|
Oracle® Application Server Installation Guide
10g Release 2 (10.1.2) for hp-ux Itanium B25193-01 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
|
Oracle® Application Server Installation Guide
10g Release 2 (10.1.2) for hp-ux Itanium B25193-01 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
This chapter includes the following sections:
Section 4.4, "Where Do I Install Oracle Application Server?"
Section 4.7, "First-Time Installation of Any Oracle Product"
Section 4.9, "Oracle Application Server Instances and Instance Names"
Section 4.10, "The ias_admin User and Restrictions on Its Password"
Section 4.11, "Comparing Installing Components Against Configuring Components"
Section 4.12, "Where Does Oracle Universal Installer Write Files?"
Section 4.13, "Can I Modify Other Oracle Application Server Instances During Installation?"
Section 4.14, "Connecting to Oracle Internet Directory Through SSL Connections"
Section 4.15, "Setting the Mount Point for the CD-ROMor DVD"
You can obtain Oracle products from Oracle E-Delivery at http://edelivery.oracle.com/. Oracle products are distributed as "E-Packs". An E-Pack is an electronic version of the software that is also available to Oracle Customers on CD-ROM or DVD. This section contains the following topics:
Section 4.1.1, "Finding and Downloading the Oracle Application Server 10g Release 2 (10.1.2) E-Pack"
Refer to the CD/Media Pack description or the list of products that you purchased on your Oracle Ordering Document. Then, view the License List to help you decide which Product Pack you need to select in order to search for the appropriate E-Pack(s) to download. Prior to downloading, verify that the product you are looking for is in the License and Options section of the E-Pack README. Oracle recommends that you print the README for reference.
Refer to the README link that is on each E-Pack Download page. In addition to listing the licensable products and options contained in the pack, the README lists downloadable files that are required to run each product and which downloadable files are optional. Oracle recommends that you print the README for reference.
In addition to having the required disk space necessary to install and run your Oracle software, you must have sufficient disk space to download all the required software files and have enough disk space to extract them.
After extracting the software from the Zip files, you can burn them onto CD-ROM and install from them, or install from your computer's hard drive.
Verify that the file size of your downloaded file matches the file size displayed on E-Delivery. Unzip each Zip file to its own temporary directory. For example, create a directory called oraAS10g on the hard drive:
/oraAS10g
Then create a new directory for each Zip file you downloaded:
/oraAS10g/Disk1/oraAS10g/Disk2
If you plan to burn the files on a CD-ROM, create a separate CD-ROM from the contents of each directory. Do not burn a CD-ROM containing the Zip file itself; you need the unzipped contents of the Zip files to do the installation. When you burn the files to CD-ROM, the contents of each disc must be at the root of the CD image.
To install from CD-ROM or from your hard drive, see Section 4.16, "Starting Oracle Universal Installer".
Oracle Application Server is made up of:
Oracle Application Server middle tier
OracleAS Infrastructure
You deploy and run your applications on Oracle Application Server middle tiers. The infrastructure provides services that are used by middle tiers. Infrastructure services can be shared by one or more middle tiers.
When you run Oracle Universal Installer, you select whether you want to install the middle tier or the infrastructure. Typically you need both, so you would run Oracle Universal Installer twice.
Figure 4-1 shows a simple Oracle Application Server installation. The J2EE and Web Cache middle tier running on computer 1 uses OracleAS Infrastructure running on computer 2. The figure shows the OracleAS Metadata Repository and two Identity Management services (OracleAS Single Sign-On and Oracle Internet Directory).
Figure 4-1 A Middle Tier Using Infrastructure Services
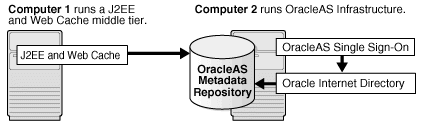
In most cases, you must install OracleAS Infrastructure first, because the middle tiers depend on OracleAS Infrastructure services. The one case where the infrastructure is optional is the J2EE and Web Cache middle-tier type. (But see Section 6.4, "Configuration Options for the J2EE and Web Cache Middle Tier")
You can install the middle tiers and the infrastructure on the same computer or on separate computers. You can get better performance if you install the infrastructure on its own computer, and the middle tiers on other computers.
