|
Oracle® Application Server Installation Guide
10g Release 2 (10.1.2) for Solaris Operating System (SPARC) B14088-03 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
|
Oracle® Application Server Installation Guide
10g Release 2 (10.1.2) for Solaris Operating System (SPARC) B14088-03 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
This chapter describes how to install Oracle Application Server in OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster configurations.
Section 11.1, "OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster: Introduction"
Section 11.2, "Pre-Installation Steps for OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster"
Section 11.3, "Installing an OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Infrastructure) Configuration"
Section 11.5, "Installing an OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Identity Management) Configuration"
Section 11.9, "Installing OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Middle-Tier)"
Section 11.11, "Post-Installation Steps for OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster"
Section 11.12, "Installing Middle Tiers Against an OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster Infrastructure"
Section 11.13, "Installing Regular Middle-Tiers on OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster Nodes"
In OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster configurations, you have an active and a passive node, and shared storage that can be accessed by either node.
During normal operation, the active node runs Oracle Application Server processes and processes requests from clients. If the active node fails, then a failover event occurs. The passive node takes over and becomes the active node. It mounts the shared storage and runs the processes.
Configurations
You can install OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster in these configurations:
OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Infrastructure). See Section 11.3.
Distributed OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Infrastructure). See Section 11.4.
OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Identity Management). See Section 11.5.
Distributed OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Identity Management). See Section 11.6.
OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Middle-Tier). See Section 11.9.
Before installing Oracle Application Server in an OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster, perform these procedures:
Section 11.2.1, "Map the Virtual Hostname and Virtual IP Address"
Section 11.2.2, "Set Up a File System That Can Be Mounted from Both Nodes"
Section 11.2.3, "Review Recommendations for Automatic Storage Management (ASM)"
Section 11.2.4, "Check That Clusterware Is Running (Automated Failovers only)"
|
Note: In addition to the requirements listed in this chapter, ensure that you meet the requirements described in Section 10.3, "Requirements for High Availability Configurations". |
Each node in an OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster configuration is associated with its own physical IP address. In addition, the active node in the cluster is associated with a virtual hostname and virtual IP address. This allows clients to access the OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster using the virtual hostname.
Virtual hostnames and virtual IP addresses are any valid hostname and IP address in the context of the subnet containing the hardware cluster.
|
Note: Map the virtual hostname and virtual IP address only to the active node. Do not map the virtual hostname and IP address to both active and secondary nodes at the same time. When you failover, only then map the virtual hostname and IP address to the secondary node, which is now the active node. |
The following example configures a virtual hostname called vhost.mydomain.com, with a virtual IP of 138.1.12.191:
Become the root user.
prompt> su Password: root_password
Determine the public network interface.
# ifconfig -a
lo0: flags=1000849<UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING,MULTICAST,IPv4> mtu 8232 index 1
inet 127.0.0.1 netmask ff000000
lo0:1: flags=1008849<UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING,MULTICAST,PRIVATE,IPv4> mtu 8232 index 1
inet 172.16.193.1 netmask ffffffff
ge0: flags=1000843<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST,IPv4> mtu 1500 index 2
inet 138.1.13.146 netmask fffffc00 broadcast 138.1.15.255
ether 8:0:20:fd:1:23
hme0: flags=1008843<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST,PRIVATE,IPv4> mtu 1500 index 3
inet 172.16.1.1 netmask ffffff80 broadcast 172.16.1.127
ether 8:0:20:fd:1:23
hme0:2: flags=1008843<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST,PRIVATE,IPv4> mtu 1500 index 3
inet 172.16.194.6 netmask fffffffc broadcast 172.16.194.7
ge1: flags=1008843<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST,PRIVATE,IPv4> mtu 1500 index 4
inet 172.16.0.129 netmask ffffff80 broadcast 172.16.0.255
ether 8:0:20:fd:1:23
From the output, ge0 is the public network interface. It is not a loopback interface and not a private interface.
Add the virtual IP to the ge0 network interface.
# ifconfig ge0 addif 138.1.12.191 up
"ge0" and the IP address are values specific to this example. Replace them with values appropriate for your cluster.
Check that new interface was added:
# ifconfig -a
lo0: flags=1000849<UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING,MULTICAST,IPv4> mtu 8232 index 1
inet 127.0.0.1 netmask ff000000
lo0:1: flags=1008849<UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING,MULTICAST,PRIVATE,IPv4> mtu 8232 index 1
inet 172.16.193.1 netmask ffffffff
ge0: flags=1000843<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST,IPv4> mtu 1500 index 2
inet 138.1.13.146 netmask fffffc00 broadcast 138.1.15.255
ether 8:0:20:fd:1:23
ge0:1: flags=1000843<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST,IPv4> mtu 1500 index 2
inet 138.1.12.191 netmask ffff0000 broadcast 138.1.255.255
hme0: flags=1008843<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST,PRIVATE,IPv4> mtu 1500 index 3
inet 172.16.1.1 netmask ffffff80 broadcast 172.16.1.127
ether 8:0:20:fd:1:23
hme0:2: flags=1008843<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST,PRIVATE,IPv4> mtu 1500 index 3
inet 172.16.194.6 netmask fffffffc broadcast 172.16.194.7
ge1: flags=1008843<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST,PRIVATE,IPv4> mtu 1500 index 4
inet 172.16.0.129 netmask ffffff80 broadcast 172.16.0.255
ether 8:0:20:fd:1:23
The virtual IP appears in the ge0:1 entry. During installation, when you enter "vhost.mydomain.com" as the virtual hostname in the Specify Virtual Hostname screen, the installer checks that "vhost.mydomain.com" is a valid interface.
If the active node fails, then the secondary node takes over. If you do not have a clusterware agent to map the virtual IP from the failed node to the secondary node, then you have to do it manually. You have to remove the virtual IP mapping from the failed node, and map it to the secondary node.
On the failed node, become superuser and remove the virtual IP.
If the failed node fails completely (that is, it does not boot up), you can skip this step and go to step 2. If the node fails partially (for example, disk or memory problems), and the node is still ping-able, you have to perform this step.
prompt> su Password: root_password # ifconfig ge0 removeif 138.1.12.191
"ge0" and the IP address are values specific to this example. Replace them with values appropriate for your cluster.
On the secondary node, add the virtual IP to the ge0 network interface.
# ifconfig ge0 addif 138.1.12.191 up
"ge0" and the IP address are values specific to this example. Replace them with values appropriate for your cluster.
On the secondary node, check that the new interface was added:
# ifconfig -a
...
ge0:1: flags=1000843<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST,IPv4> mtu 1500 index 2
inet 138.1.12.191 netmask ffff0000 broadcast 138.1.255.255
...
Although the hardware cluster has shared storage, you need to create a file system on this shared storage such that both nodes of the OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster can mount this file system. You will use this file system for the following directories:
Oracle home directory for the Oracle Application Server instance
The oraInventory directory
For disk space requirements, see Section 4.2, "System Requirements".
If you are running a volume manager on the cluster to manage the shared storage, refer to the volume manager documentation for steps to create a volume. Once a volume is created, you can create the file system on that volume.
If you do not have a volume manager, you can create a file system on the shared disk directly. Ensure that the hardware vendor supports this, that the file system can be mounted from either node of the OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster, and that the file system is repairable from either node if a node fails.
To check that the file system can be mounted from either node, do the following steps:
Set up and mount the file system from node 1.
Unmount the file system from node 1.
Mount the file system from node 2 using the same mount point that you used in step 1.
Unmount it from node 2, and mount it on node 1, because you will be running the installer from node 1.
If you plan to use ASM instances for the OracleAS Metadata Repository database, consider these recommendations:
If you plan to use ASM with Oracle database instances from multiple database homes on the same node, then you should run the ASM instance from an Oracle home that is different from the database homes.
The ASM home should be installed on every cluster node. This prevents the accidental removal of ASM instances that are in use by databases from other homes during the de-installation of a database Oracle home.
If you plan to automate failovers in the OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster, then each node in a cluster must be running hardware vendor clusterware.
To check that the clusterware is running, use the command appropriate for your clusterware.
Figure 11-1 shows an OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Infrastructure) configuration.
Figure 11-1 OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Infrastructure) Configuration
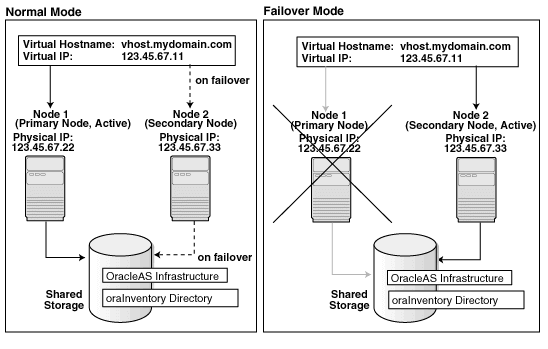
The figure shows:
two nodes running clusterware
storage devices local to each node
storage device that can be accessed by both nodes. You install OracleAS Infrastructure on this shared storage device.
During normal operation, one node ("node 1") acts as the active node. It mounts the shared storage to access the OracleAS Infrastructure files, runs OracleAS Infrastructure processes, and handles all requests.
If the active node goes down for any reason, the clusterware fails over OracleAS Infrastructure processes to the other node ("node 2"), which now becomes the active node. It mounts the shared storage, runs the processes, and handles all requests.
These nodes appear as one computer to clients through the use of a virtual address. To access the OracleAS Infrastructure, clients, including middle-tier components and applications, use the virtual address associated with the cluster. The virtual address is associated with the active node (node 1 during normal operation, node 2 if node 1 goes down). Clients do not need to know which node (node 1 or node 2) is servicing requests.
