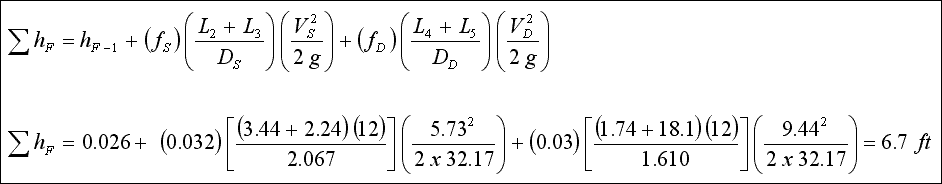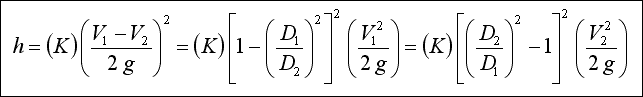Friction Losses...
Pipe Fittings...
Invariably a system containing piping will have connections which change th size and / or direction of the conduit.
These fittings and friction, called " minor losses ", to the system head. Fitting losses are generally the result of
changes in velocity and / or direction. A decreasing velocity results in more loss in head than an increasing velocity
as the former causes energy - dissipating eddies. Experimental results have indicated that minor losses vary approximately
as the square of the velocity through the fittings.
Valves and Standard Fittings...
The resistance to flow through valves and fittings may be estimated by any of the following methods. The " Hydraulic
Institute - Pipe Friction Manual ", lists losses through valves and fittings in terms of the average velocity head
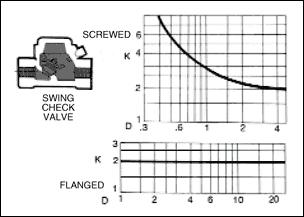
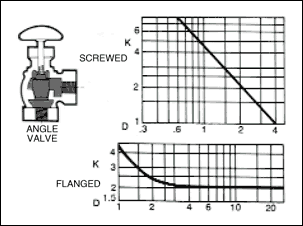
in a pipe of corresponding diameter and a " resistance coefficient " as shown in figures given below.

Source : www.gouldspumps.com

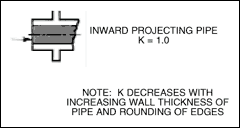
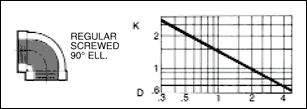
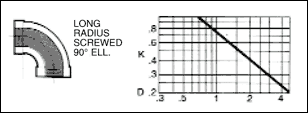
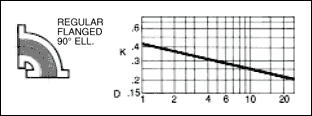
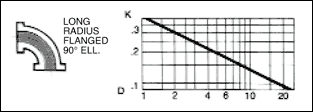
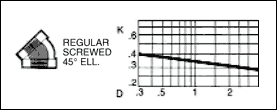
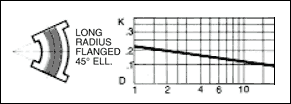
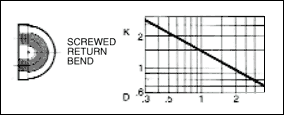
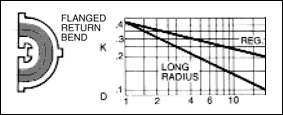
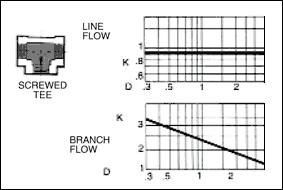
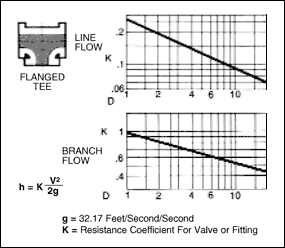
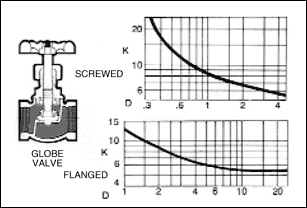
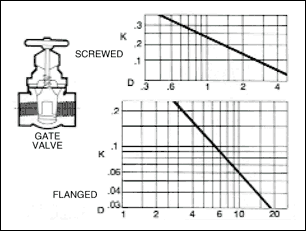
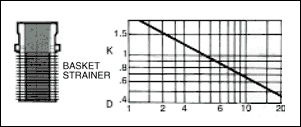
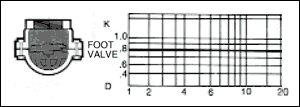
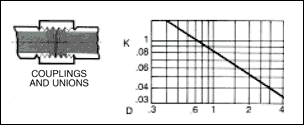
The frictional resistance in feet is found from the equation ;
h= ( K ) ( V 2 / 2 x g )
where ; K : resistance coefficient which depends on design and size of valve or fitting, V : average velocity in pipe of
corresponding diameter ( ft / s ) and g : acceleration of gravity ( = 32.17 ft / s 2 ).
