|
Oracle® Application Server Reports Services Publishing Reports to the Web
10g Release 2 (10.1.2) B14048-02 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
|
Oracle® Application Server Reports Services Publishing Reports to the Web
10g Release 2 (10.1.2) B14048-02 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
The JDBC pluggable data source (PDS) enables you to access any JDBC data sources, such as:
An RDBMS like Oracle, DB2, Sybase, or SQL Server
A non-relational data source like Microsoft Excel
Any ODBC data source through the JDBC-ODBC bridge
The JDBC PDS is installed by default with Oracle Reports to allow access to all of the JDBC supported data sources.
This chapter contains the following sections:
The jdbcpds.conf file, located in the ORACLE_HOME\reports\conf directory, is the Oracle Reports JDBC PDS configuration file. This file is preconfigured for the:
Pre-installed drivers; that is, Oracle JDBC Thin, Oracle JDBC OCI (thick), and JDBC-ODBC.
DataDirect Merant drivers available on Oracle Technology Network, (http://www.oracle.com/technology/index.html).
You need to add or modify relevant entries in the jdbcpds.conf file to include any other JDBC drivers that you want to use.
Reports Builder displays a list of drivers in the JDBC Query Connection dialog box based on the entries in the jdbcpds.conf file. Use this list to select specific drivers for your report's JDBC query.
Reports Builder reads and caches the entries in the jdbcpds.conf when it is invoked. Restart Reports Builder to view the result of any changes made to the jdbcpds.conf file, for example, adding a new JDBC driver entry.
The jdbcpds.conf file has two sections:
An Internal DTD section describing the XML format and driver configuration information
|
Caution: This section should not be modified. |
An XML section detailing the driver information like driver name, connect string format, driver class, and so on.
|
Note: You can modify or add your driver information in this section. |
Example
The following sample illustrates the contents of the jdbcpds.conf file:
<!-- DTD section - Not to be modified -->
<!DOCTYPE jdbcpds [
<!ELEMENT jdbcpds (driverInfo)>
<!ELEMENT driverInfo (driver+)>
<!ELEMENT driver (property*)>
<!ATTLIST driver name CDATA #REQUIRED
sourceDatabase (oracle |
sqlserver |
sybase |
db2 |
informix |
odbc |
other) "oracle"
mainProtocol ( jdbc ) "jdbc"
subProtocol CDATA #REQUIRED
connectString CDATA #REQUIRED
class CDATA #REQUIRED
connection CDATA #REQUIRED
loginTimeout CDATA "5"
>
<!ELEMENT property EMPTY>
<!ATTLIST property name CDATA #REQUIRED
value CDATA #REQUIRED >
]>
<!-- Add or modify the following section for your driver information -->
<!-- Following drivers are available out-of-box in 9iAS -->
<jdbcpds>
<driverInfo>
<driver name = "oracleThin"
sourceDatabase = "oracle"
subProtocol = "oracle:thin"
connectString = "mainProtocol:subProtocol:@databaseName"
class= "oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver"
connection = "oracle.reports.plugin.datasource.jdbcpds.
JDBCConnectionHandling">
</driver>
<driver name = "oracle"
sourceDatabase = "oracle"
subProtocol = "oracle:oci8"
connectString = "mainProtocol:subProtocol:@databaseName"
class = "oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver"
connection = "oracle.reports.plugin.datasource.jdbcpds.
JDBCConnectionHandling">
</driver>
<driver name = "jdbc-odbc"
sourceDatabase = "odbc"
subProtocol = "odbc"
connectString = "mainProtocol:subProtocol:databaseName"
class = "sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver"
connection = "oracle.reports.plugin.datasource.jdbcpds.
JDBCConnectionHandling">
</driver>
<driver name = "sqlserver-merant"
sourceDatabase = "sqlserver"
subProtocol = "merant:sqlserver"
connectString = "mainProtocol:subProtocol://databaseName"
class = "com.oracle.ias.jdbc.sqlserver.SQLServerDriver"
connection = "oracle.reports.plugin.datasource.jdbcpds.
JDBCConnectionHandling">
</driver>
<driver name = "sybase-merant"
sourceDatabase = "sybase"
subProtocol = "merant:sybase"
connectString = "mainProtocol:subProtocol://databaseName"
class = "com.oracle.ias.jdbc.sybase.SybaseDriver"
connection = "oracle.reports.plugin.datasource.jdbcpds.