You use the virtual hostname in URLs that access the infrastructure. For example, if vhost.mydomain.com is the virtual hostname, the URLs for the Oracle HTTP Server and the Application Server Control would look like the following:
| URL for: | Example URL |
|---|---|
| Oracle HTTP Server, Welcome page | http://vhost.mydomain.com:7777 |
| Oracle HTTP Server, secure mode | https://vhost.mydomain.com:4443 |
| Application Server Control
|
http://vhost.mydomain.com:1156 |
Oracle Application Server Middle Tiers
You can install and run the middle tiers on other nodes (nodes that are not running OracleAS Infrastructure). During installation, you set up the middle tiers to use services from the OracleAS Infrastructure installed on the shared storage device.
You can also install and run the middle tiers on the cluster nodes without using an OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster configuration for the middle tiers. In this case, you install middle tiers using the regular installation process. If you do this, make sure the middle tier ports will not conflict with the OracleAS Infrastructure ports when a failover occurs.
If you want to install and run the middle tiers in an OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster configuration on the same cluster that is running the OracleAS Infrastructure, see Section 11.10, "Installing OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Infrastructure) and OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Middle-Tier) on the Same Nodes".
To set up an OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Infrastructure) configuration, perform these steps:
Table 11-1 Overview of Installation Steps for OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Infrastructure)
|
|
Step | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
1. |
Perform Pre-Installation Steps |
Pre-installation tasks, described in Section 11.2, include: |
|
2. |
Install OracleAS Infrastructure |
Install OracleAS Infrastructure on the shared storage. |
|
3. |
Perform Post-Installation Steps |
This post-installation step configures the CSS daemon. This step is required only if you are using ASM (Automatic Storage Management) feature of the Oracle database, and you do not have an existing Oracle database. |
This section lists the steps for installing OracleAS Infrastructure in an OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Infrastructure) configuration.
Step 1 Perform Pre-Installation Steps
Perform the pre-installation steps listed in Section 11.2, "Pre-Installation Steps for OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster".
Step 2 Install OracleAS Infrastructure
For OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Infrastructure), you install both OracleAS Metadata Repository and Oracle Identity Management in the same Oracle home by selecting Identity Management and OracleAS Metadata Repository in the Select Installation Type screen. This option creates a new database for the OracleAS Metadata Repository and a new Oracle Internet Directory.
Key Points
The destination directory must be on the shared disk.
Remember to select High Availability and Replication in the Select Configuration Options screen. By default, this option is not selected.
You enter the virtual hostname in the Specify Virtual Hostname screen.
Installer Screens
Run the installer and follow the screen sequence shown in Table 11-2:
Table 11-2 Installing OracleAS Infrastructure in an OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Infrastructure)
|
|
Screen | Action |
|---|---|---|
|
1. |
-- |
Start up the installer and complete the first few screens. See Section 6.27, "Install Fragment: The First Few Screens of the Installation" for details. Notes:
|
|
Select Configuration Options |
Select Oracle Internet Directory. Select Oracle Application Server Single Sign-On. Select Oracle Application Server Delegated Administration Services. Select Oracle Application Server Directory Integration and Provisioning. Select Oracle Application Server Certificate Authority (OCA) if you want a certificate authority. Select High Availability and Replication. Click Next. |
|
|
3. |
Specify Port Configuration Options |
If you want to use default ports for the components, select Automatic. If you do not want to use the default ports, and you have created a staticports.ini file, select Manual and enter the fullpath to your staticports.ini file in the provided field. Click Next. |
|
4. |
Select High Availability or Replication Option |
Select Virtual Host, and click Next. |
|
5. |
Specify Namespace in Internet Directory |
Select the suggested namespace, or enter a custom namespace for the location of the default Oracle Identity Management realm. Ensure the value shown in Suggested Namespace meets your deployment needs. If not, enter the desired value in Custom Namespace. See Section 6.16, "What Do I Enter in the "Specify Namespace in Internet Directory" Screen?". Click Next. |
|
Specify Virtual Hostname |
Note: This is a critical screen when installing the infrastructure in an OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster. If you do not see this screen, check the following:
Virtual Hostname: Enter the virtual hostname for the OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster configuration. Example: Click Next. |
|
|
7. |
OCA screens |
If you selected Oracle Application Server Certificate Authority (OCA) in the Select Configuration Options screen, the installer displays screens for configuring OCA. See Section 6.30, "Install Fragment: OCA Screens" for details. |
|
8. |
Specify Database Configuration Options |
Global Database Name: Enter a name for the OracleAS Metadata Repository database. Append a domain name to the database name. This domain name for the global database name can be different from your network domain name. The domain name portion of the global database name has the following naming restrictions:
The database name portion of the global database name has the following naming restrictions:
Example: Note: Be sure that you do not enter two or more periods together, for example,
SID: Enter the system identifier for the OracleAS Metadata Repository database. Typically this is the same as the global database name, but without the domain name. The SID must be unique across all databases. SIDs have the following naming restrictions:
Example:
Database Character Set: Select the character set to use. See also Section 6.15, "Support for NE8ISO8859P10 and CEL8ISO8859P14 Characters Sets". Database File Location: Enter the full path to the parent directory for the data files directory. This parent directory must already exist, and you must have write permissions in this directory. The installer will create a subdirectory in this parent directory, and the subdirectory will have the same name as the SID. The data files will be placed in this subdirectory. Example: If you enter Click Next. |
|
9. |
Specify Database Schema Passwords |
Set the passwords for these privileged database schemas: SYS, SYSTEM, SYSMAN, and DBSNMP. You can set different passwords for each schema, or you can set the same password for all the schemas. See Section 6.14, "Restrictions on the Passwords for the SYS, SYSTEM, SYSMAN, and DBSNMP Users" for rules on setting passwords for these accounts. Click Next. |
|
10. |
Specify Instance Name and ias_admin Password |
Instance Name: Enter a name for this infrastructure instance. Instance names can contain alphanumeric characters and the _ (underscore) character. If you have more than one Oracle Application Server instance on a computer, the instance names must be unique. See Section 5.9, "Oracle Application Server Instances and Instance Names" for instance name details. Example: ias_admin Password and Confirm Password: Enter and confirm the password for the ias_admin user. This is the administrative user for this infrastructure instance. See Section 5.10, "The ias_admin User and Restrictions on its Password" for password requirements. Example: Click Next. |
|
11. |
-- |
Finish the installation. See Section 6.28, "Install Fragment: The Last Few Screens of the Installation" for details. |
Step 3 Perform Post-Installation Steps
The following step is required only if you meet both of these requirements:
You plan to use the Automatic Storage Management (ASM) feature of Oracle Database 10g for the OracleAS Metadata Repository.
Your computer does not have an existing Oracle Database 10g.
If you meet these requirements, you need to configure the Cluster Synchronization Services (CSS) daemon on the other node. The CSS daemon synchronizes ASM instances with the database instances that use the ASM instances for database file storage.
To configure the CSS daemon:
Stop all the processes in the OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Infrastructure) home.
Stop the CSS daemon. You can do this by running the following command as root.
# /etc/init.d/init.cssd stop
Fail over the IP and the disk to the other node.
On the other node, run the following command as root:
# $ORACLE_HOME/root.sh
ORACLE_HOME is where you installed the OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Infrastructure).
Figure 11-2 shows a distributed OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Infrastructure) configuration.
This configuration is similar to the configuration described in Section 11.3, "Installing an OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Infrastructure) Configuration", except that the OracleAS Single Sign-On and Oracle Delegated Administration Services components are installed separately on other nodes in an active-active configuration.
Figure 11-2 Distributed OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Infrastructure) Configuration
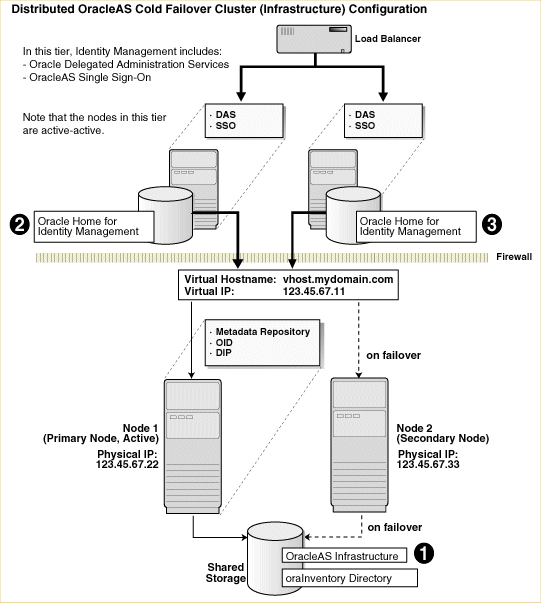
In a distributed OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Infrastructure) configuration, you run the OracleAS Metadata Repository, Oracle Internet Directory, and Oracle Directory Integration and Provisioning in an active-passive configuration.
However, the OracleAS Single Sign-On and Oracle Delegated Administration Services components run in an active-active configuration. You have a load balancer to direct requests to the nodes running these components.
To set up a distributed OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Infrastructure) configuration, perform these steps:
Table 11-3 Overview of Installation Steps for Distributed OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Infrastructure)
|
|
Step | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
1. |
Perform Pre-Installation Steps |
Pre-installation tasks, described in Section 11.2, include: |
|
2. |
Install OracleAS Infrastructure |
In this step, you install OracleAS Infrastructure on the shared storage. You install all components except OracleAS Single Sign-On, Oracle Delegated Administration Services, and OCA. |
|
3. |
Perform Post-Installation Steps |
This post-installation step configures the CSS daemon. This step is required only if you are using ASM (Automatic Storage Management) feature of the Oracle database, and you do not have an existing Oracle database. |
|
4. |
Install OracleAS Single Sign-On and Oracle Delegated Administration Services |
In this step, you install OracleAS Single Sign-On and Oracle Delegated Administration Services. |
Step 1 Perform Pre-Installation Steps
Perform the pre-installation steps listed in Section 11.2, "Pre-Installation Steps for OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster".