Table given below indicates the wide variation in published values of K.
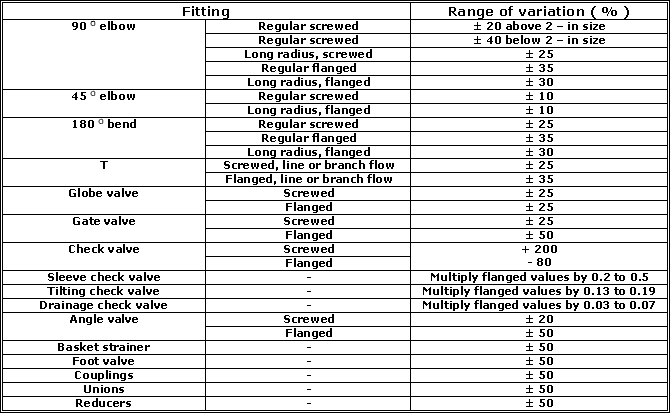
A comparison of the " Darcy - Weisbach " equation and the above equation suggests that K = f ( L / D ) to produce the same
head loss in a straight pipe as in the valve or fitting. The ratio ( L / D ) or " equivalent length in pipe diameters "
of straight pipe may then be used as another method to estimate valve and fitting losses. Tests have shown that while
K decreases with size of different lines of valves and fittings, ( L / D ) is almost constant. In the zone of complete
turbulence, as shown in figure below, K for a given size and ( L / D ) for all sizes of valves and fittings are constant.
In the transition zone K increases as does the friction factor f with decreasing.
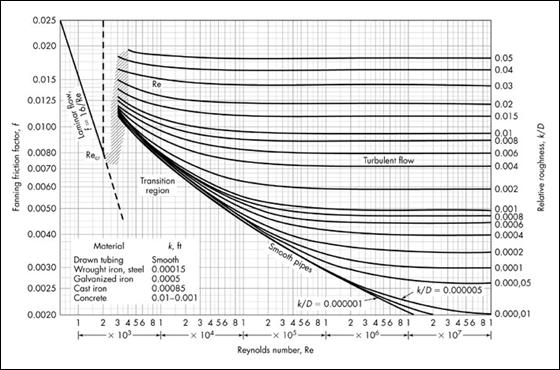
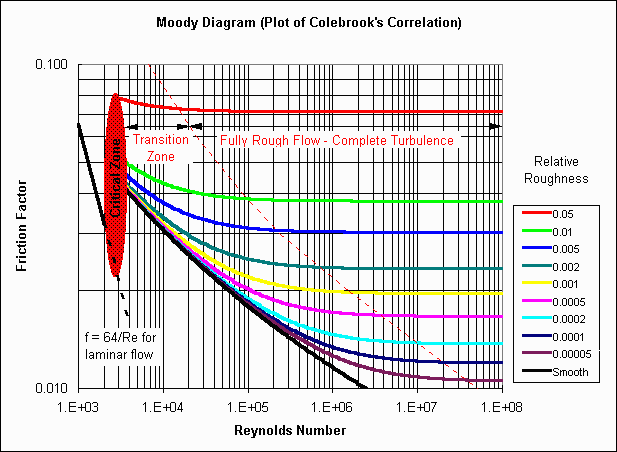
" Reynolds " number Re while L / D remains approximately constant. Table given below lists suggested values of L / D for
various valves and fittings.
