|
Oracle® Application Server Adapter for SAP R/3 User's Guide
10g Release 2 (10.1.2) B14061-02 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
|
Oracle® Application Server Adapter for SAP R/3 User's Guide
10g Release 2 (10.1.2) B14061-02 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
Oracle Application Server connects to an SAP system through Oracle Application Server Adapter for SAP R/3 (OracleAS Adapter for SAP). OracleAS Adapter for SAP provides connectivity and executes interactions on an SAP system. This chapter discusses the following topics:
OracleAS Adapter for SAP provides a means to exchange real-time business data between SAP systems and other applications, databases, or external business partner systems. The adapter enables external applications to perform inbound and outbound processing with SAP. OracleAS Adapter for SAP can be deployed as a J2EE Connector Architecture (J2CA) version 1.0 resource adapter. This deployment is referred to as OracleAS Adapter J2CA. It can also be deployed as a Web services servlet and is referred to as OracleAS Adapter Business Services Engine (BSE).
OracleAS Adapter for SAP uses XML messages to enable non-SAP applications to communicate and exchange transactions with SAP using services and events.The role of services and events is outlined.
Services: Enable applications to call an SAP business object or business operation.
Events: Enable applications to access SAP data only when an SAP business event occurs.
To support event functionality, the following two features are implemented:
Port: A port associates a particular business object exposed by an adapter with a particular disposition. A disposition defines the protocol and location of the event data. The port defines the end point of the event consumption.
The port is the Oracle adapter component that pushes the event received from the enterprise information system (EIS) to the adapter client. The port supported in this release is Remote Method Invocation (RMI).
|
Note: You do not need to create or configure ports for use with BPEL Process Manager. |
Channel: A channel represents configured connections to particular instances of back-end or other types of systems. A channel binds one or more event ports to a particular listener managed by an adapter.
The channel is the adapter component that receives events in real time from the EIS application. The channel component can be a File reader, an HTTP listener, a TCP/IP listener, or an FTP listener.
A channel is always EIS specific. The adapter supports multiple channels for a particular EIS. This enables the user to choose the optimal channel component based on deployment requirements. In the case of this adapter, the channel is an RFC server.
OracleAS Adapter for SAP provides:
Support for bidirectional message interactions.
OracleAS Adapter Application Explorer (Application Explorer), a GUI tool which uses SAP object repository metadata to build XML schemas and Web services to handle adapter requests or event data.
Support for Remote Function Calls (RFC), Business Application Programming Interfaces (BAPI), and Intermediate Documents (IDoc) interfaces to SAP.
XML schemas for the J2CA 1.0 resource adapter.
Web services for BSE.
SAP has certified OracleAS Adapter for SAP for use with all versions of SAP, including mySAP.com solutions.OracleAS Adapter for SAP provides state-of-the-art middleware solutions for SAP Basis and SAP Web application server-based systems. This adapter has achieved the following three interface certifications that promote cost-effective and low-risk solutions.
CA-ALE (Certified Adapter - Application Link Enabling) certification. Enhances electronic data interchange (EDI) subsystem interface with SAP Basis and SAP Web Application Server. Using direct program-to-program remote communication and transformation from non-SAP systems to SAP solution-based systems, OracleAS Adapter for SAP expedites the conversion, import, and export of critical intermediate documents (IDocs).
CA-AMS (Andrew Message System) certification. Rapidly bridges SAP Basis and SAP Web Application Server data exchange with other applications through pure message delivery. As an ALE (Application Link Enabling) Message Handler, the adapter sends IDoc messages without a requirement for conversion from one or more SAP solution-based systems.
CA-XML (Extensible Markup Language) certification. Eases the communication between external middleware with SAP Basis and SAP Web Application Server over the Internet using XML, HTTP, or HTTPS. The adapter immediately transfers SAP solution specifications into XML for straight transfer into application subsystem repositories. The CA-XML-certified adapter directly receives and converts messages to be pulled or pushed into XML formats to or from SAP solution-based systems over the Internet.