JDBCConnectionHandling"
loginTimeout = "0">
</driver>
<driver name = "db2-merant"
sourceDatabase = "db2"
subProtocol = "merant:db2"
connectString = "mainProtocol:subProtocol://databaseName"
class = "com.oracle.ias.jdbc.db2.DB2Driver"
connection = "oracle.reports.plugin.datasource.jdbcpds.
JDBCConnectionHandling"
loginTimeout = "0">
</driver>
<driver name = "informix-merant"
sourceDatabase = "informix"
subProtocol = "merant:informix"
connectString = "mainProtocol:subProtocol://databaseName"
class = "com.oracle.ias.jdbc.informix.InformixDriver"
connection = "oracle.reports.plugin.datasource.jdbcpds.
JDBCConnectionHandling">
</driver>
</driverInfo>
</jdbcpds>
Table 9-1 outlines the various attributes that can be associated with a driver.
Table 9-1 Driver Attributes
| Attribute Name | Description | Sample |
|---|---|---|
|
|
A unique user-defined value used to refer to a specific JDBC driver in Oracle Reports. |
|
|
Database referenced by the driver. The valid entries are:
|
|
|
|
Driver sub protocol added with the database URL before creating a database connection. This is driver-specific information and can be found in the driver documentation. Example: The sub protocol used for connecting to the Merant driver: Sybase is SQL Server is |
|
|
|
Format of the driver's connect string format is |
|
|
|
Driver class name used to register to |
|
|
|
Driver's connection handling class. The JDBC PDS can have different connection handling classes for each driver. Oracle Reports' default connection handling class, which is sufficient for most drivers, is Refer to the Oracle Reports Java API Reference for more information on how to extend your JDBC Connection class |
|
|
|
Driver-specific parameter. Specify the value in seconds. Please refer to the driver documentation for more information. |
|
|
|
Specify any additional properties of your driver as Attribute Name and Value. |
|
When you submit your report's connection details, the connection information is combined with the driver's configuration information specified in the jdbcpds.conf file. The resulting connection information is submitted to the database as a complete connection URL. Refer to Table 9-3, Table 9-4, Table 9-5, Table 9-6, and Table 9-7 for more information on sample connection information.
Figure 9-1 shows a list of all drivers configured in the jdbcpds.conf file.
Figure 9-1 JDBC Connect Dialog Box in Reports Builder
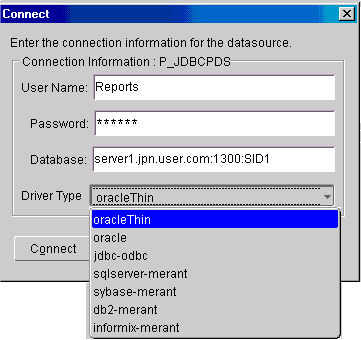
Drivers like SQL Server and Excel with JDBC-ODBC, Oracle JDBC Thin, and Oracle JDBC OCI (thick) are installed and configured with Oracle Reports. These drivers do not require any additional JAR files to be installed.
You can use SQL Server / Excel with the JDBC-ODBC driver. This entry is preconfigured in the jdbcpds.conf file. Before you can use SQL Server or Excel with JDBC-ODBC, you need to create an ODBC data source. Refer to Windows help, for more information on how to create an ODBC data source.
|
Note: Oracle Application Server provides Merant DataDirect drivers which can also be used to access SQL Server. |
Oracle provides a set of Merant DataDirect drivers (Version 3.2) that can be downloaded from OTN (http://www.oracle.com/technology/index.html). The driver configuration file; that is, jdbcpds.conf contains relevant entries for the Merant DataDirect drivers. Additionally, the JDBC Connect dialog (Table 9-1) lists the entries for the set of Merant DataDirect drivers provided by Oracle.
However, you need to install the appropriate JAR files and specify them in Oracle Reports specific classpath entries, in order to make them available to Reports Builder and OracleAS Reports Services
The drivers provided by Oracle for use with Oracle Application Server / Oracle Developer Suite are:
You can also install and configure a Custom Driver for use with Oracle Application Server and Oracle Developer Suite.
The following procedure outlines the generic steps involved in configuring the Merant DataDirect drivers. To configure specific Merant DataDirect drivers refer to the appropriate sections.
To configure the Merant DataDirect drivers:
Install the relevant JAR files in your Oracle Application Server and Oracle Developer Suite directory.
Include an entry in REPORTS_CLASSPATH to make the files available to Reports Builder and OracleAS Reports Services.
|
Note: TheREPORTS_CLASSPATH variable is located in the reports.sh file for all UNIX platforms.
|
Refer to the relevant driver in this section for information on the required JAR files.