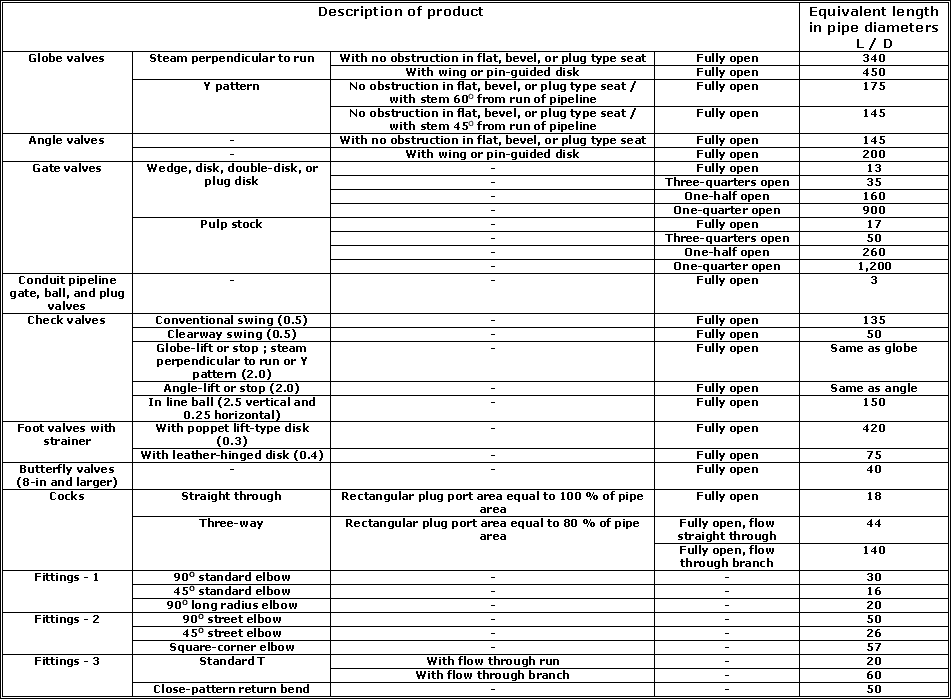
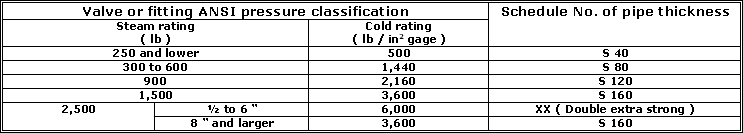
Multiplying L / D by the inside diameter of pipe corresponding to the schdule number shown in table given below gives the
equivalent length of straight pipe.
When using the equivalent length method, the friction head loss is determined by employing the " Darcy - Weisbach "
equation. This method therefore takes into consideration the viscosity of the liquid, which in turn determines the
" Reynolds " number and the friction factor.
The loss of head through valves, particularly control valves, is sometimes expressed in terms of the " flow coefficient,
C V ". The flow in gpm at 60 O F to produce a pressure drop of 1 lb / in 2 is defined
as the flow coefficient for a particular valve opening. Values of C V may be obtained from various
manufacturers for their different lines of valves. The pressure loss for liquids with viscosity close to water at
60 O F may be found for different flows from ;
lb / in 2 = sp gr at 60 O F ( gpm / C V ) 2
The following examples illustrate the use of the " resistance coefficient, K " and the " equivalent length in pipe
diameters, L / D " methods for estimating losses in valves and fittings.
Example - 1...
A pumping system consists of 20 ft of 2 - in suction pipe and 300 ft of 1 1/2 - in discharge pipe, both " Schedule "
40 new steel. Also included are a bellmouth inlet, a 90 O LR suction elbow, a suction - gate valve, a
discharged - gate valve and a swing - check valve. The valves and fittings are screw - connected and the same size
as the connecting pipe. Determine the pipe, valve, and fitting losses when pumping 60 gpm of 60 O F oil
having a sp gr of 0.855. Use the resistance coefficient method.
Solution...