For example, Figure 4-2 shows a topology with four computers:
Computer 1 runs a J2EE and Web Cache instance that is not using any infrastructure services.
Computer 2 runs a Portal and Wireless middle tier that uses infrastructure services from the infrastructure instance running on Computer 4.
Computer 3 runs another Portal and Wireless middle tier that uses infrastructure services from the infrastructure instance running on Computer 4.
Computer 4 runs OracleAS Infrastructure.
Refer to Chapter 14, "Recommended Topologies" for topology examples.
Figure 4-2 Configuration with Multiple Middle Tiers and an Infrastructure

|
Note: You can install different middle tiers and infrastructure components on different platforms. The only exception is that if you want to cluster multiple J2EE and Web Cache middle tiers, they must be on the same platform. However, the infrastructure for this cluster can still be on a different platform. |
The directory in which you install Oracle Application Server is called the Oracle home. During installation, you specify the full path to this directory and a name for this Oracle home.
For example, you can install OracleAS Infrastructure in /opt/oracle/OraHome_Infra, and you can name it "Infra".
Names of Oracle homes must be 128 characters or fewer, and can contain only alphanumeric characters and underscores.
|
Note: Spaces are not allowed anywhere in the Oracle home directory path. For example, you cannot install in "/opt/oracle/app server/Infra" because of the space character in "app server". Oracle Universal Installer does not check for this until several screens after you have entered the path.
|
If you plan to install a middle tier and an infrastructure on the same computer, you must install them in different Oracle home directories. Oracle Universal Installer does not allow you to install a middle tier and an infrastructure in the same Oracle home. Section 14.2, "Portal and Wireless Developer Topology" describes a configuration where you install a middle tier and an infrastructure on the same computer.
|
Note: If you install multiple Oracle Application Server instances (for example, an OracleAS Infrastructure and a middle tier) on the same computer, create scripts for setting the environment for each instance. This is to ensure that you run the binaries from the proper Oracle home. Environment variables that you need to set includeORACLE_HOME and PATH.
|
Generally, you cannot install Oracle Application Server in an existing Oracle home. Refer to "Oracle home directory" for a list of combinations that are not allowed. Two exceptions to the rule are:
You can install Oracle Application Server middle tiers into an existing Oracle home that contains Oracle Developer Suite 10g Release 2 (10.1.2). However, before you install, check that in the file ORACLE_HOME/j2ee/home/config/default-web-site.xml, the protocol is set to "ajp13" (not http), and the port is set to 0 (zero).
|
Note: If you choose to install Oracle Application Server in an existing Oracle Developer Suite 10g Release 2 (10.1.2) home, you will lose some Oracle Developer Suite functionality. Specifically, you can no longer access directly the OC4J home instance in Oracle Developer Suite using the hostname:8888 URL.
|
You can install Oracle Application Server middle tier into an existing middle tier if you are expanding it. Refer to Section 6.13, "Expanding a MiddleTier" for details.
You cannot install Oracle Application Server in a directory that already contains some files, except for the cases mentioned in Section 4.5.1, "Installing in an Existing Oracle Home". For example, if you cancel an installation, or if an installation failed, you have to clean up the directory before you can reinstall Oracle Application Server in it. Also, Oracle Universal Installer cannot "repair" an installation. Refer to Section G.2.2, "Message About Installing in a Non-Empty Directory" for instructions on how to clean up the directory.
You can create symbolic links before installing Oracle Application Server and use them during installation. For example, if you run the following commands:
mkdir /home/basedir ln -s /home/linkdir /home/basedir
then, when you run Oracle Universal Installer, you can specify /home/linkdir as the Oracle Home.
After installation, you cannot create symbolic links to the Oracle Home. You also may not move the Oracle Home to a different location and create a symbolic link to the original Oracle Home.
If Oracle Application Server is the first Oracle product to be installed on a computer, Oracle Universal Installer displays a screen where you specify an inventory directory (also called the oraInventory directory). This inventory directory is used by Oracle Universal Installer to keep track of all Oracle products installed on the computer.
The inventory directory is separate from the Oracle home directory for Oracle Application Server.
To ensure other users in the oinstall group have access to the inventory directory (so that they can install Oracle products), do not use the oracle user home directory as the inventory directory because home directories might not have the proper permissions set up for the oinstall group. Instead, you can put the inventory directory in the /opt/oracle directory (for example, /opt/oracle/oraInventory).
