify which commands are used for the current operating system. |
| post | Specifies the parameters to be passed inside the post script besides the standard parameters.
|
| pre | Specifies the parameters to be passed inside the pre script besides the standard parameters.
|
| retry | Specifies how many times the OPatch utility should try in case of an inventory lock failure. |
| silent | Suppresses user interaction, and defaults any answers to "yes." |
| verbose | Prints output to the screen as well as to the log file. |