- Suction pipe :
* ID = 2.067 in
* EPSILON / D = 0.00087
* NU = 0.0009 ft 2 / s
* V = ( 60 / 2.067 2 ) ( 0.408 ) = 5.73 ft / s
* ( V ) ( D" ) = ( 5.73 ) ( 2.067 ) = 11.8 ft / sec . in
* Re = 1 x 10 4
* f = 0.032
h FS = ( 0.032 ) [ ( 20 ) ( 12 ) / ( 2.067 ) ] [ ( 5.73 2 ) / ( 2 ) ( 32.17 ) ] = 1.9 ft
- Discharge pipe :
* ID = 1.610 in
* EPSILON / D = 0.0011
* NU = 0.00009 ft 2 / s
* V = ( 60 / 1.610 2 ) ( 0.408 ) = 9.44 ft / s
* ( V ) ( D" ) = ( 9.44 ) ( 1.610 ) = 15.2 ft / sec . in
* Re = 1.5 x 10 4
* f = 0.030
h FD = ( 0.030 ) [ ( 300 ) ( 12 ) / ( 1.610 ) ] [ ( 9.44 2 ) / ( 2 ) ( 32.17 ) ] = 92.9 ft
- Valve and fitting losses :
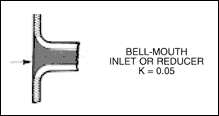
* 2 - in bellmouth, K = 0.05
h F - 1 = ( 0.05 ) [ ( 5.73 2 ) / ( 2 ) ( 32.17 ) ] = 0.026 ft
* 2 - in LR, 90 O elbow, K = 0.4 +- 25 %
h F - 2 = ( 0.4 ) [ ( 5.73 2 ) / ( 2 ) ( 32.17 ) ] = 0.202 +- 0.051 ft
* 2 - in gate valve, K = 0.16 +- 25 %
h F - 3 = ( 0.16 ) [ ( 5.73 2 ) / ( 2 ) ( 32.17 ) ] = 0.082 +- 0.021 ft
* 1 1/2 - in gate valve, K = 0.19 +- 25 %
h F - 4 = ( 0.19 ) [ ( 9.44 2 ) / ( 2 ) ( 32.17 ) ] = 0.263 +- 0.066 ft
* 1 1/2 - in swing - check valve, K = 2.4 +- 30 %
h F - 5 = ( 2.4 ) [ ( 9.44 2 ) / ( 2 ) ( 32.17 ) ] = 3.32 +- 1.0 ft
- Total pipe, valve and fitting losses :
TOTAL h F = 1.9 + 92.9 + 0.026 + 0.202 + 0.082 + 0.263 + 3.32 = 98.69 ft
TOTAL variation = +- ( 0.202 + 0.021 + 0.066 + 1.0 ) = +- 1.29 ft
Example - 2...
Determine the value and fittings losses in examle given above by the equivalent length pipe diameters method and compare
results.
Solution...
* 2 - in bellmouth, h F - 1 = 0.026 ft
* 2 - in LR, 90 O elbow, L / D = 20
L 2 = ( 20 ) ( 2.067 / 12 ) = 3.44 ft
* 2 - in gate valve, L / D = 13
L 3 = ( 13 ) ( 2.067 / 12 ) = 2.24 ft
* 1 1/2 - in gate valve, L / D = 13
L 4 = ( 13 ) ( 1.610 / 12 ) = 1.74 ft
* 1 1/2 swing - check valve, L / D = 135
L 5 = ( 135 ) ( 1.610 / 12 ) = 18.1 ft
Using f from example given above, total valve and fitting losses are ;
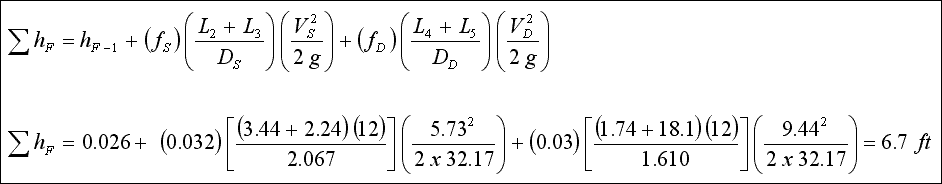
Total valve and fitting losses from example given above ;
TOTAL h F = ( 0.026 + 0.202 + 0.082 + 0.263 + 3.32 ) +- 1.29 = 3.89 +- 1.29 ft
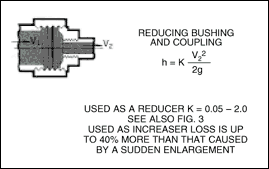
Increasers :
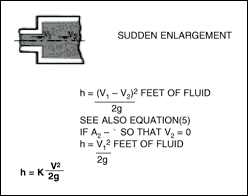
The loss of head for a sudden increase in diameter with velocity changing from V 1 to V 2 in the
direction of the flow can be calculated analytically. Computed results have been confirmed experimentally to be true to
within +- 3 percent. The head loss is expressed as shown below with K computed to be equal to unity ;
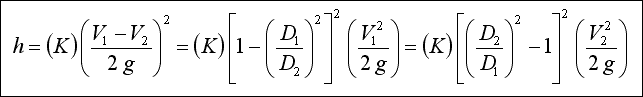
The value of K is also approximately equal to unity if a pipe discharges into a relatively large reservoir. This indicates
that all the kinetic energy V 1 2 / 2g is lost, and V 2 equals zero. The loss of head
for a gradual increase in diameter through a diffuser can be found from figure given below.