If you have installed an Oracle product previously on the computer, Oracle Universal Installer uses the existing inventory directory. Ensure that you have write permissions on that directory. The best way of ensuring this is to run Oracle Universal Installer as the same operating system user who installed the existing Oracle products.
Oracle recommends creating an operating system user to perform all tasks related to installation of Oracle products. Refer to Section 3.7, "Operating System User".
By default, Oracle Universal Installer installs Oracle Application Server with text in English and in the operating system language. If you need additional languages, click the Product Languages button in the "Select a Product to Install" screen.
When you select additional languages to install, Oracle Universal Installer installs text in the selected languages. It also installs fonts required to display the languages.
For some components, languages are installed only if you select them during installation. In this case, if you access the application in a language that is not available, it will fall back on the server locale language.
For other components, available languages are installed, regardless of what you select during installation. In this case, however, fonts are installed only for the languages that are explicitly selected. When you access the application, it uses text in your language because the language was installed. However, if you do not have the appropriate fonts to render the text, the text appears as square boxes. This usually applies to the Chinese, Japanese, and Korean languages.
You can install fonts after installation. Refer to Section G.2.7, "User Interface Does Not Display in the Desired Language, or Does Not Display Properly".
|
Note:
|
When you install the infrastructure or middle tier, what you get is an Oracle Application Server instance. Oracle Universal Installer prompts you to provide a name for the Oracle Application Server instance you are installing. For example, you can name an instance "infra" or "J2EE". This name can be different from the Oracle home name.
You cannot change this name after installation.
Oracle Application Server appends the hostname and domain name to the given instance name to form a complete instance name. For example, if you are installing an instance on a computer named c1, and you name the instance infra1, then the full name of the instance is infra1.c1.mydomain.com, assuming the domain name is mydomain.com.
Valid Characters in Instance Names
Instance names can consist only of the alphanumeric characters (A-Z, a-z, 0-9) and the _ (underscore) character.
The maximum length for an instance name is 64 characters.
Restrictions on Oracle Application Server Instance Names
Do not use the hostname of the computer when naming Oracle Application Server instances.
If you are planning to place the Oracle Application Server instance in an OracleAS Cluster, the instance name must not contain the following:
hostname or IP address of any computer in the OracleAS Cluster
Oracle home of any Oracle Application Server installation in the OracleAS Cluster
How Oracle Application Server Uses Instance Names
Instance names are important because Oracle Application Server uses them to uniquely identify instances. This means that if you install multiple Oracle Application Server instances on the same computer (for example, an OracleAS Infrastructure and a J2EE and Web Cache instance), you must give them different names.
When you administer Oracle Application Server using Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g Application Server Control (or Application Server Control for short), the instance name appears on the screens. You can click the instance name to see details about the instance, such as the components that are installed in that instance, if the components are running or stopped, and the log files for the components. The Application Server Control is a browser-based administration tool for Oracle Application Server. Refer to Oracle Application Server Administrator's Guide for details about this administration tool.
In addition, some dcmctl commands require an instance name as a parameter. dcmctl is a command-line tool for administering Oracle Application Server instances. Refer to Distributed Configuration Management Administrator's Guide for details about dcmctl.
Oracle Universal Installer prompts you to specify the password for the ias_admin user. The ias_admin user is the administrative user for Oracle Application Server instances. To manage Oracle Application Server instances using Application Server Control, you log in as ias_admin.
On a computer, you can install multiple Oracle Application Server instances, each with its own unique instance name, but the name of the administrative user is ias_admin for all instances. The password for the ias_admin user can be different for each instance.
Password for the ias_admin User
The password for the ias_admin user must conform to Oracle Internet Directory password policy:
If you are using the Oracle Internet Directory that is shipped with this release of Oracle Application Server and you did not change the default password policy, passwords have the following restrictions:
The minimum length is five alphanumeric characters.
At least one of the characters must be a number.
If you are using any other version of Oracle Internet Directory (for example, you are using an existing Oracle Internet Directory), your Oracle Internet Directory administrator might have defined a different password policy. The password you enter for the ias_admin user must conform to the existing Oracle Internet Directory password policy.
In addition to the password policy defined in Oracle Internet Directory, the password for the ias_admin user has these restrictions:
Passwords must be shorter than 30 characters.