Step 2 Install OracleAS Infrastructure
In a distributed OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Infrastructure) configuration, you install both OracleAS Metadata Repository and Oracle Identity Management components (except for OracleAS Single Sign-On, Oracle Delegated Administration Services, and OCA) in the same Oracle home by selecting Identity Management and OracleAS Metadata Repository in the Select Installation Type screen. This option creates a new database for the OracleAS Metadata Repository and a new Oracle Internet Directory.
The steps are the same as those listed in step 2, "Install OracleAS Infrastructure", except that in the Select Configuration Options screen, do not select OracleAS Single Sign-On, Oracle Application Server Delegated Administration Services, and OracleAS Certificate Authority (OCA).
Step 3 Perform Post-Installation Steps
The following step is required only if you meet both of these requirements:
You plan to use the Automatic Storage Management (ASM) feature of Oracle Database 10g for the OracleAS Metadata Repository.
Your computer does not have an existing Oracle Database 10g.
If you meet these requirements, you need to configure the CSS daemon on the other node. The CSS daemon synchronizes ASM instances with the database instances that use the ASM instances for database file storage.
To configure the CSS daemon:
Stop all the processes in the OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Infrastructure) home.
Stop the CSS daemon. You can do this by running the following command as root.
# /etc/init.d/init.cssd stop
Fail over the IP and the disk to the other node.
On the other node, run the following command as root:
# $ORACLE_HOME/root.sh
ORACLE_HOME is where you installed the OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Infrastructure).
Step 4 Install OracleAS Single Sign-On and Oracle Delegated Administration Services
You install OracleAS Single Sign-On and Oracle Delegated Administration Services on the local disks of each node. You perform these installations separately.
Pre-Installation Steps
This installation is actually an OracleAS Cluster (Identity Management) installation. As such, you perform the OracleAS Cluster (Identity Management) setup steps in Chapter 12, "Installing in High Availability Environments: OracleAS Cluster (Identity Management)":
Section 12.2.1, "Use the Same Path for the Oracle Home Directory (recommended)"
Section 12.2.3, "Configure Virtual Server Names and Ports for the Load Balancer"
Section 12.2.5, "Set up Cookie Persistence on the Load Balancer"
Installation Steps
The steps are the same as those listed in Section 12.6.5, "Installing OracleAS Single Sign-On and Oracle Delegated Administration Services on Each Node".
Figure 11-3 shows an OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Identity Management) configuration.
This configuration is suitable if you have the OracleAS Metadata Repository database in a separate highly available environment and you want to use an active-passive configuration for the Oracle Identity Management components. You install the Oracle Identity Management components on a shared disk different from the share disk that contains the OracleAS Metadata Repository database.
This configuration includes:
two clustered nodes
storage devices local to each node
two shared disks that can be accessed by both nodes. One shared disk contains the Oracle home for the database (on which you will load the OracleAS Metadata Repository), and on the other shared disk, you will install Oracle Identity Management.
During normal operation, node 1, which is the primary node, is the active node. It mounts both shared disks to access the Oracle Identity Management and database files, runs the Oracle Identity Management and database processes, and handles all requests.
If node 1 goes down for any reason, the clusterware fails over the Oracle Identity Management and database processes to node 2. Node 2 becomes the active node, mounts both shared disks, runs the processes, and handles all requests.
To access the active node in an OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster, clients, including middle-tier components and applications, use the virtual hostname associated with the OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster. The virtual hostname is associated with the active node (node 1 during normal operation, node 2 if node 1 goes down). Clients do not need to know which node (primary or secondary) is servicing requests.
You also use the virtual hostname in URLs that access the infrastructure. For example, if vhost.mydomain.com is the name of the virtual host, the URLs for the Oracle HTTP Server and the Application Server Control would look like the following:
| URL for: | Example URL |
|---|---|
| Oracle HTTP Server, Welcome page | http://vhost.mydomain.com:7777 |
| Oracle HTTP Server, secure mode | https://vhost.mydomain.com:4443 |
| Application Server Control
|
http://vhost.mydomain.com:1156 |
Figure 11-3 OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Identity Management) Configuration

To create an OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Identity Management) configuration against an existing cold failover cluster database, perform these steps:
Table 11-4 Overview of Installation Steps for OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Identity Management) Configuration
|
|
Step | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
1. |
Perform Pre-Installation Steps |
Pre-installation tasks, described in Section 11.2, include: |
|
2. |
Install OracleAS Metadata Repository |
Install OracleAS Metadata Repository on your existing cold failover cluster database. |
|
3. |
Install the Oracle Identity Management Components |
Install the Oracle Identity Management components. |
Perform the following steps to install Oracle Application Server in an OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Identity Management) configuration.
Step 1 Perform Pre-Installation Steps
Perform the pre-installation steps listed in Section 11.2, "Pre-Installation Steps for OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster".
Step 2 Install OracleAS Metadata Repository
Use the OracleAS Metadata Repository Creation Assistant to install the OracleAS Metadata Repository in an existing database. See the Oracle Application Server Metadata Repository Creation Assistant User's Guide for details.
If you do not have an existing database, you can use the installer to create one. Note that you have to create the database with a virtual hostname. The database should run in an active-passive configuration, typically on a hardware cluster. See Section 11.8, "Installing Only the OracleAS Metadata Repository in an OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster Environment" for details.
Step 3 Install the Oracle Identity Management Components
You install the Oracle Identity Management on the other shared disk. Follow the installation steps described in Table 11-5.
Key Points
When the installer prompts you for the Oracle home path, enter a path on the shared disk. Make sure that both nodes can access this path.
In the Select High Availability or Replication Option screen, select Virtual Host.
In the Specify Virtual Hostname screen, enter the virtual hostname.
Installer Screens
Table 11-5 Installing Oracle Identity Management Components
|
|
Screen | Action |
|---|---|---|
|
1. |
-- |
Start up the installer and complete the first few screens. See Section 6.27, "Install Fragment: The First Few Screens of the Installation" for details. Note: In the Select Installation Type screen, select Oracle Identity Management. |
|
2. |
Select Configuration Options |
Select Oracle Internet Directory. Select Oracle Application Server Single Sign-On. Select Oracle Application Server Delegated Administration Services. Select Oracle Application Server Directory Integration and Provisioning. Select Oracle Application Server Certificate Authority (OCA) if you want a certificate authority. Select High Availability and Replication. Click Next. |
|
3. |
Specify Port Configuration Options |
If you want to use default ports for the components, select Automatic. If you do not want to use the default ports, and you have created a staticports.ini file, select Manual and enter the fullpath to your staticports.ini file in the provided field. Click Next. |
|
4. |
Specify Repository |
Username: Enter the username to use to log in to the OracleAS Metadata Repository database. The user must have DBA privileges. Password: Enter the user's password. Hostname and Port: Enter the name of the computer where the database is running, and the port number at which it is listening. Use the format: Service Name: Enter the service name of the database. Note that the service name must include the database domain name. Example: Click Next. |
|
5. |
Select High Availability or Replication Option |
Select Virtual Host, and click Next. |
|
6. |
Specify Namespace in Internet Directory |
Select the suggested namespace, or enter a custom namespace for the location of the default Oracle Identity Management realm. Ensure the value shown in Suggested Namespace meets your deployment needs. If not, enter the desired value in Custom Namespace. See Section 6.16, "What Do I Enter in the "Specify Namespace in Internet Directory" Screen?". Click Next. |
|
7. |
Specify Virtual Hostname |
Note: This is a critical screen when installing the infrastructure in an OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster. If you do not see this screen, check the following:
Virtual Hostname: Enter the virtual hostname for the OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster configuration. Example: Click Next. |
|
8. |
OCA screens |
If you selected Oracle Application Server Certificate Authority (OCA) in the Select Configuration Options screen, the installer displays screens for configuring OCA. See Section 6.30, "Install Fragment: OCA Screens" for details. |
|
9. |
Specify Instance Name and ias_admin Password |
Instance Name: Enter a name for this infrastructure instance. Instance names can contain alphanumeric characters and the _ (underscore) character. If you have more than one Oracle Application Server instance on a computer, the instance names must be unique. See Section 5.9, "Oracle Application Server Instances and Instance Names" for instance name details. Example: ias_admin Password and Confirm Password: Set the password for the ias_admin user. This is the administrative user for the instance. See Section 5.10, "The ias_admin User and Restrictions on its Password" for restrictions on the password. Example: Click Next. |
|
10. |
-- |
Finish the installation. See Section 6.28, "Install Fragment: The Last Few Screens of the Installation" for details. |
This configuration is suitable:
if you want to run Oracle Internet Directory and Oracle Directory Integration and Provisioning on the same tier as your database, and Oracle Delegated Administration Services and OracleAS Single Sign-On on a different tier
if you want to install the OracleAS Metadata Repository in an existing cold failover cluster database
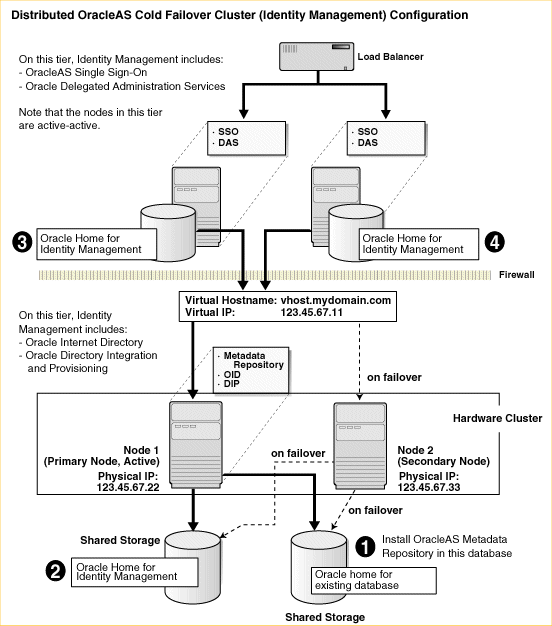
Figure 11-4 shows a distributed OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Identity Management) configuration.