The following SAP platforms are supported by OracleAS Adapter for SAP:
SAP Web Application Server Version 6.2 and higher
SAP R/3 4.0 and higher
SAP Enterprise R/3 4.7
All or portions of: MySAP.com technology solutions (SAP BW, SAP APO, SAP CRM, SAP SRM, SAP EBP, SAP SEM, SAP WP, SAP KW)
|
Note: Release versions may vary by product component. In addition, SAP functions may vary by SAP product version and support package. |
OracleAS Adapter for SAP is supported on the following operating systems:
Windows 2000/2003/XP
Solaris Version 2.8, 2.9, and higher
Linux x86 Redhat Advanced Server Version 2.1 and higher, Suse Version 8.1 and higher, United Linux Version 1.0 and higher
IBM AIX Version 5.1 and higher
HP-UX Version 11i and higher
HP Tru64 Version 5.1a and higher
OracleAS Adapter for SAP is designed to provide standard access to SAP business objects such as Remote Function Call (RFC) modules, BAPIs (Business Application Programming Interfaces), and IDocs (Intermediate Documents) that are used to support existing business processes. The business objects and methods are available to the adapter as requests of SAP and to the event adapter when SAP initiates its remote requests. These objects work in the following ways:
Business Application Programming Interfaces (BAPI) are interfaces within the business framework that link SAP components to one another or to third-party components. BAPIs are called synchronously and return information.
Remote Function Call (RFC) Modules are SAP application interfaces that enable clients to utilize SAP technologies and receive responses.
|
Note: Depending on the release or service pack installed, certain RFCs, for example,RFC_CUSTOMER_GET, may not exist in your particular SAP system. Therefore, the examples included in this documentation may not be relevant to your system. If this is the case, you should use the examples as a general reference for adapter functionality and choose an RFC that exists within your SAP application environment.As described in SAP Release Note 109533, SAP Function Modules (RFCs) can be delivered with different release statuses. SAP supports only RFCs that are awarded with the Released for Customer status. There is no claim to the release independencies of the interfaces and the continued existence/functionality of the modules. For more information on the status of a specific function module, consult your SAP Service Marketplace.
|
Intermediate Documents (IDocs) are the "logical messages" that correspond to different business processes. They enable different application systems to be linked by a message-based interface. The IDoc type indicates the SAP format to use to transfer the data for a business transaction. An IDoc is a real business process in the form of an IDoc type that can transfer several message types. An IDoc type is described by the following components:
Control records. A control record contains data that identifies the sender, the receiver, and the IDoc structure. An IDoc contains one control record.
Data records. A data record consists of a fixed administration part and a data part (segment). The number and format of the segments can be different for each IDoc type.
Status records. A status record describes the processing stages through which an IDoc passes.
The following scenario is an example of IDoc functionality and its components:
Purchase order number 4711 was sent to a vendor as IDoc number 0815. IDoc number 0815 is formatted in IDoc type ORDERS01 and has the status records "created" and "sent." The purchase order corresponds to the logical message ORDERS.
You can use OracleAS Adapter for SAP to initiate an SAP business process, such as add/update account, or you can use the adapter as part of an integration effort to connect SAP and non-SAP systems.BAPI and RFC are called synchronously by the adapter and always return data (either technical error information or a well-formed response document). IDocs are processed asynchronously.The adapter is bidirectional and can process an event in SAP by receiving RFC and IDocs directly from SAP. The SAP system can be configured to send an IDoc or RFC out to a logical system when a certain event occurs, in this case, to the adapter. The output sent by SAP can be in any of the following forms:
A BAPI request, for example, BAPI_COMPANYCODE_GETLIST
An IDoc
For request processing, OracleAS Adapter for SAP can send requests to SAP using the BAPI, RFC, or IDoc interfaces.OracleAS Adapter for SAP integrates SAP IDocs, RFC, and BAPI with mission-critical SAP system applications and other enterprise applications. The benefits of the adapter include:
Elimination of the requirement for custom coding.
Consistent data representation—a standard XML representation of event data and request/response documents for SAP. The developer is freed from the specific details of the SAP interface (BAPI, RFC, IDoc,) and the specific configuration details of the target SAP system.
Adherence to SAP ABAP serialization rules and SAP Interface Repository standards published by SAP AG.
OracleAS Adapter for SAP works in conjunction with the following components:
Application Explorer (used to configure SAP connections and create Web services and events) can be configured to work in a Web services environment in conjunction with BSE or J2CA. When working in a J2CA environment, the connector uses the Common Client Interface (CCI) to provide integration services using adapters instead of Web services.