Passwords can contain only alphanumeric characters from your database character set, the underscore (_), the dollar sign ($), and the number sign (#).
Passwords must begin with an alphabetic character. Passwords cannot begin with a number, the underscore (_), the dollar sign ($), or the number sign (#).
Passwords cannot be Oracle reserved words. The Oracle Database SQL Reference lists the reserved words. You can find this guide on Oracle Technology Network
http://www.oracle.com/technology/documentation.
You can also avoid using words that sound like they might be reserved words.
|
Note: When entering your password, check that the state of the Caps Lock key is what you want it to be. Passwords are case-sensitive. |
You must remember the password because you need to enter it to perform the following tasks:
When you log on to Application Server Control to manage Oracle Application Server, you log on as the ias_admin user.
For middle-tier installations: if you want to install a larger middle tier in an ORACLE_HOME that already contains a middle tier (for example, you want to install the Portal and Wireless type over an existing J2EE and Web Cache type), you must enter the existing password during the installation.
If you forget the password, you can reset it. Refer to Oracle Application Server Administrator's Guide for details.
When you select components on the Select Configuration Options screen, Oracle Universal Installer installs and configures the selected components. For the unselected components, Oracle Universal Installer still installs them, but does not configure them.
In most cases, you can configure components that you did not select on the Select Configuration Options screen after installation using the Application Server Control. Refer to Oracle Application Server Administrator's Guide for details.
Oracle Universal Installer writes files to the following directories:
Table 4-1 Directories Where Oracle Universal Installer Writes Files
| Directory | Description |
|---|---|
|
Oracle home directory |
This directory contains Oracle Application Server files. You specify this directory when you install Oracle Application Server. |
|
When you install the first Oracle product on a computer, you specify this directory, which Oracle Universal Installer uses to keep track of which Oracle products are installed on the computer. In subsequent installations, Oracle Universal Installer uses the same inventory directory. |
|
|
This directory contains information about locations of Oracle homes on the computer. If you installed Oracle9iAS release 2 (9.0.2) on your computer, this directory also contains files that provide information for Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g. |
|
|
Oracle Universal Installer writes files needed only during installation to a "temporary" directory. By default, the "temporary" directory is |
During the installation of an Oracle Application Server instance, you should not change the configuration or passwords of other installations in your environment. For example, if there is an OracleAS Infrastructure installation in your environment, you should not modify it during the installation of a middle tier.
When you install OracleAS Infrastructure or middle tiers, you can specify that Oracle Application Server components connect to Oracle Internet Directory only through SSL connections. On screens where you specify the hostname and port for Oracle Internet Directory, you can select the Use Only SSL Connections With This Oracle Internet Directory option.
Note that Oracle HTTP Server is not set up for SSL connections during installation. If you need Oracle HTTP Server to use SSL, you can set it up after installation. Refer to Oracle HTTP Server Administrator's Guide for details.
The Oracle Application Server CD-ROMs are in RockRidge format. The DVD is in DVD format.
To mount the first disc:
Insert Oracle Application Server disk 1 into the disk drive.
Create the /SD_CDROM directory if it does not already exist:
# /usr/bin/mkdir /SD_CDROM
Enter a command similar to the following:
# /usr/sbin/mount -F cdfs -o rr /dev/dsk/cxdytz /SD_CDROM
In the preceding example, /SD_CDROM is the disk mount point directory and /dev/dsk/cxdytz is the device name for the disk device, for example /dev/dsk/c0d2t0.
If your computer does not mount CD-ROMs or DVD automatically, you need to set the mount point manually. Refer to Section 4.15, "Setting the Mount Point for the CD-ROMor DVD" for details.
Log in as the oracle user.
If you are installing Oracle Application Server on a multihomed computer, create the ORACLE_HOSTNAME environment variable. Set this variable to point to the hostname of the computer on which you are installing Oracle Application Server.
CD-ROM users: Insert Oracle Application Server Disk 1 into the CD-ROM drive.
DVD users: Insert the Oracle Application Server DVD into the DVD drive.
Run the Oracle Universal Installer using the command shown after the note:
|
Note:
|
prompt> cd prompt> mount_point/10.1.2disk1/runInstaller
prompt> cd prompt> mount_point/application_server/runInstaller
This launches Oracle Universal Installer through which you install Oracle Application Server.