It consists of:
two nodes running Oracle Delegated Administration Services and OracleAS Single Sign-On. These nodes are accessed through a load balancer.
two nodes running in an active-passive configuration. These nodes will run the existing cold failover cluster database, Oracle Internet Directory, and Oracle Directory Integration and Provisioning.
storage devices local to each node
two shared disks. One shared disk contains the database Oracle home. On the other shared disk, you will install Oracle Internet Directory and Oracle Directory Integration and Provisioning.
firewalls to separate the tiers
Tier Running the Oracle Internet Directory, Oracle Directory Integration and Provisioning, and Database
In this tier, during normal operation, the active node mounts the shared disks to access the Oracle Identity Management and database; runs the Oracle Internet Directory, Oracle Directory Integration and Provisioning, and database processes; and handles all requests.
If the active node goes down for any reason, the clusterware fails over the processes to the secondary node (node 2), which becomes the new active node, mounts the shared disks, runs the processes, and handles all requests.
To access the active node, clients, including middle-tier components and applications, use the virtual hostname. The virtual hostname is associated with the active node (which is the primary node during normal operation, the secondary node upon failover). Clients do not need to know which node (primary or secondary) is servicing requests.
You need to use the virtual hostname in URLs to access the active node. For example, if vhost.mydomain.com is the virtual hostname, the URLs for the Oracle HTTP Server and the Application Server Control for this tier would look like the following:
| URL for: | Example URL |
|---|---|
| Oracle HTTP Server, Welcome page | http://vhost.mydomain.com:7777 |
| Oracle HTTP Server, secure mode | https://vhost.mydomain.com:4443 |
| Application Server Control
|
http://vhost.mydomain.com:1156 |
Tier Running Oracle Delegated Administration Services and OracleAS Single Sign-On
Note that the nodes in this tier are not clustered. Both nodes are active at the same time, and you install the files locally on each node. To access these nodes, clients go through a load balancer. For example, if the name of the load balancer is loadbalance1.mydomain.com, the URLs for the Oracle HTTP Server and the Application Server Control for this tier would look like the following:
| URL for: | Example URL |
|---|---|
| Oracle HTTP Server, Welcome page | http://vhost.mydomain.com:7777 |
| Oracle HTTP Server, secure mode | https://vhost.mydomain.com:4443 |
| Application Server Control
|
http://vhost.mydomain.com:1156 |
Figure 11-4 Distributed OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Identity Management) Configuration
To create a distributed OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Identity Management) configuration against an existing cold failover cluster database, perform these steps:
Table 11-6 Overview of Installation Steps for Distributed OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Identity Management) Configuration
|
|
Step | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
1. |
Perform Pre-Installation Steps |
Pre-installation tasks, described in Section 11.2, include: |
|
2. |
Install OracleAS Metadata Repository |
Install OracleAS Metadata Repository on your existing cold failover cluster database. |
|
3. |
Install Oracle Internet Directory and Oracle Directory Integration and Provisioning |
Install the Oracle Internet Directory and Oracle Directory Integration and Provisioning components. |
|
4. |
Install OracleAS Single Sign-On and Oracle Delegated Administration Services |
Install the OracleAS Single Sign-On and Oracle Delegated Administration Services components. |
Step 1 Perform Pre-Installation Steps
Perform the pre-installation steps listed in Section 11.2, "Pre-Installation Steps for OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster".
Step 2 Install OracleAS Metadata Repository
Use the OracleAS Metadata Repository Creation Assistant to install the OracleAS Metadata Repository in an existing database. See the Oracle Application Server Metadata Repository Creation Assistant User's Guide for details.
If you do not have an existing database, you can use the installer to create one. Note that you have to create the database with a virtual hostname. See Section 11.8, "Installing Only the OracleAS Metadata Repository in an OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster Environment" for details.
Step 3 Install Oracle Internet Directory and Oracle Directory Integration and Provisioning
Install the Oracle Internet Directory and Oracle Directory Integration and Provisioning components on the other shared disk. Follow the installation steps described in Table 11-7.
Key Points
In the Select Installation Type screen, select Identity Management.
In the Select Configuration Options screen, select Oracle Internet Directory, Oracle Application Server Directory Integration and Provisioning, and High Availability and Replication.
In the Select High Availability or Replication Option screen, select Virtual Host.
In the Specify Virtual Hostname screen, enter the virtual hostname.
Installer Screens
Table 11-7 Installing Oracle Internet Directory and Oracle Directory Integration and Provisioning
|
|
Screen | Action |
|---|---|---|
|
1. |
-- |
Start up the installer and complete the first few screens. See Section 6.27, "Install Fragment: The First Few Screens of the Installation" for details. Note: In the Select Installation Type screen, select Identity Management. |
|
2. |
Select Configuration Options |
Select Oracle Internet Directory. Do not select Oracle Application Server Single Sign-On. Do not select Oracle Application Server Delegated Administration Services. Select Oracle Application Server Directory Integration and Provisioning. Do not select Oracle Application Server Certificate Authority (OCA). Select High Availability and Replication. Click Next. |
|
3. |
Specify Port Configuration Options |
If you want to use default ports for the components, select Automatic. If you do not want to use the default ports, and you have created a staticports.ini file, select Manual and enter the fullpath to your staticports.ini file in the provided field. Click Next. |
|
4. |
Specify Repository |
Username: Enter the username to use to log in to the OracleAS Metadata Repository database. The user must have DBA privileges. Password: Enter the user's password. Hostname and Port: Enter the name of the computer where the database is running, and the port number at which it is listening. Use the format: Service Name: Enter the service name of the database. Note that the service name must include the database domain name. Example: Click Next. |
|
5. |
Select High Availability or Replication Option |
Select Virtual Host, and click Next. |
|
6. |
Specify Namespace in Internet Directory |
Select the suggested namespace, or enter a custom namespace for the location of the default Oracle Identity Management realm. Ensure the value shown in Suggested Namespace meets your deployment needs. If not, enter the desired value in Custom Namespace. See Section 6.16, "What Do I Enter in the "Specify Namespace in Internet Directory" Screen?". Click Next. |
|
7. |
Specify Virtual Hostname |
Note: This is a critical screen when installing the infrastructure in an OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster. If you do not see this screen, check the following:
Virtual Hostname: Enter the virtual hostname for the OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster configuration. Example: Click Next. |
|
8. |
Specify Instance Name and ias_admin Password |
Instance Name: Enter a name for this infrastructure instance. Instance names can contain alphanumeric characters and the _ (underscore) character. If you have more than one Oracle Application Server instance on a computer, the instance names must be unique. See Section 5.9, "Oracle Application Server Instances and Instance Names" for instance name details. Example: ias_admin Password and Confirm Password: Set the password for the ias_admin user. This is the administrative user for the instance. See Section 5.10, "The ias_admin User and Restrictions on its Password" for restrictions on the password. Example: Click Next. |
|
9. |
-- |
Finish the installation. See Section 6.28, "Install Fragment: The Last Few Screens of the Installation" for details. |
Step 4 Install OracleAS Single Sign-On and Oracle Delegated Administration Services
Install these components in an OracleAS Cluster (Identity Management) configuration. In this configuration, you install them on the local disks of each node. You perform these installations separately.
Pre-Installation steps: Because this installation is actually an OracleAS Cluster (Identity Management) installation, you can follow the OracleAS Cluster (Identity Management) setup steps in Chapter 12, "Installing in High Availability Environments: OracleAS Cluster (Identity Management)":
Section 12.2.1, "Use the Same Path for the Oracle Home Directory (recommended)"
Section 12.2.3, "Configure Virtual Server Names and Ports for the Load Balancer"
Section 12.2.5, "Set up Cookie Persistence on the Load Balancer"
Installation steps: The installation steps are described in Section 12.6.5, "Installing OracleAS Single Sign-On and Oracle Delegated Administration Services on Each Node".
The configuration described in this section is similar to that described in Section 11.4, "Installing a Distributed OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Infrastructure) Configuration". The difference is that in the configuration described in this section, OracleAS Single Sign-On and Oracle Delegated Administration Services run in an OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster configuration.
You need two sets of clustered nodes. See Figure 11-5. One set runs the OracleAS Metadata Repository and Oracle Internet Directory, and another set runs Oracle Delegated Administration Services and OracleAS Single Sign-On.
For each set, you need a shared storage and a virtual hostname. You install Oracle homes for the various Oracle Application Server components on the shared storage.
Figure 11-5 Oracle Delegated Administration Services and OracleAS Single Sign-On in a Cold Failover Cluster

Table 11-8 Overview of Steps for Installing Oracle Delegated Administration Services and OracleAS Single Sign-On in an OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster
|
|
Step | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
1. |
Perform Pre-Installation Steps |
Pre-installation tasks, described in Section 11.2, include:
|
|
2. |
(optional) Create staticports.ini Files |
If you wish, create two staticports.ini files, one for each set of nodes. |
|
3. |
Install OracleAS Metadata Repository and Oracle Internet Directory |
From node 1, install OracleAS Metadata Repository and Oracle Internet Directory on the shared disk. The steps are the same as those listed in step 2, "Install OracleAS Infrastructure", except that in the Select Configuration Options screen, do not select OracleAS Single Sign-On and Oracle Application Server Delegated Administration Services. |
|
4. |
Install Oracle Delegated Administration Services and OracleAS Single Sign-On from Node 3 |
From node 3, install Oracle Delegated Administration Services and OracleAS Single Sign-On on the shared disk. |
|
5. |
Stop the OracleAS Infrastructure Processes on Node 1 |
From node 1, stop the OracleAS Infrastructure processes. |
|
6. |
Stop the OracleAS Infrastructure Processes on Node 3 |
From node 1, stop the OracleAS Infrastructure processes. |
|
7. |
Perform Post-Installation Steps |
This post-installation step configures the CSS daemon. This step is required only if you are using ASM (Automatic Storage Management) feature of the Oracle database, and you do not have an existing Oracle database. |
Step 1 Perform Pre-Installation Steps
Perform the pre-installation steps listed in Section 11.2, "Pre-Installation Steps for OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster".