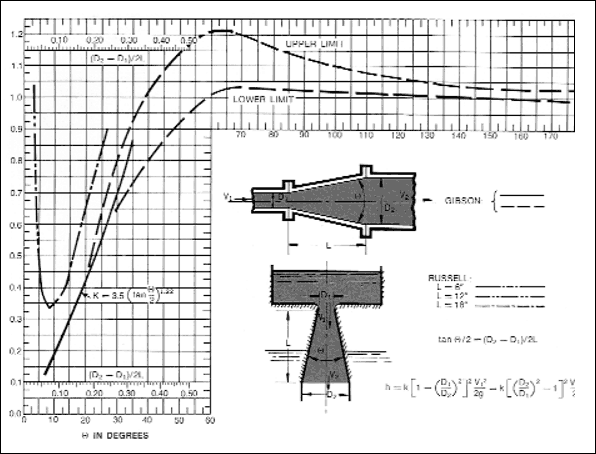
The diffuser converts some of the kinetic energy into pressure. Values for the coefficient used with the above equations
for calculating head loss are shown in the figure. The optimum total angle appears to be 7.5 O . Angles
greater than this result in shorter diffusers and less friction, but separation and turbulence occur. For angles greater
than 50 O it is preferable to use a sudden enlargement.
Reducers :
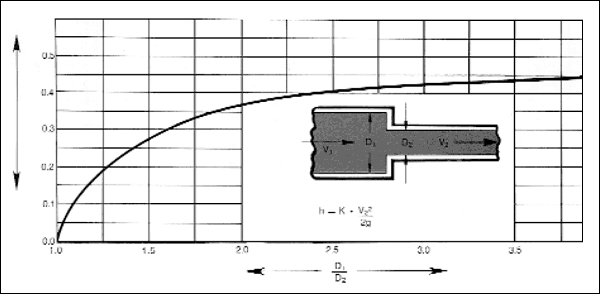
Figure shown below gives values of the resistance coefficient to be used for sudden reducers.
Bends :
Figure given below may be used to determine the resistance coefficient for 90 O pipe bends of uniform
diameter.
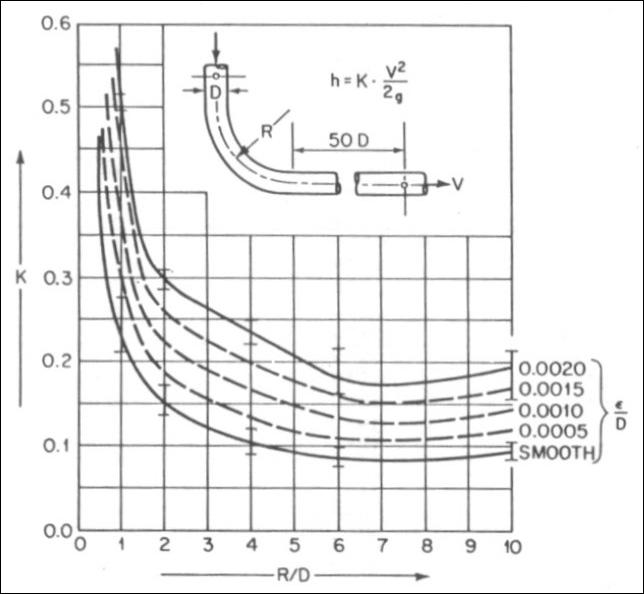
Figure shown below gives resistance coefficients for less than 90 O pipe bends and can be used for surfaces
having moderate roughness such as clean steel and cast iron.