Reports Builder: Prefix the driver location to the existing entries in REPORTS_CLASSPATH.This variable is located in the registry for Windows users and in the reports.sh file for UNIX users. Refer to the relevant driver in this section for an example.
rwbuilder.conf: Append the driver location to the engine classPath attribute in the rwbuilder.conf configuration file. Refer to the relevant driver in this section for an example.
Reports Server: Append the driver location to the classPath attribute of the engine, in the Reports Server configuration file. Refer to the relevant driver in this section for an example
jdbcpds.conf: Located in the ORACLE_HOME\reports\conf directory. Refer to Table 9-1 for more information on the parameters. Refer to the relevant driver in this section for an example.
Install the relevant JAR files in your Oracle Application Server and Oracle Developer Suite directory.
Jar files required: YMutil.jar, YMsybase.jar, and YMbase.jar.
Include an entry in the REPORTS_CLASSPATH to make the files available to Reports Builder and OracleAS Reports Services.
|
Note: TheREPORTS_CLASSPATH variable is located in the reports.sh file for all UNIX platforms.
|
Reports Builder: Prefix the driver location to the existing entries in REPORTS_CLASSPATH.This variable is located in the registry for Windows users and in the reports.sh file for UNIX users.
Example: D:\sybase_installed\YMutil.jar;D:\sybase_installed\YMsybase.jar;D:\sybase_ installed\YMbase.jar;existing classpath entries
rwbuilder.conf: Append the driver location to the engine classPath attribute in the rwbuilder.conf configuration file.
Example: <engine id="rwEng" class="oracle.reports.engine.EngineImpl" initEngine="1" maxEngine="1" minEngine="0" engLife="50" maxIdle="30" callbackTimeOut="60000" classPath="D:\sybase_ installed\YMutil.jar;D:\sybase_installed\YMsybase.jar;D:\sybase_ installed\YMbase.jar;"> ... </engine>
Reports Server: Append the driver location to the classPath attribute of the engine in the Reports Server configuration file.
Example: <engine id="rwEng" class="oracle.reports.engine.EngineImpl" initEngine="1" maxEngine="1" minEngine="0" engLife="50" maxIdle="30" callbackTimeOut="60000" classPath="D:\sybase_ installed\YMutil.jar;D:\sybase_installed\YMsybase.jar;D:\sybase_ installed\YMbase.jar;"> ... </engine>
jdbcpds.conf: Located in the ORACLE_HOME\reports\conf directory. Refer to Table 9-1 for more information on the required parameters.
Example:
<driver name = "sybase-merant"
sourceDatabase = "sybase"
subProtocol = "merant:sybase"
connectString = "mainProtocol:subProtocol://databaseName"
class = "com.oracle.ias.jdbc.sybase.SybaseDriver"
connection = "oracle.reports.plugin.datasource.jdbcpds.
JDBCConnectionHandling"
loginTimeout = "0">
</driver>
Install the relevant JAR files in your Oracle Application Server and Oracle Developer Suite directory.
JAR files required: YMutil.jar, YMdb2.jar, and YMbase.jar
Include an entry in REPORTS_CLASSPATH to make the files available to Reports Builder and OracleAS Reports Services.
|
Note: TheREPORTS_CLASSPATH variable is located in the reports.sh file for all UNIX platforms.
|
Reports Builder: Prefix the driver location to the existing entries in REPORTS_CLASSPATH. This variable is located in the registry for Windows users and in the reports.sh file for UNIX users.
Example: D:\db2_installed\YMutil.jar;D:\db2_installed\YMdb2.jar;D:\db2_ installed\YMbase.jar;existing classpath entries
rwbuilder.conf: Append the driver location to the engine classPath attribute in the rwbuilder.conf configuration file.
Example: <engine id="rwEng" class="oracle.reports.engine.EngineImpl" initEngine="1" maxEngine="1" minEngine="0" engLife="50" maxIdle="30" callbackTimeOut="60000" classPath="D:\db2_installed\YMutil.jar;D:\db2_ installed\YMdb2.jar;D:\db2_installed\YMbase.jar"> ... </engine>
Reports Server: Append the driver location to the classPath attribute of the engine in the Reports Server configuration file.
Example: <engine id="rwEng" class="oracle.reports.engine.EngineImpl" initEngine="1" maxEngine="1" minEngine="0" engLife="50" maxIdle="30" callbackTimeOut="60000" classPath="D:\db2_installed\YMutil.jar;D:\db2_ installed\YMdb2.jar;D:\db2_installed\YMbase.jar"> ... </engine>
jdbcpds.conf: Located in the ORACLE_HOME\reports\conf directory. Refer to Table 9-1 for more information on the parameters.