Step 2 (optional) Create staticports.ini Files
If you wish, you may set up two staticports.ini files, one for each set of nodes. For information on staticports.ini, see Section 4.6.3, "Using Custom Port Numbers (the "Static Ports" Feature)".
Step 3 Install OracleAS Metadata Repository and Oracle Internet Directory
Install OracleAS Metadata Repository and Oracle Internet Directory in the same Oracle home by selecting Identity Management and OracleAS Metadata Repository in the Select Installation Type screen. This option creates a new database for the OracleAS Metadata Repository and a new Oracle Internet Directory.
The steps are the same as those listed in step 2, "Install OracleAS Infrastructure", with these differences:
In the Select Configuration Options screen, select these components/options:
Oracle Internet Directory
Oracle Application Server Directory Integration and Provisioning
High Availability and Replication
Do not select these components:
Oracle Application Server Single Sign-On
Oracle Application Server Delegated Administration Services
Oracle Application Server Certificate Authority (OCA)
In the Specify Port Configuration Options screen, select Manual and enter the fullpath to the staticports.ini file that you created in the previous step.
Step 4 Install Oracle Delegated Administration Services and OracleAS Single Sign-On from Node 3
From node 3, install Oracle Delegated Administration Services and OracleAS Single Sign-On on the shared disk by following the steps in Table 11-9.
Key Points
When the installer prompts you for the Oracle home path, enter a path on the shared disk. Make sure that both nodes can access this path.
In the Select High Availability or Replication Option screen, select Virtual Host.
In the Specify Virtual Hostname screen, enter the virtual hostname.
Table 11-9 Installing Oracle Delegated Administration Services and OracleAS Single Sign-On
|
|
Screen | Action |
|---|---|---|
|
1. |
-- |
Start up the installer and complete the first few screens. See Section 6.27, "Install Fragment: The First Few Screens of the Installation" for details. Note: In the Select Installation Type screen, select Oracle Identity Management. |
|
2. |
Select Configuration Options |
Do not select Oracle Internet Directory. Select Oracle Application Server Single Sign-On. Select Oracle Application Server Delegated Administration Services. Do not select Oracle Application Server Directory Integration and Provisioning. Do not select Oracle Application Server Certificate Authority (OCA). Select High Availability and Replication. Click Next. |
|
3. |
Specify Port Configuration Options |
Select Manual and enter the fullpath to your staticports.ini file in the provided field. You created the staticports.ini file in step 2, "(optional) Create staticports.ini Files". Click Next. |
|
4. |
Select High Availability Option |
Select Virtual Host, and click Next. |
|
5. |
Register with Oracle Internet Directory |
Enter connect information for the Oracle Internet Directory that you installed earlier. Hostname: Enter the virtual hostname to access the Oracle Internet Directory host. Port: Enter the port on which Oracle Internet Directory is listening. See Section 6.17, "How to Determine Port Numbers Used by Components" if you do not know the port number. Use Only SSL Connections with this Oracle Internet Directory: Select this option if you want to use only SSL to connect to Oracle Internet Directory. Click Next. |
|
6. |
Specify Oracle Internet Directory Login |
Username: Enter the username to log in to the Oracle Internet Directory. Password: Enter the password for the username. Realm: Enter the realm against which to validate the username. This field appears only if your Oracle Internet Directory has multiple realms. Click Next. |
|
7. |
Specify Virtual Hostname |
Note: This is a critical screen when installing in an OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster. If you do not see this screen, check the following:
Virtual Hostname: Enter the virtual hostname for the OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster configuration. Example: Click Next. |
|
8. |
Specify Instance Name and ias_admin Password |
Instance Name: Enter a name for the instance. Instance names can contain alphanumeric characters and the _ (underscore) character. If you have more than one Oracle Application Server instance on a computer, the instance names must be unique. See Section 5.9, "Oracle Application Server Instances and Instance Names" for instance name details. Example: ias_admin Password and Confirm Password: Set the password for the ias_admin user. This is the administrative user for the instance. See Section 5.10, "The ias_admin User and Restrictions on its Password" for restrictions on the password. Example: Click Next. |
|
9. |
-- |
Finish the installation. See Section 6.28, "Install Fragment: The Last Few Screens of the Installation" for details. |
Step 5 Stop the OracleAS Infrastructure Processes on Node 1
Stop the processes that are running in the Oracle home where you installed the OracleAS Metadata Repository and Oracle Internet Directory.
Stop the Application Server Control.
prompt> ORACLE_HOME/bin/emctl stop iasconsole
Stop the components.
prompt> ORACLE_HOME/opmn/bin/opmnctl stopall
Stop the OracleAS Metadata Repository.
Set the ORACLE_HOME environment variable to the OracleAS Infrastructure home.
Set the ORACLE_SID environment variable to the SID of the OracleAS Metadata Repository (for example, orcl).
Stop the OracleAS Metadata Repository instance.
prompt> ORACLE_HOME/bin/sqlplus /nolog SQL> connect SYS as SYSDBA SQL> shutdown SQL> quit
Stop the listener.
prompt> ORACLE_HOME/bin/lsnrctl stop
Stop the Oracle Enterprise Manager 10g 10g Database Control.
prompt> ORACLE_HOME/bin/emctl stop dbconsole
Step 6 Stop the OracleAS Infrastructure Processes on Node 3
Stop the processes that are running in the Oracle home where you installed Oracle Delegated Administration Services and OracleAS Single Sign-On.
Stop the Application Server Control.
prompt> ORACLE_HOME/bin/emctl stop iasconsole
Stop the components.
prompt> ORACLE_HOME/opmn/bin/opmnctl stopall
Step 7 Perform Post-Installation Steps
The following step is required only if you meet both of these requirements:
You plan to use the Automatic Storage Management (ASM) feature of Oracle Database 10g for the OracleAS Metadata Repository.
Your computer does not have an existing Oracle Database 10g.
If you meet these requirements, you need to configure the CSS daemon on the other node. The CSS daemon synchronizes ASM instances with the database instances that use the ASM instances for database file storage.
To configure the CSS daemon:
Stop all the processes in the OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Infrastructure) home.
Stop the CSS daemon. You can do this by running the following command as root.
# /etc/init.d/init.cssd stop
Fail over the IP and the disk to the other node.
On the other node, run the following command as root:
# $ORACLE_HOME/root.sh
ORACLE_HOME is where you installed the OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Infrastructure).
This section describes how to install the OracleAS Metadata Repository in a new database (that is, the installer will create a new database for you and populate it with the OracleAS Metadata Repository). You can use this database in an OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster environment.
Prerequisites:
Check that you have configured a virtual hostname and virtual IP.
Table 11-10 Installing the OracleAS Metadata Repository Only
|
|
Screen | Action |
|---|---|---|
|
1. |
-- |
Start up the installer and complete the first few screens. See Section 6.27, "Install Fragment: The First Few Screens of the Installation" for details. Notes:
|
|
2. |
Select Configuration Options |
Do not select Oracle Internet Directory. Do not select Oracle Application Server Single Sign-On. Do not select Oracle Application Server Delegated Administration Services. Do not select Oracle Application Server Directory Integration and Provisioning. Do not select Oracle Application Server Certificate Authority (OCA). Select High Availability and Replication. Click Next. |
|
3. |
Specify Port Configuration Options |
Select Automatic. Click Next. |
|
4. |
Select High Availability Option |
Select Virtual Host. Click Next. |
|
5. |
Register Oracle Application Server Metadata Repository |
If you already have an Oracle Internet Directory and know its connect information, select Yes and enter the name of the computer where Oracle Internet Directory is running and the port number. See Section 6.17, "How to Determine Port Numbers Used by Components" if you do not know the port number. Use Only SSL Connections with this Oracle Internet Directory: Select this option if you want Oracle Application Server components to use only SSL to connect to Oracle Internet Directory. If you do not have an Oracle Internet Directory, or do not know its connect information, select No. Click Next. |
|
6. |
Specify Oracle Internet Directory login |
This screen appears only if you selected Yes in the previous screen. Username: Enter the username for logging into Oracle Internet Directory. The user must belong to the iAS Admins group in Oracle Internet Directory. Password: Enter the password. Realm: This field appears only if your Oracle Internet Directory contains multiple realms. Enter the name of the realm against which to authenticate the user. Click Next. |
|
7. |
Specify Virtual Hostname |
Virtual Hostname: Enter the name of the virtual host. Click Next. |
|
8. |
Oracle Database screens |
Enter information for the OracleAS Metadata Repository database. See Section 6.29, "Install Fragment: Database Screens". |
|
9. |
Specify Instance Name and ias_admin Password |
Instance Name: Enter a name for this instance. Instance names can contain alphanumeric characters and the _ (underscore) character. If you have more than one Oracle Application Server instance on a computer, the instance names must be unique. See Section 5.9, "Oracle Application Server Instances and Instance Names" for instance name details. Example: ias_admin Password and Confirm Password: Set the password for the ias_admin user. This is the administrative user for the instance. See Section 5.10, "The ias_admin User and Restrictions on its Password" for restrictions on the password. Example: Click Next. |
|
10. |
-- |
Finish the installation. See Section 6.28, "Install Fragment: The Last Few Screens of the Installation" for details. |
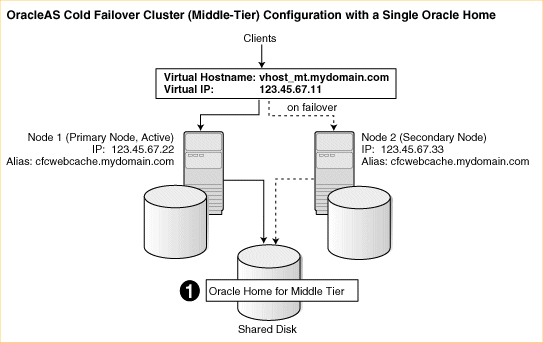
You can also install Oracle Application Server middle tiers in an OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster configuration with separate Oracle Homes on the local storage of each node (see Figure 11-6) or a single Oracle Home on a shared disk (see Figure 11-7).
OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Middle-Tier) configurations have an active node and a passive node. Unlike OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Infrastructure), you can install OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Middle-Tier) on a shared disk or you can install in separate Oracle Homes, one on each node of the cluster. Each installation option for OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Middle-Tier) has different benefits:
A single Oracle Home installation is easier to manage, patch, and maintain because you only need to update the configuration on one Oracle Home.
Separate Oracle Homes allow for rolling upgrades and patches of the instance.
Note that single Oracle Home install is not supported for installations that include OracleAS Wireless.
The following sections contain instructions for installing OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Middle-Tier):
Additionally, instructions for expanding an existing installation are in the following section:
Virtual Hostname
Clients access the active node (for example, node 1) using the virtual hostname (vhost_mt.mydomain.com in Figure 11-6 and Figure 11-7). If node 1 fails, the virtual hostname points to node 2, and node 2 becomes the active node.
Figure 11-6 OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Middle-Tier) Configuration with Separate Oracle Homes

Figure 11-7 OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Middle-Tier) Configuration with a Single Oracle Home
To install OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Middle-Tier) in separate Oracle Homes, perform the following steps.
Before installing the middle tier, perform the following generic pre-installation step listed near the beginning of this chapter:
In addition, you also need to perform the following steps:
Both installations must use the same ports. To do this, set up a staticports.ini file to use when installing the middle tiers. See Section 4.6.3, "Using Custom Port Numbers (the "Static Ports" Feature)" for details on creating the staticports.ini file.
|
Note: The ports used for the middle tiers must be different from the ones used for any OracleAS Infrastructure installed on the same cluster. The ports must also be different from those used for other Oracle Homes on the same node. To check the ports assigned to components in any Oracle Home, see the Ports page on the Application Server Control Console. |
If you plan to include OracleAS Web Cache in the Oracle Application Server instances, you should create an alias for the hostnames.
You do this by adding a line to the /etc/hosts file on each node.
Lines in the hosts file have the following format. You can have one or more aliases.
ip_address official_hostname aliases...
For example, if the nodes are called node1 and node2, and you want the alias to be called cfcwebcache, then you would add these lines to the hosts file:
In the hosts file on node1, add this line:
123.45.67.22 node1.mydomain.com node1 cfcwebcache.mydomain.com
In the hosts file on node2, add this line:
123.45.67.33 node2.mydomain.com node2 cfcwebcache.mydomain.com
Install the middle tiers on the local storage of each node.
|
Tip: To save time, you can install the middle tiers on both nodes at the same time, instead of doing them sequentially. |
Note the following when performing the installations:
Use the same Oracle home paths for both installations.
Specify the staticports.ini file that you created in Section 11.9.1.1, "Pre-Installation Steps" during the installation.
Use the same instance name for both installations. This is not mandatory, but recommended.
To install J2EE and Web Cache middle tiers, see Section 7.9, "Installing J2EE and Web Cache in a Database-Based Farm Repository and with Oracle Identity Management Access".
To install Portal and Wireless or Business Intelligence and Forms middle tiers, see Section 7.13, "Installing Portal and Wireless or Business Intelligence and Forms".
Before the middle tiers can run in cold failover cluster mode, perform the following post-installation steps:
Section 11.9.1.3.1, "(optional) Configure the Middle-Tier Instances to Use SSL"
Section 11.9.1.3.2, "Back up the Installations (Middle-Tier and OracleAS Infrastructure)"
Section 11.9.1.3.5, "Update Component Configuration on Node 1"
Section 11.9.1.3.6, "Update Component Configuration on Node 2"
The last section, Section 11.9.1.3.8, "Restoring Files to a Known State", describes how to revert to a known state if an unrecoverable error occurred during conversion.
If you want the middle-tier instances to use SSL, follow the steps in the Oracle Application Server Administrator's Guide. You should perform this SSL configuration before you configure the middle tiers for OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster.
Before running the chgtocfmt script (in Section 11.9.1.3.5, "Update Component Configuration on Node 1"), you should back up the middle tiers on both nodes and also your OracleAS Infrastructure, including the OracleAS Metadata Repository and the Oracle Identity Management components. You can do this using the OracleAS Backup and Recovery Tool, described in the Oracle Application Server Administrator's Guide. You then have backup files, from which you can perform a restore operation in case you encounter errors during the conversion.
On node1, log in as root and run the following command:
# ifconfig interface_name addif virtual_IP up
See Section 11.2.1, "Map the Virtual Hostname and Virtual IP Address" for details.
If you are using OracleAS JMS with file-based persistence, create a file system on the shared disk for the OracleAS JMS queues, and mount this file system from node1.
Perform the following steps to update some component configuration on the middle-tier Oracle home that you installed on node 1.
Run the conversion command chgtocfmt on node 1.
|
Note: If you changed any of the component port numbers after installation, you must manually update the file located atORACLE_HOME/install/portlist.ini before performing this step.
|
prompt> $ORACLE_HOME/bin/chgtocfmt -vvhost_mt.mydomain.com-ppassword-n [-s] [-b] [-e] [-wcfcwebcache.mydomain.com]
where
-v specifies the fully qualified virtual hostname to which the install is being converted. The virtual hostname should be enabled on the current host.
-p specifies the password for the Oracle Internet Directory.
-n indicates that the install is not on a shared disk.
-s indicates that SSL is enabled on the middle-tier.
-b indicates to perform a backup of the current configuration before converting the instance to run in the OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Middle-Tier). This option invokes the OracleAS Backup and Recovery Tool to perform the backup. This means that you must have configured the OracleAS Backup and Recovery Tool before you can use this option. To do this, see the Oracle Application Server Administrator's Guide.
Although you can use the -b option for all middle tiers, it is highly recommended that you use it only for standalone middle tiers (middle tiers not associated with an OracleAS Infrastructure). The reason is that it backs up only the middle tier; it does not back up the OracleAS Infrastructure. For middle tiers that use an OracleAS Infrastructure, use the OracleAS Backup and Recovery Tool to back up both the middle tiers and OracleAS Infrastructure.
-e indicates that you are expanding a OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Middle-Tier) installation. Only use this option if you adding new components or configuring additional components in an existing OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Middle-Tier).
-w specifies the alias located in /etc/hosts that is used for the OracleAS Web Cache on this node.
Check the following log files for errors:
chgtocmt.log
chgip0.log
chgip1.log
These files are located in the ORACLE_HOME/chgip/log directory.
Verify the changes on node 1.
To verify the installation, access the Application Server Control page using the virtual hostname in the URL (for example: http://vhost_mt.mydomain.com:1156).
The default port number is 1156. You can verify the port number by looking in the ORACLE_HOME/install/portlist.ini file.
Modify OracleAS JMS
In the jms.xml file for the OC4J instance that you plan to use, set the host attribute in jms-server to the virtual hostname (example: vhost_mt.mydomain.com).
<jms-server host="vhost_mt.mydomain.com" port="9127">
...
</jms-server>
If for a queue, file-based message persistence is being used, the location for the file should ideally be on a shared disk. In this case, the shared disk needs to fail over with the virtual IP. To configure this, the value of the persistence-file attribute for queue should be a file on the shared disk.
<queue name="Demo Queue" location="jms/demoQueue"
persistence-file="/path/to/shared_file_system/demoQueueFile">
<description>A dummy queue</description>
</queue>
Update the DCM repository and restart the components.
prompt> $ORACLE_HOME/dcm/bin/dcmctl updateConfig -ct oc4j prompt> $ORACLE_HOME/bin/emctl stop iasconsole prompt> $ORACLE_HOME/opmn/bin/opmnctl stopall prompt> $ORACLE_HOME/opmn/bin/opmnctl startall prompt> $ORACLE_HOME/bin/emctl start iasconsole
Fail over the Virtual IP to Node 2
Stop all Oracle Application Server processes on node 1.
prompt> $ORACLE_HOME/bin/emctl stop iasconsole prompt> $ORACLE_HOME/opmn/bin/opmnctl stopall
Fail over the virtual hostname vhost_mt.mydomain.com from node 1 to node 2.
On node1, run the following command as root:
# ifconfig interface removeif virtual_ip_address
On node2, run the following command as root:
# ifconfig interface addif virtual_ip_address up
Perform these steps on the middle-tier Oracle home that you installed on node 2.
Run the conversion command chgtocfmt on node 2 as you did in Step 1 in Section 11.9.1.3.5.
Check the log files on node 2 as you did in Step 2 in Section 11.9.1.3.5
Verify the changes on node 2 as you did in Step 3 in Section 11.9.1.3.5.
Modify OracleAS JMS on node 2 as you did in Step 4 in Section 11.9.1.3.5
After successfully converting the middle tiers to an OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Middle-Tier) topology, you should back up your files again because previous backups that you have are no longer valid (because of the configuration changes you just made). You need to back up all your middle tiers (on both nodes), plus your OracleAS Infrastructure.
You can perform the backups using the OracleAS Backup and Recovery Tool, which is documented in the Oracle Application Server Administrator's Guide.
This section describes how to restore files to a known state, if errors occurred during the conversion.
If an unrecoverable error occurred during conversion, you can restore the middle tiers and OracleAS Infrastructure to a known state using the backup files that you created in Section 11.9.1.3.2, "Back up the Installations (Middle-Tier and OracleAS Infrastructure)". You use the OracleAS Backup and Recovery Tool to perform the restore operation.
Note that re-running the chgtocfmt script will not work for "separate Oracle homes" installations. Re-running the script works only if you installed the Oracle home for the middle tier on the shared disk (the "single Oracle home" type). However, see Section G.3.19, "Re-running chgtocfmt Does Not Work" for a possible workaround.