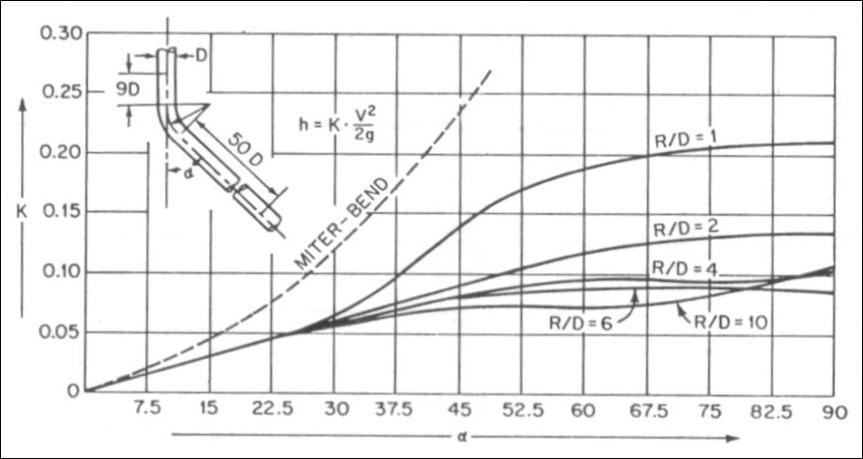
These two figures are not recommended for elbows with R / D below 1.
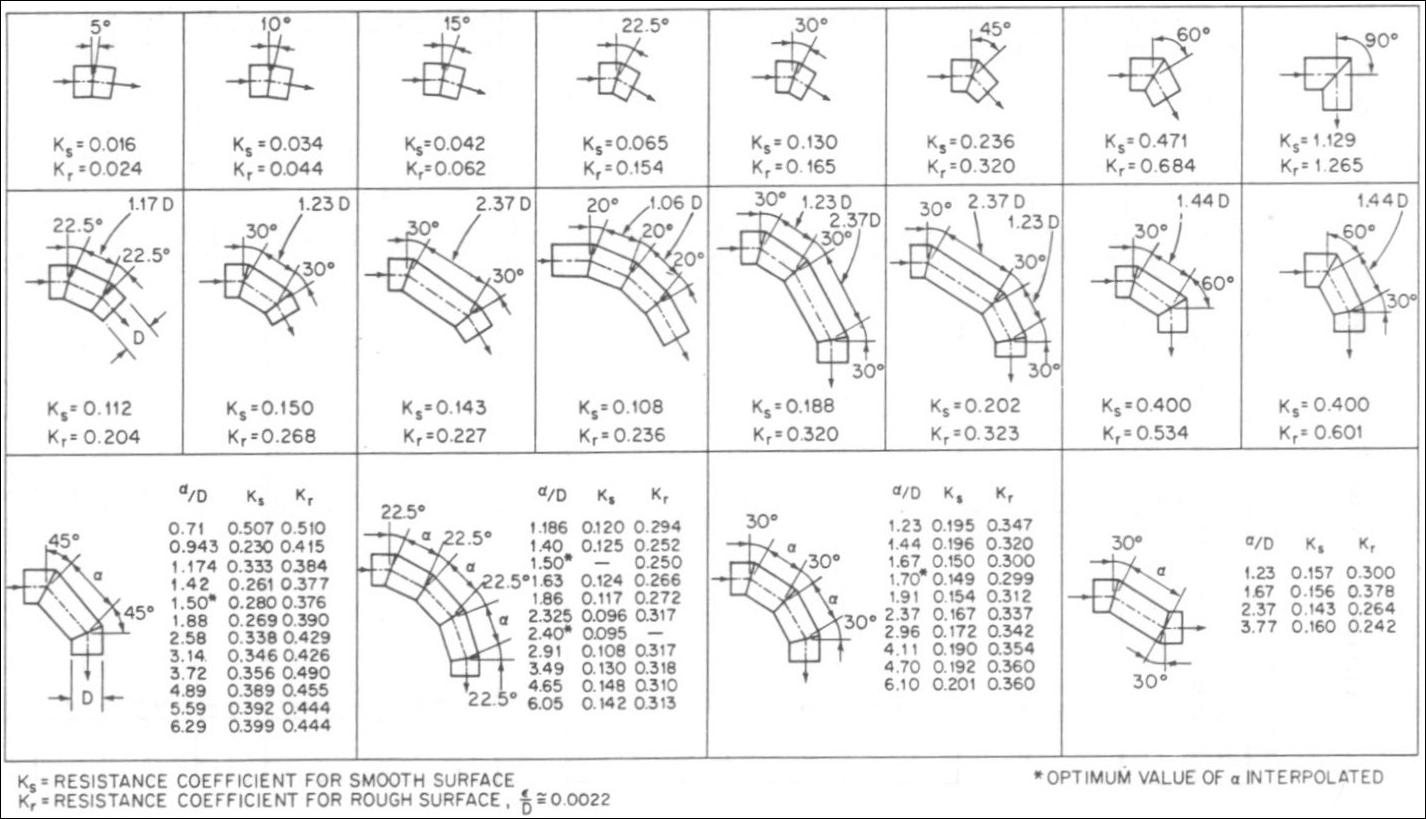
Table shown below gives values of resistance coefficients for miter bends.
