|
Oracle® Application Server Adapter for PeopleSoft User's Guide
10g Release 2 (10.1.2) B14060-02 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
|
Oracle® Application Server Adapter for PeopleSoft User's Guide
10g Release 2 (10.1.2) B14060-02 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
Oracle Application Server connects to a PeopleSoft system through Oracle Application Server Adapter for PeopleSoft (OracleAS Adapter for PeopleSoft). OracleAS Adapter for PeopleSoft provides connectivity and executes interactions on a PeopleSoft system. This chapter discusses the following topics:
OracleAS Adapter for PeopleSoft provides a means to exchange real-time business data between PeopleSoft systems and other applications, databases, and external business partner systems. The adapter enables inbound and outbound processing with PeopleSoft. OracleAS Adapter for PeopleSoft can be deployed as a J2EE Connector Architecture (J2CA) version 1.0 resource adapter. This deployment is referred to as OracleAS Adapter J2CA. It can also be deployed as a Web services servlet and is referred to as Oracle Application Server Adapter Business Services Engine (BSE).
OracleAS Adapter for PeopleSoft uses XML messages to enable non-PeopleSoft applications to communicate and exchange transactions with PeopleSoft using services and events. The role of services and events is outlined
Services: Enable applications to initiate a PeopleSoft business event.
Events: Enable applications to access PeopleSoft data only when a PeopleSoft business event occurs.
To support event functionality, the following two features are implemented:
Port: A port associates a particular business object exposed by an adapter with a particular disposition. A disposition defines the protocol and location of the event data. The port defines the end point of the event consumption.
The port is the Oracle adapter component that pushes the event received from the enterprise information system (EIS) to the adapter client. The port supported in this release is Remote Method Invocation (RMI).
|
Note: You do not need to create or configure ports for use with BPEL Process Manager. |
Channel: A channel represents configured connections to particular instances of back-end or other types of systems. A channel binds one or more event ports to a particular listener managed by an adapter.
The channel is the adapter component that receives events in real time from the enterprise information system (EIS) application. The channel component can be a File reader, an HTTP listener, a TCP/IP listener, or an FTP listener. A channel is always EIS specific. The adapter supports multiple channels for a particular EIS. This enables the user to choose the optimal channel component based on deployment requirements.
OracleAS Adapter for PeopleSoft provides:
Synchronous and asynchronous, bidirectional message interactions for PeopleSoft component interfaces and PeopleSoft Application Messaging Manager.
Oracle Application Server Adapter Application Explorer (Application Explorer), a GUI tool that explores PeopleSoft metadata and builds XML schemas or Web services.
XML schemas for the J2CA 1.0 resource adapter.
Web services for BSE.
The adapter connects to the PeopleSoft Application Server by accessing APIs for the component interfaces that correspond to its supported business objects. Every component interface contains data and business logic for the business component, thus alleviating a requirement for the adapter to duplicate the processes defined within the business component.
PeopleSoft provides for integration with other applications and systems through its component interface framework and its Integration Broker (in release 8.4) or Application Messaging (in release 8.1) facility. OracleAS Adapter for PeopleSoft uses the PeopleSoft framework and leverages various integration access methods to provide the greatest amount of flexibility and functionality. Integration access methods supported by OracleAS Adapter for PeopleSoft include:
In the PeopleSoft environment, a component interface is a container for distributing PeopleSoft application data among PeopleSoft logical systems and for exchanging PeopleSoft application data with non-PeopleSoft systems.
The component interface is based on an existing business process within PeopleSoft. An example is a purchase order entry, which can be a PeopleSoft-delivered process or a user-developed process. The component interface also inherits its methods (Add, Update, and so on) and its business logic from the underlying business process.
PeopleSoft delivers generic component interfaces with each of its applications. These are called Enterprise Integration Points (EIP). Customers can also develop their own custom component interfaces, or they can modify EIP as required. OracleAS Adapter for PeopleSoft supports both types of component interfaces.
OracleAS Adapter for PeopleSoft enables you to:
Access a PeopleSoft component using a component interface. Component methods are also referred to as services.
Receive messages from a PeopleSoft application. Messages are also referred to as events.
When you access a PeopleSoft component from another application, you work with:
Component interfaces. If a component interface does not exist, create, secure, and test one. If the component interface exists, but you modified it, secure and test it. For more information, see your PeopleSoft documentation. Alternatively, you can secure and test the component interface and create the component interface API after you generate schemas or Web services.
Component interface APIs. Create an API for the component interface.
Schemas and Web services. Create schemas or Web services for the component methods.