To install OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Middle-Tier) on a shared disk, perform the following steps.
|
Note: Single Oracle Home install is not supported for installations that include OracleAS Wireless. |
Before installing the middle tier, perform the following generic pre-installation steps listed near the beginning of this chapter:
Section 11.2.1, "Map the Virtual Hostname and Virtual IP Address"
Section 11.2.2, "Set Up a File System That Can Be Mounted from Both Nodes"
In addition, you also need to perform the following steps:
If you plan to include OracleAS Web Cache in the Oracle Application Server instances, you should create an alias for the hostnames.
You do this by adding a line to the /etc/hosts file on each node.
Lines in the hosts file have the following format. You can have one or more aliases.
ip_address official_hostname aliases...
For example, if the nodes are called node1 and node2, and you want the alias to be called cfcwebcache, then you would add these lines to the hosts file:
In the hosts file on node1, add this line:
123.45.67.22 node1.mydomain.com node1 cfcwebcache.mydomain.com
In the hosts file on node2, add this line:
123.45.67.33 node2.mydomain.com node2 cfcwebcache.mydomain.com
If you wish, you may set up a staticports.ini file to use when installing the middle tier. See Section 4.6.3, "Using Custom Port Numbers (the "Static Ports" Feature)" for details on creating the staticports.ini file.
|
Note: The ports used for the middle tiers must be different from the ones used for any OracleAS Infrastructure installed on the same cluster. The ports must also be different from those used for other Oracle Homes on the same node. To check the ports assigned to components in any Oracle Home, see the Ports page on the Application Server Control Console. |
On node1, log in as root and run the following command:
# ifconfig interface_name addif virtual_IP up
See Section 11.2.1, "Map the Virtual Hostname and Virtual IP Address" for details.
Install the middle tier on the shared disk of the hardware cluster from either node of the cluster.
|
Note: If you created a staticports.ini file in Section 11.9.2.1, "Pre-Installation Steps", specify it during the installation. |
To install J2EE and Web Cache middle tiers, see Section 7.9, "Installing J2EE and Web Cache in a Database-Based Farm Repository and with Oracle Identity Management Access".
To install Portal and Wireless or Business Intelligence and Forms middle tiers, see Section 7.13, "Installing Portal and Wireless or Business Intelligence and Forms".
Before the middle tiers can run in cold failover cluster mode, perform the following post-installation steps:
Section 11.9.2.3.1, "(optional) Configure the Middle-Tier Instances to Use SSL"
Section 11.9.2.3.2, "Back up the Installations (Middle-Tier and OracleAS Infrastructure)"
The last section, Section 11.9.2.3.6, "Restoring Files to a Known State", describes how to revert to a known state if an unrecoverable error occurred during conversion.
If you want the middle-tier instances to use SSL, follow the steps in the Oracle Application Server Administrator's Guide. You should perform this SSL configuration before you configure the middle tiers for OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster.
Before running the chgtocfmt script (in Section 11.9.2.3.4, "Update Component Configuration"), you should back up the middle tiers and also your OracleAS Infrastructure, including the OracleAS Metadata Repository and the Oracle Identity Management components. You can do this using the OracleAS Backup and Recovery Tool, described in the Oracle Application Server Administrator's Guide. You then have backup files, from which you can perform a restore operation in case you encounter errors during the conversion.
If you are using OracleAS JMS with file-based persistence, create a file system on the shared disk for the OracleAS JMS queues, and mount this file system from node 1.
Perform the following steps to update some component configuration on the middle-tier Oracle home on the shared disk.
Run the conversion command chgtocfmt on node 1.
|
Note: If you changed any of the component port numbers after installation, you must manually update the file located atORACLE_HOME/install/portlist.ini before performing this step.
|
prompt> $ORACLE_HOME/bin/chgtocfmt -vvhost_mt.mydomain.com-ppassword[-n] [-s] [-b] [-e] [-wcfcwebcache.mydomain.com]
where
-v specifies the fully qualified virtual hostname to which the install is being converted. The virtual hostname should be enabled on the current host.
-p specifies the password for the Oracle Internet Directory.
-n indicates that the install is not on a shared disk.
-s indicates that SSL is enabled on the middle-tier.
-b indicates to perform a backup of the current configuration before converting the instance to run in the OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Middle-Tier). This option invokes the OracleAS Backup and Recovery Tool to perform the backup. This means that you must have configured the OracleAS Backup and Recovery Tool before you can use this option. To do this, see the Oracle Application Server Administrator's Guide.
Although you can use the -b option for all middle tiers, it is highly recommended that you use it only for standalone middle tiers (middle tiers not associated with an OracleAS Infrastructure). The reason is that it backs up only the middle tier; it does not back up the OracleAS Infrastructure. For middle tiers that use an OracleAS Infrastructure, use the OracleAS Backup and Recovery Tool to back up both the middle tiers and OracleAS Infrastructure.
-e indicates that you are expanding a OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Middle-Tier) installation. Only use this option if you adding new components or configuring additional components in an existing OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Middle-Tier).
-w specifies the alias located in /etc/hosts that is used for the OracleAS Web Cache on this node.
Check the following log files for errors:
chgtocmt.log
chgip0.log
chgip1.log
These files are located in the ORACLE_HOME/chgip/log directory.
Verify the changes on node 1.
To verify the installation, access the Application Server Control page using the virtual hostname in the URL (for example: http://vhost_mt.mydomain.com:1156).
The default port number is 1156. You can verify the port number by looking in the ORACLE_HOME/install/portlist.ini file.
Modify OracleAS JMS
In the jms.xml file for the OC4J instance that you plan to use, set the host attribute in jms-server to the virtual hostname (example: vhost_mt.mydomain.com).
<jms-server host="vhost_mt.mydomain.com" port="9127">
...
</jms-server>
If for a queue, file-based message persistence is being used, the location for the file should ideally be on a shared disk. In this case, the shared disk needs to fail over with the virtual IP. To configure this, the value of the persistence-file attribute for queue should be a file on the shared disk.
<queue name="Demo Queue" location="jms/demoQueue"
persistence-file="/path/to/shared_file_system/demoQueueFile">
<description>A dummy queue</description>
</queue>
Update the DCM repository and restart the components.
prompt> $ORACLE_HOME/dcm/bin/dcmctl updateConfig -ct oc4j prompt> $ORACLE_HOME/bin/emctl stop iasconsole prompt> $ORACLE_HOME/opmn/bin/opmnctl stopall prompt> $ORACLE_HOME/opmn/bin/opmnctl startall prompt> $ORACLE_HOME/bin/emctl start iasconsole
Copy the files located at /var/opt/oracle/oratab and /var/opt/oracle/oraInst.loc from node 1 to node 2.
Fail over the Virtual IP to node 2.
Stop all Oracle Application Server processes on node 1.
prompt> $ORACLE_HOME/bin/emctl stop iasconsole prompt> $ORACLE_HOME/opmn/bin/opmnctl stopall
Fail over the virtual hostname vhost_mt.mydomain.com from node 1 to node 2.
On node 1, run the following command as root:
# ifconfig interface removeif virtual_ip_address
On node 2, run the following command as root:
# ifconfig interface addif virtual_ip_address up
Fail over the shared disk hosting the Oracle Home.
Verify the installation on node 2 as you did in Step 3.
After successfully converting the middle tier to an OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Middle-Tier) topology, you should back up your files again because previous backups that you have are no longer valid (because of the configuration changes you just made). You need to back up your middle tier, plus your OracleAS Infrastructure.
You can perform the backups using the OracleAS Backup and Recovery Tool, which is documented in the Oracle Application Server Administrator's Guide.
This section describes how to restore files to a known state, if errors occurred during the conversion.
If an unrecoverable error occurred during conversion, you can restore the middle tiers and OracleAS Infrastructure to a known state using the backup files that you created in Section 11.9.1.3.2, "Back up the Installations (Middle-Tier and OracleAS Infrastructure)". You use the OracleAS Backup and Recovery Tool to perform the restore operation.
If you do not have backup files, you can try reversing the changes made by the chgtocfmt script by running the script again, but this time you use the physical hostname for both the -v and -w options. For example:
prompt> $ORACLE_HOME/bin/chgtocfmt -vphyshost_mt.mydomain.com-ppassword-n [-s] [-b] [-e] [-wphyshost_mt.mydomain.com]
Note that re-running the script may not work. If the script gave errors when you were converting to a virtual host-based environment, you might get the same errors when you re-run the script to convert back to a physical host-based environment.
After installing the OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Middle-Tier), you may decide you need a component that is not installed or configured on the middle tier.
If you decide to add additional components, see Section 7.14, "Expanding a MiddleTier" for installation instructions. If you need to configure components that were not previously configured, see the Oracle Application Server Administrator's Guide. For installations in separate Oracle homes, you will need to expand the middle tiers on both nodes of the cluster.
Note that the OracleAS Wireless component is not supported for a OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Middle-Tier) installed in single Oracle home.
After adding or configuring additional components, you need to run the chgtocfmt command using the -e option. All of the other options should be the same as the first time you ran it. For example, if you ran this command the first time:
prompt> $ORACLE_HOME/bin/chgtocfmt -v vhost_mt.mydomain.com -p password -w cfcwebcache.mydomain.com
then you should run the following command after expanding the middle tiers:
prompt> $ORACLE_HOME/bin/chgtocfmt -v vhost_mt.mydomain.com -p password -w cfcwebcache.mydomain.com -e
For installations in separate Oracle homes, you will need to run the chgtocfmt command on both nodes of the cluster.
This configuration is a combination of Section 11.3, "Installing an OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Infrastructure) Configuration" and Section 11.9, "Installing OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Middle-Tier)". This section describes how to install these configurations on the same nodes.
Figure 11-8 shows where you would install the components, and on which nodes they would be running.