Example:
<driver name = "db2-merant"
sourceDatabase = "db2"
subProtocol = "merant:db2"
connectString = "mainProtocol:subProtocol://databaseName"
class = "com.oracle.ias.jdbc.db2.DB2Driver"
connection = "oracle.reports.plugin.datasource.jdbcpds.
JDBCConnectionHandling"
loginTimeout = "0">
</driver>
Install the relevant .jar files in your Oracle Application Server and Oracle Developer Suite directory.
Jar files required: YMutil.jar, YMsqlserver.jar, and YMbase.jar
Include an entry in the REPORTS_CLASSPATH to make the files available to Reports Builder and OracleAS Reports Services.
|
Note: TheREPORTS_CLASSPATH variable is located in the reports.sh file for all UNIX platforms.
|
Reports Builder: Prefix the driver location to the existing entries in REPORTS_CLASSPATH.This variable is located in the registry for Windows users and in the reports.sh file for UNIX users.
Example: D:\sqlserver_installed\YMutil.jar;D:\sqlserver_ installed\YMsqlserver.jar;D:\sqlserver_installed\YMbase.jar;existing classpath entries
rwbuilder.conf: Append the driver location to the engine classPath attribute in the rwbuilder.conf configuration file.
Example: <engine id="rwEng" class="oracle.reports.engine.EngineImpl" initEngine="1" maxEngine="1" minEngine="0" engLife="50" maxIdle="30" callbackTimeOut="60000" classPath="D:\sqlserver_ installed\YMutil.jar;D:\sqlserver_installed\YMsqlserver.jar;D:\sqlserver_ installed\YMbase.jar;"> ... </engine>
Reports Server: Append the driver location to the classPath attribute of the engine in the Reports Server configuration file.
Example: <engine id="rwEng" class="oracle.reports.engine.EngineImpl" initEngine="1" maxEngine="1" minEngine="0" engLife="50" maxIdle="30" callbackTimeOut="60000" classPath="D:\sqlserver_ installed\YMutil.jar;D:\sqlserver_installed\YMsqlserver.jar;D:\sqlserver_ installed\YMbase.jar;"> ... </engine>
jdbcpds.conf: Located in the ORACLE_HOME\reports\conf directory. Refer to Table 9-1 for more information on the parameters.
Example:
<driver name = "sqlserver-merant"
sourceDatabase = "sqlserver"
subProtocol = "merant:sqlserver"
connectString = "mainProtocol:subProtocol://databaseName"
class = "com.oracle.ias.jdbc.sqlserver.SQLServerDriver"
connection = "oracle.reports.plugin.datasource.jdbcpds.
JDBCConnectionHandling">
</driver>
Install the relevant JAR files in your Oracle Application Server and Oracle Developer Suite directory.
JAR files required: YMutil.jar, YMinformix.jar, and YMbase.jar
Include an entry in the REPORTS_CLASSPATH to make the files available to Reports Builder and OracleAS Reports Services.
|
Note: TheREPORTS_CLASSPATH variable is located in the reports.sh file for all UNIX platforms.
|
Reports Builder: Prefix the driver location to the existing entries in REPORTS_CLASSPATH.This variable is located in the registry for Windows users and in the reports.sh file for UNIX users.
Example: D:\informix_installed\YMutil.jar;D:\informix_ installed\YMinformix.jar;D:\informix_installed\YMbase.jar;existing classpath entries
rwbuilder.conf:Append the driver location to the engine classPath attribute in the rwbuilder.conf configuration file.
Example: <engine id="rwEng" class="oracle.reports.engine.EngineImpl" initEngine="1" maxEngine="1" minEngine="0" engLife="50" maxIdle="30" callbackTimeOut="60000" classPath="D:\informix_ installed\YMutil.jar;D:\informix_installed\YMinformix.jar;D:\informix_ installed\YMbase.jar"> ... </engine>
Reports Server: Append the driver location to the classPath attribute of the engine in the Reports Server configuration file.
Example: <engine id="rwEng" class="oracle.reports.engine.EngineImpl" initEngine="1" maxEngine="1" minEngine="0" engLife="50" maxIdle="30" callbackTimeOut="60000" classPath="D:\informix_ installed\YMutil.jar;D:\informix_installed\YMinformix.jar;D:\informix_ installed\YMbase.jar"> ... </engine>
jdbcpds.conf: Located in the ORACLE_HOME\reports\conf directory. Refer to Table 9-1 for more information on the parameters.