See Chapter 2, "Configuring OracleAS Adapter for PeopleSoft" for more information.
To receive a message from PeopleSoft, you work with:
The Integration environment. Configure and test your PeopleSoft Integration Broker (release 8.4) or Application Messaging environment (release 8.1). To ensure that the environment is properly configured, see your PeopleSoft documentation.
Message routing. Configure TCP/IP Target Connector (release 8.4), HTTP Target Connector (release 8.4), or TCP/IP Handler (release 8.1).
OracleAS Adapter for PeopleSoft works in conjunction with the following components:
Application Explorer can be configured to work in a Web services environment in conjunction with BSE or J2CA. When working in a J2CA environment, the connector uses the Common Client Interface (CCI) to provide integration services using adapters instead of Web services.
Oracle Application Server Adapter Business Services Engine (BSE) Architecture
Figure 1-1 shows the generic architecture for the Oracle Web service adapter for packaged applications. The adapter works in conjunction with BSE, as deployed to a Web container in a J2EE application server.
Oracle Application Server Adapter Application Explorer (Application Explorer), a design-time tool deployed along with BSE, is used to configure adapter connections, browse EIS objects, configure services, and configure listeners to listen for EIS events. Metadata created while you perform these operations are stored in the repository by BSE.
BSE uses SOAP as a protocol for consuming requests from clients, interacting with the EIS, and sending responses from the EIS back to clients.
Figure 1-1 Oracle Application Server Adapter Business Services Engine (BSE) Architecture

|
Note: Do not use a file repository for BSE in production environments. |
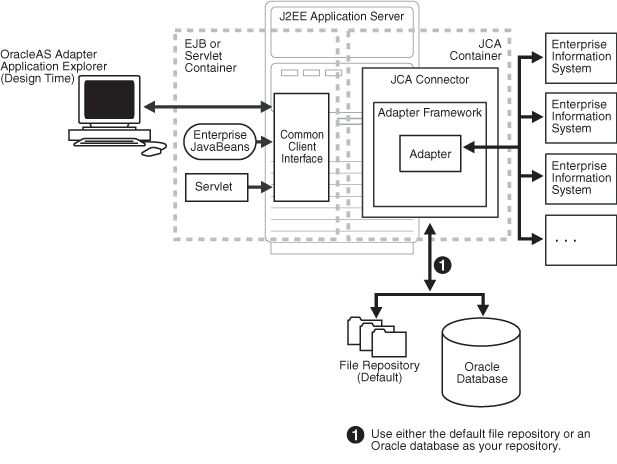
Oracle Application Server Adapter Generic J2CA Architecture
Figure 1-2 shows the generic architecture for OracleAS Adapter J2CA for packaged applications. OracleAS Adapter J2CA is deployed to a standard J2CA Container and serves as host container to the adapters. The connector is configured with a repository. The repository can be a file system or an Oracle database. It is deployed as a RAR file and has an associated deployment descriptor called ra.xml. You can create multiple connector factories by editing the OC4J deployment descriptor oc4j-ra.xml. See Chapter 3, "OC4J Deployment and Integration" for more information on OC4J deployment.Application Explorer, a design tool that works in conjunction with the connector, is used to configure adapter connections, browse EIS objects, configure services, and configure listeners to listen for EIS events. Metadata created while you perform these operations are stored in the repository by the connector.
Figure 1-2 Oracle Application Server Adapter Generic J2CA Architecture
If using OracleAS Adapter for PeopleSoft with BPEL Process Manager, please note that:
Only OracleAS Adapter J2CA deployment supports inbound integration (event notification) with BPEL Process Manager.
Both OracleAS Adapter J2CA and BSE deployments support outbound integration (request-response service) with BPEL Process Manager.
The following four factors explain the differences between deploying the BSE and OracleAS Adapter J2CA. Understanding the factors can help in selecting a deployment option.
BSE is the preferred deployment option because it:
Can be deployed in a separate instance of Oracle Application Server.
Provides better distribution of load.
Provides better isolation from any errors from third party libraries.
Provides better capability to isolate issues for debugging purposes.
Conforms more closely to Service Oriented Architecture (SOA) model for building applications.
OracleAS Adapter J2CA provides slightly better performance
OracleAS Adapter J2CA does provide slightly better performance than BSE; however, the difference decreases as the transaction rate increases.
OracleAS Adapter J2CA and the BSE option both provide identity propagation at runtime
The BSE option provides the capability to pass identity using the SOAP header. For OracleAS Adapter J2CA, user name and password can be passed using the connection spec of the CCI.
Transactions