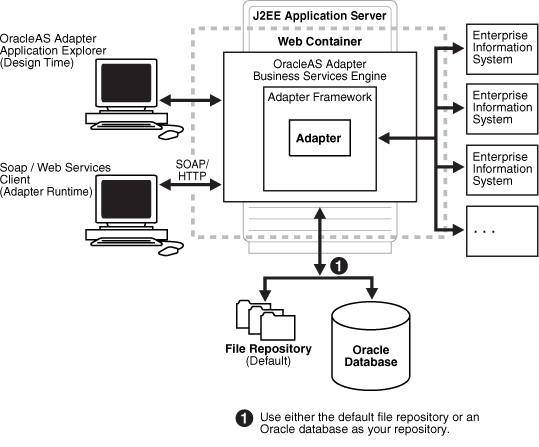
Oracle Application Server Adapter Business Services Engine (BSE) Architecture
Figure 1-1 shows the generic architecture for BSE for packaged applications. Application Explorer works in conjunction with BSE, as deployed to the OC4J (Oracle Containers for J2EE) container of the Oracle Application Server.
Application Explorer, a design-time tool deployed along with BSE, is used to configure adapter connections, browse EIS objects, configure services, and configure listeners to listen for EIS events. Metadata created while you perform these operations are stored in the repository by BSE.
BSE uses SOAP as a protocol for consuming requests from clients, interacting with the EIS, and sending responses from the EIS back to clients.
BSE supports both a file-based and an Oracle database repository. The BSE repository stores the EIS connection information and the WSDL for adapter services. A single instance of BSE can connect to multiple EIS applications.
|
Note: Do not use a file repository for BSE in production environments. |
Figure 1-1 Oracle Application Server Adapter Business Services (BSE) Architecture
Oracle Application Server Adapter Generic J2CA Architecture
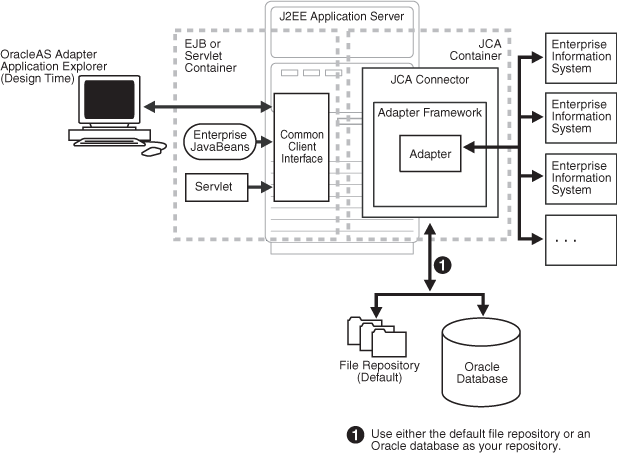
Figure 1-2 shows the generic architecture for OracleAS Adapter J2CA for packaged applications. This is a pure J2CA 1.0 Resource Adapter deployed in managed mode in the OC4J container of the Oracle Application Server. It is a universal adapter. One adapter can connect to many EIS applications.
The OracleAS Adapter J2CA repository contains the list of EIS connection names and the associated connection parameters. The repository can be a file system or an Oracle database. It is deployed as a RAR file and has an associated deployment descriptor called ra.xml. You can create multiple connector factories by editing the OC4J deployment descriptor oc4j-ra.xml. See Chapter 3, "OC4J Deployment and Integration" for more information on OC4J deployment.
Figure 1-2 Oracle Application Server Adapter Generic J2CA Architecture
If using OracleAS Adapter for SAP with BPEL Process Manager, please note that:
Only OracleAS Adapter J2CA deployment supports inbound integration (event notification) with BPEL Process Manager.
Both OracleAS Adapter J2CA and BSE deployments support outbound integration (request-response service) with BPEL Process Manager.
The following four factors explain the differences between deploying BSE and OracleAS Adapter J2CA. Understanding the factors can help in selecting a deployment option.
BSE is the preferred deployment option because it:
Can be deployed in a separate instance of Oracle Application Server.
Provides better distribution of load.
Provides better isolation from any errors from third party libraries.
Provides better capability to isolate issues for debugging purposes.
Conforms more closely to Service Oriented Architecture (SOA) model for building applications.
OracleAS Adapter J2CA provides slightly better performance
OracleAS Adapter J2CA does provide slightly better performance than BSE; however, the difference decreases as the transaction rate increases.
OracleAS Adapter J2CA and the BSE option both provide identity propagation at runtime
The BSE option provides the capability to pass identity using the SOAP header. For OracleAS Adapter J2CA, user name and password can be passed using the connection spec of the CCI.
Transactions