Example:
<driver name = "informix-merant"
sourceDatabase = "informix"
subProtocol = "merant:informix"
connectString = "mainProtocol:subProtocol://databaseName"
class = "com.oracle.ias.jdbc.informix.InformixDriver"
connection = "oracle.reports.plugin.datasource.jdbcpds.
JDBCConnectionHandling">
</driver>
Any driver that is not provided by Oracle must be installed and configured:
Install the relevant JAR files in your Oracle Application Server and Oracle Developer Suite directory.
Include an entry in REPORTS_CLASSPATH to make the files available to Reports Builder and OracleAS Reports Services.
|
Note: TheREPORTS_CLASSPATH variable is located in the reports.sh file for all UNIX platforms.
|
Jar files required: Refer to the relevant driver documentation.
Reports Builder: Prefix the driver location to the existing entries in REPORTS_CLASSPATH. This variable is located in the registry for Windows users and in the reports.sh file for UNIX users.
Example: driver location\1st jar file;driver location\2nd jar file2;existing classpath entries
rwbuilder.conf: Append the driver location to the engine classPath attribute in the rwbuilder.conf configuration file.
Example: <engine id="rwEng" class="oracle.reports.engine.EngineImpl" initEngine="1" maxEngine="1" minEngine="0" engLife="50" maxIdle="30" callbackTimeOut="60000" classPath="driver location\1st jar file;driver location\2nd jar file;"> ... </engine>
Reports Server: Append the driver location to the classPath attribute of the engine in the Reports Server configuration file.
Example: <engine id="rwEng" class="oracle.reports.engine.EngineImpl" initEngine="1" maxEngine="1" minEngine="0" engLife="50" maxIdle="30" callbackTimeOut="60000" classPath="driver location\1st jar file;driver location\2nd jar file;"> ... </engine>
jdbcpds.conf: Located in the ORACLE_HOME\reports\conf directory. Add relevant driver configuration information to the jdbcpds.conf file. Refer to Table 9-1 for more information on the required parameters.
Example:
<driver name = "<driver name>"
sourceDatabase = "<sourceDatabase>"
subProtocol = "<subProtocol>"
connectString = "mainProtocol:subProtocol://databaseName"
class = "<driver class name>"
connection ="<connection handling class">
</driver>
|
Note: This value can still beconnection = "oracle.reports.plugin.datasource.jdbcpds.JDBCConnectionHandling"for your custom drivers, if you do not want to implement a custom connection dialog
|
After configuring the relevant JDBC drivers, you can define and run a JDBC query using either SQL or a stored procedure.
To define a JDBC query:
Start Reports Builder.
Invoke the Reports Wizard.
Select the data source type as JDBC Query and click Next. For more information on how to work with the Report Wizard, refer to the Oracle Reports online Help.
In the Data Source Definition window, click Query Definition.
Define one of the following:
A SQL query:
SELECT * FROM DEPARTMENT;
A stored procedure:
Enter the complete call syntax of your database's stored procedure. For example:
TestProc(40)
For more information on the call syntax, refer to your database documentation.
JDBC PDS submits the calling statement to the driver as specified, to invoke the stored procedure.
Table 9-2 Specifying an Excel Data Source
| Query (Single Worksheet) | Query (Muitiple Worksheets) |
|---|---|
|
Where Where the first worksheet row value is taken as a column name for the query Note: If a value is not mentioned in any of the columns in the first row, then the default name is FcolumnNumber. For example, the 8th column will be F8, the ninth column will be F9, and so on. |
Where Where the first worksheet row is taken as a column name for the query Note: If a value is not mentioned in any of the columns in the first row, then the default name is FcolumnNumber. For example, the 8th column will be F8, the ninth column will be F9, and so on. |
Specify a sign-on parameter name. This sign-on parameter is associated with the connection information when run against a database. The default sign-on parameter name is P_JDBCPDS (see Section A.3.69, "P_JDBCPDS"):
Enter a new sign-on name and click Connect. Use this sign-on parameter to specify a database connection when you are running your report using OracleAS Reports Services.
Enter the connection information (user name, password, and database name) for the driver type. Refer to Table 9-3, Table 9-4, Table 9-5, Table 9-6, and Table 9-7 for sample connection information.
Select the driver type. The driver list is displayed based on the values entered in the jdbcpds.conf file.
Click Connect to gain access to the database using the new sign-on. The connect string formed internally is a combination of:
The connectString driver attribute (Table 9-1) defined in the jdbcpds.conf file
The connection information supplied in the Connect dialog will be used to fill the database name portion of the connectString.
Click OK to execute the JDBC query.
The Reports Wizard displays the query description (Figure 9-4).