In normal mode, OracleAS Infrastructure runs on node 1, while the middle tier runs on node 2. Unlike normal cold failover cluster configurations, both nodes are active in this case but running different components (either the OracleAS Infrastructure components or the middle-tier components).
Virtual Hostnames
You need two virtual hostnames: one virtual hostname (for example, vhost_infra) points to the node running OracleAS Infrastructure, and the other virtual hostname (for example, vhost_mt) points to the node running the middle tier.
Failover
If node 1 fails (Figure 11-9), the OracleAS Infrastructure processes fail over to node 2. The virtual hostname that was pointing to node 1 now points to node 2.
If node 2 fails (Figure 11-10), the middle-tier processes fail over to node 1. The virtual hostname that was pointing to node 2 now points to node 1. Note that you need to configure the middle tier after installation for it to fail over to the other node.
Location of Oracle Homes
You install the OracleAS Infrastructure on the shared storage, and the middle tier on the local storage of each node. You install the middle tier twice, once for each node.
To access the OracleAS Infrastructure or the middle tier, clients use the virtual hostname associated with the node running the OracleAS Infrastructure or middle-tier components.
You also use the virtual hostname in URLs. For example, if vhost_infra.mydomain.com is the name of the virtual host for the OracleAS Infrastructure, the URLs for the Oracle HTTP Server and the Application Server Control would look like the following:
| URL for: | Example URL |
|---|---|
| Oracle HTTP Server, Welcome page | http://vhost.mydomain.com:7777 |
| Oracle HTTP Server, secure mode | https://vhost.mydomain.com:4443 |
| Application Server Control
|
http://vhost.mydomain.com:1156 |
Figure 11-8 OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Infrastructure) with OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Middle-Tier) on the Same Nodes
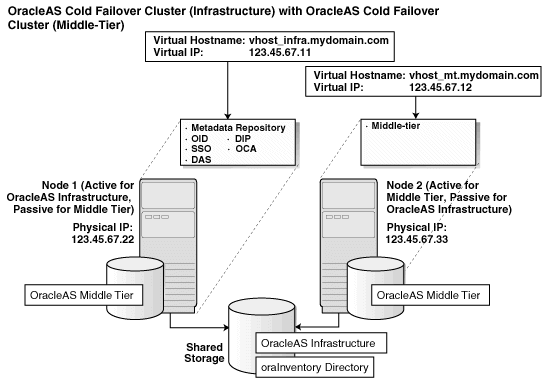
To create this configuration:
Set up the environment.
Create an alias for the hostnames.
You do this by adding a line to the /etc/hosts file on each node.
Lines in the hosts file use the following format. You can have one or more aliases.
ip_address official_hostname aliases...
For example, if the nodes are called node1 and node2, and you want the alias to be called cfcwebcache, then you would add these lines to the hosts file:
In the hosts file on node1, add this line:
123.45.67.22 node1.mydomain.com node1 cfcwebcache.mydomain.com
In the hosts file on node2, add this line:
123.45.67.33 node2.mydomain.com node2 cfcwebcache.mydomain.com
Install OracleAS Infrastructure on the shared storage. See Section 11.3.2, "OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Infrastructure): Details of Installation Steps".
Create a staticports.ini file for the middle tiers. This is to ensure that the middle tiers use the same ports, and that the ports are different from the ports used by the OracleAS Infrastructure.
When either node fails, a failover event occurs and all the OracleAS Infrastructure and middle-tier components will run on the same node. For the components to continue working, there must not be any port conflicts.
Install the middle tier on the local storage of each node.
Notes for installing the middle tiers:
You need to use the same Oracle home path for both nodes.
You need to use the same Oracle Application Server instance name.
When the installer prompts you to enter the hostname for the Oracle Internet Directory, enter the virtual hostname for the OracleAS Infrastructure.
To install a J2EE and Web Cache middle tier, see Section 7.9, "Installing J2EE and Web Cache in a Database-Based Farm Repository and with Oracle Identity Management Access".
To install a Portal and Wireless middle tier, see Section 7.13, "Installing Portal and Wireless or Business Intelligence and Forms".
Perform the post-installation steps for node1 and node2 listed in Section 11.9.2.3, "Post-Installation Steps".
Section 11.11.1, "Edit the ORACLE_HOME/Apache/Apache/htdocs/index.html File"
Section 11.11.2, "Copy the /var/opt/oracle Directory to the Other Node"
Section 11.11.3, "Running Database Console against a Cold Failover Cluster Database"
Section 11.11.4, "Create a Clusterware Agent for Automatic Failover"
In the ORACLE_HOME/Apache/Apache/htdocs/index.html file, change all occurrences of the physical hostname (example: node1) to the virtual hostname (example: vhost), where node1 appears as a hostname.
Note that if node1 is used as part of the Oracle Application Server instance name, do not change it.
After the OracleAS Infrastructure installation is complete, copy the /var/opt/oracle directory from the node where you performed the installation to the other node in the OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster. This ensures that you can run the installer to update the Oracle home from either node in the cluster.
Be sure to keep the two /var/opt/oracle directories in sync. Whenever you run the installer to update the infrastructure, you need to copy the oracle directory to the other node.
The /var/opt/oracle directory is not used during runtime by Oracle Application Server. It is used only by the installer.
Before you can start, stop or check the status of Database Console against a cold failover cluster database, you need to set the ORACLE_HOSTNAME environment variable to the virtual hostname. For example, in Figure 11-1, the virtual hostname is vhost.mydomain.com. You would set ORACLE_HOSTNAME as follows:
C shell:
$ setenv ORACLE_HOSTNAME vhost.mydomain.com
Bourne or Korn shell:
% ORACLE_HOSTNAME=vhost.mydomain.com % export ORACLE_HOSTNAME
After setting the variable, you can then run the "emctl action dbconsole" commands, where action is start, stop, or status (for example, emctl start dbconsole).
An OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster environment provides the framework for a manual failover of OracleAS Infrastructure. To achieve automatic failover, you must set up an agent using the clusterware. An example of automatic failover is setting up the secondary node to monitor the heart beat of the primary node and when the secondary node detects that the primary node is down, the virtual IP address, shared storage, and all the OracleAS Infrastructure processes are failed over to the secondary node.
This section describes how to install middle tiers that are not in a cold failover cluster configuration against an OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster infrastructure.
If you want to install middle tiers that can take advantage of cold failover cluster features, see Section 11.9, "Installing OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Middle-Tier)" or Section 11.10, "Installing OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Infrastructure) and OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster (Middle-Tier) on the Same Nodes".
For non-cold failover cluster middle tiers to work with OracleAS Infrastructure in an OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster, you can install the middle tiers on computers outside the cluster, or on nodes within the cluster.
|
Note: The preferred solution is to install and run the non-cold failover cluster middle tiers on nodes outside the OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster. |
If you plan to install a non-cold failover cluster middle tier on an OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster node (primary or secondary), perform these tasks before installing the middle tier:
Section 11.12.1.1, "Create a staticports.ini File for the Middle Tier"
Section 11.12.1.2, "Rename the /var/opt/oracle Directory Used for the Infrastructure"
Ensure that the ports used by the middle tier are not the same as the ports used by the infrastructure. The reason is that the infrastructure can fail over from the primary to the secondary node (and vice versa), and there must not be any port conflicts on either node. The same ports must be reserved for the infrastructure on both nodes.
If the infrastructure is running on the same node where you want to install the middle tier, the installer can detect which ports are in use and select different ports for the middle tier. For example, if the infrastructure is running on the primary node, and you run the installer on the primary node to install the middle tier, then the installer can assign different ports for the middle tier.
However, if the infrastructure is running on a node different from where you want to install the middle tier, the installer cannot detect which ports are used by the infrastructure. For example, if the infrastructure is running on the primary node but you want to install the middle tier on the secondary node, the installer is unable to detect which ports the infrastructure is using. In this situation, you need to set up a staticports.ini file to specify port numbers for the middle tier. See Section 4.6.3, "Using Custom Port Numbers (the "Static Ports" Feature)" for details.
To see which ports the infrastructure is using, view the ORACLE_HOME/install/portlist.ini file, where ORACLE_HOME refers to the directory where you installed the infrastructure.
Set up the environment so that the middle tier will have its own inventory directory, instead of using the same inventory directory used by the infrastructure. To do this, you need to rename the /var/opt/oracle directory to something else so that the installer will prompt you to enter a new inventory directory. The following example renames it to oracle.infra.
prompt> su Password: root_password # cd /var/opt # mv oracle oracle.infra
When the installer prompts for the inventory directory, specify a directory on the local storage or on a disk other than the one where you installed the OracleAS Infrastructure.
When the middle-tier installation is complete, do the following rename operations:
prompt> su Password: root_password # cd /var/opt # mv oracle oracle.mt see (1) # mv oracle.infra oracle see (2)
(1) This command renames the oracle directory created by the installer when it installed the middle tier.
(2) This command renames the oracle.infra directory back to oracle.
The /var/opt/oracle directory is not used during Oracle Application Server runtime. The only time you need it is when you run the installer (for example, to de-install an instance or to expand an instance).
Be sure the correct oracle directory is in place before you run the installer.
To install middle tiers against OracleAS Infrastructure in an OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster, follow the procedures as documented in Chapter 7, "Installing Middle Tiers", but with these differences:
In the Register with Oracle Internet Directory screen, enter the virtual hostname in the Hostname field.
If you are installing the middle tier on an OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster node, you must follow these additional requirements:
If you install middle-tiers that are not in a cold failover cluster configuration on the same nodes as an OracleAS Cold Failover Cluster infrastructure, then the ports used for the middle tiers must be different from the ones used for any OracleAS Infrastructure installed on the same cluster. The ports must also be different from those used for other Oracle Homes on the same node. To check the ports assigned to components in any Oracle Home, see the Ports page on the Application Server Control Console.
When you install the middle-tiers, you should use a staticports.ini file. See Section 4.6.3, "Using Custom Port Numbers (the "Static Ports" Feature)" for details.