Follow the steps in the wizard to define the layout and to run the report based on your JDBC query.
Table 9-3, Table 9-4, Table 9-5, Table 9-6, Table 9-7,Table 9-8, and Table 9-9 lists sample connection information for use with:
Pre-installed drivers; that is, Oracle JDBC Thin, Oracle JDBC OCI (thick), and JDBC-ODBC.
DataDirect Merant drivers available on Oracle Technology Network, (http://www.oracle.com/technology/index.html).
Table 9-3 Oracle Thin Driver
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
|
Username |
|
|
Password |
|
|
Database |
Example: |
Table 9-4 Oracle Thick Driver
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
|
Username |
|
|
Password |
|
|
Database |
where |
Table 9-5 JDBC-ODBC Driver
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
|
Username |
N/A |
|
Password |
This password is set at the time of establishing an ODBC connection. |
|
Database |
where |
Table 9-6 Sybase
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
|
Username |
|
|
Password |
|
|
Database |
Example: |
Table 9-7 DB2
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
|
Username |
|
|
Password |
|
|
Database |
Example1: Example2: |
Table 9-8 SQL Server
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
|
Username |
|
|
Password |
|
|
Database |
Example1: |
Table 9-9 Informix
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
|
Username |
|
|
Password |
|
|
Database |
Example2: |
When you run a report containing a JDBC query (Reports Server or rwrun engine), use the sign-on parameter to submit the connection information for the JDBC data source. This sign-on parameter is defined for your JDBC query in Reports Builder during design time.
For example, if your report has a JDBC query to a Sybase data source, a JDBC query to a DB2 data source, and a SQL query to an Oracle data source, then the request could be defined as:
http://your_ias_ server:port//reports/rwservlet?report=my.rdf&userid=user/pwd@oracledb &desformat=pdf&destype=cache&p_sybasepds=sybaseuser/pw@sybasehost:port &p_db2pds=db2user/pwd@db2host:port
where:
userid is the value for connecting the SQL query to the Oracle database. You do not need to specify the userid if your report does not have a SQL query or a REF cursor query.
p_sybasepds is the sign-on parameter associated with the Sybase JDBC query.
p_db2pds is the sign-on parameter associated with the DB2 JDBC query defined in the report at design time.
The default sign-on parameter name P_JDBCPDS will be used if you have not specified a name in the JDBC Query dialog box while designing the report in Reports Builder.
This section lists:
JDBC PDS error messages (Error Messages)
JDBC query troubleshooting (Trace Information).
Table 9-10, Table 9-11, and Table 9-12 lists troubleshooting information related to the JDBC PDS.
Table 9-10 Error Messages Related to the Database Connection
| Error Message | Cause | Action |
|---|---|---|
|
|
Invalid connection class specified in the |
Ensure that the driver connection class specified in the |
|
|
Invalid connection information. |
Ensure the validity of the username, password, database, and driver type. |
|
|
Invalid sign-on parameter for the specified query or procedure. |
Ensure the sign-on parameter is available and valid for the report's JDBC query type. |
|
|
Invalid connect string for the specified sign-on parameter. |
Ensure that the specified connect string for this sign-on parameter is valid for the selected driver. |
Table 9-11 Error messages Related to Executing the Data Source
| Error Message | Cause | Action |
|---|---|---|
|
|
The driver used to connect to database does not support the Date data type as a reference parameter. |
Use either: The String data type as the reference parameter. A different JDBC driver that supports the Date data type as a reference parameter. |
|
|
Invalid lexical parameter used in the query or procedure. |
Ensure that the query or procedure uses valid lexical parameters. Create a new parameter if it is not available. |
|
|
SQL syntax error in the specified query or procedure. |
Ensure that the syntax of the query or procedure is valid. Refer to the relevant data source's documentation. |
|
|
Invalid query or procedure syntax. |
Ensure that the syntax of the query or procedure is valid. Refer to the relevant data source's documentation. |
|
|
Invalid reference parameter value. |
Verify that the reference column types and values are correct. |
|
|
The query or procedure text field is empty. |
Enter a valid query or procedure in the text field. |
|
|
Invalid database URL.
|
Verify the validity of the specified database name and the selected driver type. |
|
|
The data fetched does not match the number of columns or column types specified in the query definition. |
Ensure that the number of columns and the column types match the query definition. |
|
|
This column type is not supported by the Oracle Reports JDBC query interface. |
Ensure that only column types supported by the Oracle Reports JDBC query interface are used. Refer to the JDBC specification and Oracle Reports documentation for a list of all supported types. |
Table 9-12 Isolating Driver / PDS Issues
| Error Message | Cause | Action |
|---|---|---|
|
|
The format of the inline DTD section in the |
If the DTD format is modified, ensure the validity of configuration file against the JDBC PDS requirement. |
|
|
An error was found on the specified line of the |
Correct the error on the specified line. |
|
|
The |
Ensure that the |
|
|
The XML section in the |
Ensure that the XML section in the |
|
|
The driver used in the query is not specified in the |
Ensure that the entry for the required driver along with the related driver information is in the |
Use the detailed trace information (ORACLE_HOME\reports\logs\) generated by Oracle Reports to debug your JDBC query.
Design time (building a JDBC query) and run time (running a JDBC query)
The trace information generated is helpful to find out the following:
Lexical and bind parameters.
Final connect string formed to connect to the driver.
Metadata information received from the driver.
Final query submitted to the database.
See Example 9-1 for sample design-time trace output.
See Example 9-2 for sample run-time trace output.
Sample trace output
Example 9-1 Building a JDBC Query from JDBC Query Dialog
Connection handling trace showing final connect string [2003/4/7 5:41:38:686] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): handleConnectButtonEvent : start [2003/4/7 5:41:38:686] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): handleConnectButtonEvent : subProtocol :sybase-merant [2003/4/7 5:41:38:686] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): handleConnectButtonEvent : connection class :oracle.reports.plugin.datasource.jdbcpds.JDBCConnectionHandling [2003/4/7 5:41:38:696] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): handleConnectButtonEvent : combine string :jdbc:merant:sybase://server1.us.oracle.com:1300 [2003/4/7 5:41:38:696] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): JDBCDataSource : setJDBCQueryType: sybase [2003/4/7 5:41:41:350] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): JDBCUIEventHandler : handleConnectEvent : Valid Connection com.oracle.ias.jdbc.sybase.SybaseConnection@56fc16 [2003/4/7 5:41:41:350] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): JDBCUIEventHandler : handleConnectEvent : END com.oracle.ias.jdbc.sybase.SybaseConnection@56fc16 Design time metadata of query [2003/3/31 6:35:46:363] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): JDBCUIEventHandler : handleOKEvent : Serialize XML<jdbcpds DTDVersion=" 1.0"><JDBCQuery>jdbcpdspkg.proc_with_param(1,2,3,4,5)</JDBCQuery><QueryDefinition>1</QueryDefinition><driverType>oracle </driverType><connectionClass>oracle.reports.plugin.datasource.jdbcpds.JDBCConnect ionHandling</connectionClass><SignOnParameter>P_JDBCPDS</SignOnParameter><jdbcElements><elementname = "EMPNO" type = "2" typeName = "NUMBER" columnSize = "4" columnScale = "0" /><element name = "ENAME" type = "12" typeName ="VARCHAR2" columnSize = "10" columnScale = "0" /><element name = "JOB" type = "12" typeName = "VARCHAR2" columnSize = "9" columnScale ="0" /><element name = "MGR" type = "2" typeName = "NUMBER" columnSize = "4" columnScale = "0" /><element name = "HIREDATE" type = "93" typeName = "DATE" columnSize = "16" columnScale = "0" /><element name = "SAL" type = "2" typeName = "NUMBER" columnSize = "7" columnScale= "2" /><element name = "COMM" type = "2" typeName = "NUMBER" columnSize = "7" columnScale = "2" /><element name = "DEPTNO" type = "2" typeName = "NUMBER" columnSize = "2" columnScale = "0" /></jdbcElements><referenceColumns></referenceColumns></jdbcpds> [2003/3/31 6:35:46:383] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): JDBCUIEventHandler :handleOKEvent END
Example 9-2 Running a JDBC Query
[2003/3/18 5:45:17:707] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): JDBCDataSource : startRuntime method : START Describing the JDBC Query: [2003/3/18 5:45:17:707] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): JDBCDataSource : describe : START [2003/3/18 5:45:17:707] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): applyXML: Extract the Serilzed XML containing Query Meta Data <jdbcpds DTDVersion=" 1.0"><JDBCQuery>select * from emp</JDBCQuery><QueryDefinition>0</QueryDefinition><driverType>oracle</driverType> <connectionClass>oracle.reports.plugin.datasource.jdbcpds.JDBCConnectionHandling</ connectionClass>... ConnectionHandling At Runtime: [2003/3/18 5:45:17:737] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): JDBCDataSource : startRuntime : Create a new connection and handle it [2003/3/18 5:45:17:737] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): JDBCExecuteQuerySource : handleConnection : START [2003/3/18 5:45:17:778] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): JDBCExecuteQuerySource : handleConnection : set driver [2003/3/18 5:45:17:778] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): JDBCExecuteQuerySource : handleConnection : Check if Connection for the sign on parameter is pooled [2003/3/18 5:45:17:778] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): JDBCExecuteQuerySource :handleConnection : connection available in pool [2003/3/18 5:45:17:778] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): handleConnection : END [2003/3/18 5:45:17:778] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): JDBCDataSource : startRuntime : END Runtime execution of jdbc query [2003/3/31 6:36:2:836] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): JDBCDataSource : execute : run Query [2003/3/31 6:36:2:836] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): JDBCExecuteQuerySource : getOutputFromDatabase : START [2003/3/31 6:36:2:836] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): JDBCExecuteQuerySource : getOutputFromDatabase: start Query stringto be submitted jdbcpdspkg.proc_with_param(1,2,3,4,5) [2003/3/31 6:36:2:836] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): JDBCExecuteQuerySource : getOutputFromDatabase : check connection [2003/3/31 6:36:2:836] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): JDBCExecuteQuerySource : getOutputFromDatabase : QSource Id: 1 [2003/3/31 6:36:2:836] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): JDBCExecuteQuerySource: executeOracleProcedure:Start [2003/3/31 6:36:2:836] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): JDBCExecuteQuerySource: executeOracleProcedure:Procedure to be submitted { call jdbcpdspkg.proc_with_param(?,?,?,?,?,?) } [2003/3/31 6:36:2:836] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): JDBCExecuteQuerySource: executeOracleProcedure: Set parameters for the procedure call [2003/3/31 6:36:2:836] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): JDBCExecuteQuerySource: executeOracleProcedure: execute procedure [2003/3/31 6:36:2:847] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): JDBCDataSource : execute : query execution over andresulset object is oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleResultSetImpl@751a9e [2003/3/31 6:36:2:847] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): JDBCDataSource : execute : END Running Report trace with Result set info 2003/4/7 5:26:6:996] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): JDBCDataSource : execute : replace lexical columns withactual string for the query [2003/4/7 5:26:6:996] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): JDBCDataSource : execute : run Query [2003/4/7 5:26:6:996] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): JDBCExecuteQuerySource : getOutputFromDatabase : START [2003/4/7 5:26:6:996] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): JDBCExecuteQuerySource : getOutputFromDatabase: start Query stringto be submitted select * from reports [2003/4/7 5:26:7:6] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): JDBCExecuteQuerySource : getOutputFromDatabase : check connection [2003/4/7 5:26:7:6] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): JDBCExecuteQuerySource : getOutputFromDatabase : QSource Id: 4 [2003/4/7 5:26:7:6] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): JDBCExecuteQuerySource : getOutputFromDatabase : Query source is SQL query [2003/4/7 5:26:7:6] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): JDBCExecuteQuerySource:executeQuery Start [2003/4/7 5:26:7:6] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): executeQuery prepareStatement select * from reports [2003/4/7 5:26:7:6] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): executeQuery : bind parameters set for the query [2003/4/7 5:26:7:6] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): executeQuery : JDBC Query executed [2003/4/7 5:26:7:387] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): JDBCExecuteQuerySource : getOutputFromDatabase : Query result col 0 test col 1 10 [2003/4/7 5:26:7:387] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): JDBCExecuteQuerySource:executeQuery Start [2003/4/7 5:26:7:387] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): executeQuery prepareStatement select * from reports [2003/4/7 5:26:7:387] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): executeQuery : bind parameters set for the query [2003/4/7 5:26:7:387] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): executeQuery : JDBC Query executed [2003/4/7 5:26:7:767] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): JDBCDataSource : execute : query execution over andresulset object is com.oracle.ias.jdbc.base.BaseResultSet@56c3cf [2003/4/7 5:26:7:767] Debug 50103 (jdbcpds): JDBCDataSource : execute : END
|
Note: Oracle Reports exposes the PDS API and also contains a tutorial that describes in detail how to implement or customize your own PDS. For more information, refer to the Reports Software Development Kit (RSDK), available on the Oracle Technology Network (OTN): on the Oracle Reports 10g page (http://www.oracle.com/technology/products/reports/index.html), click SDK. Using this API, you can implement an unlimited number of PDSs to access any kind of data sources that you have.
|
The main tasks you must perform to add your JDBC PDS are:
For information on how to configure the jdbcpds.conf file, refer to Section 9.1, "JDBC Configuration File".
For information on how to install the driver's JAR files, refer to Section 9.1.2.5, "Custom Driver" .