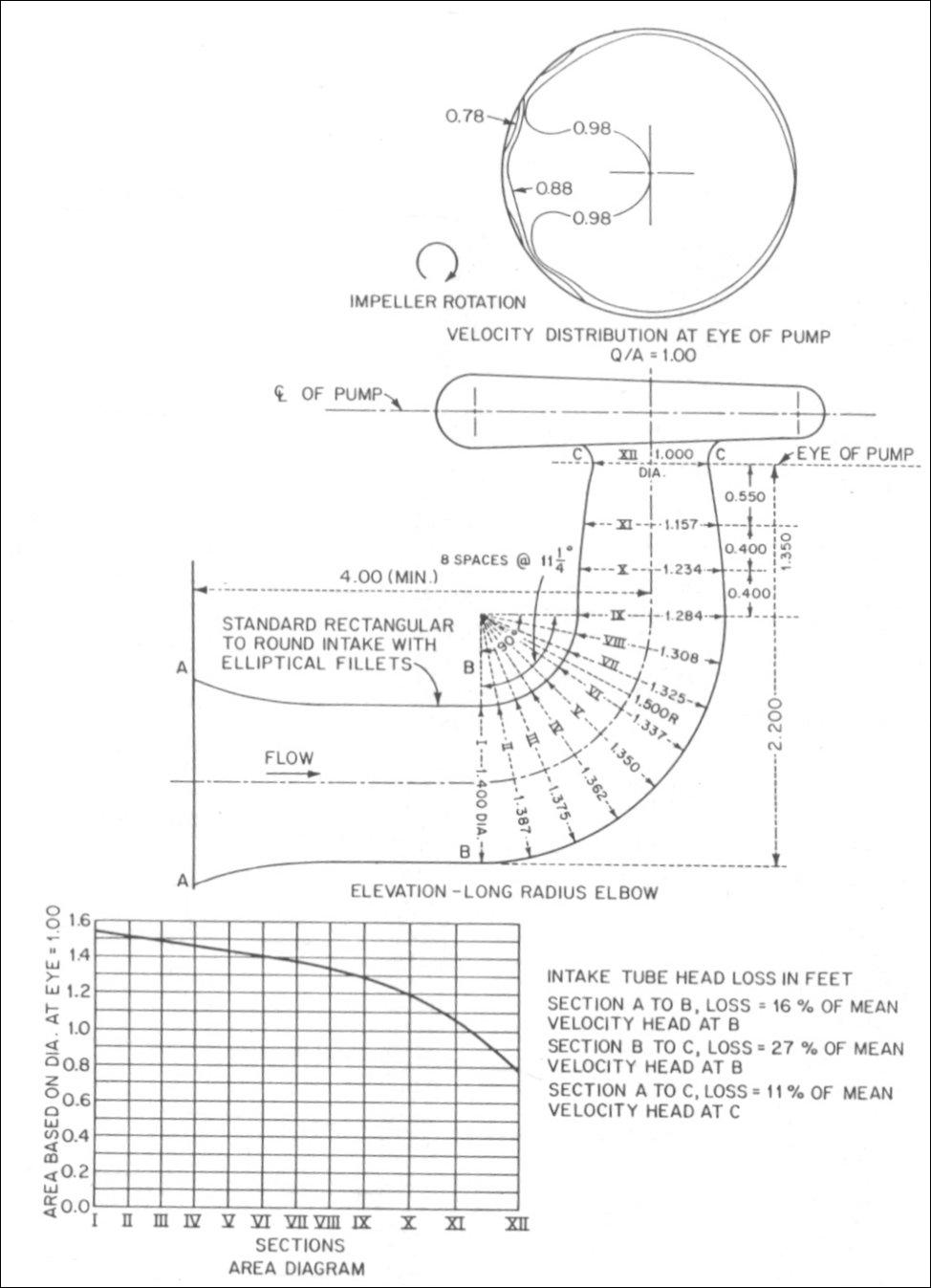
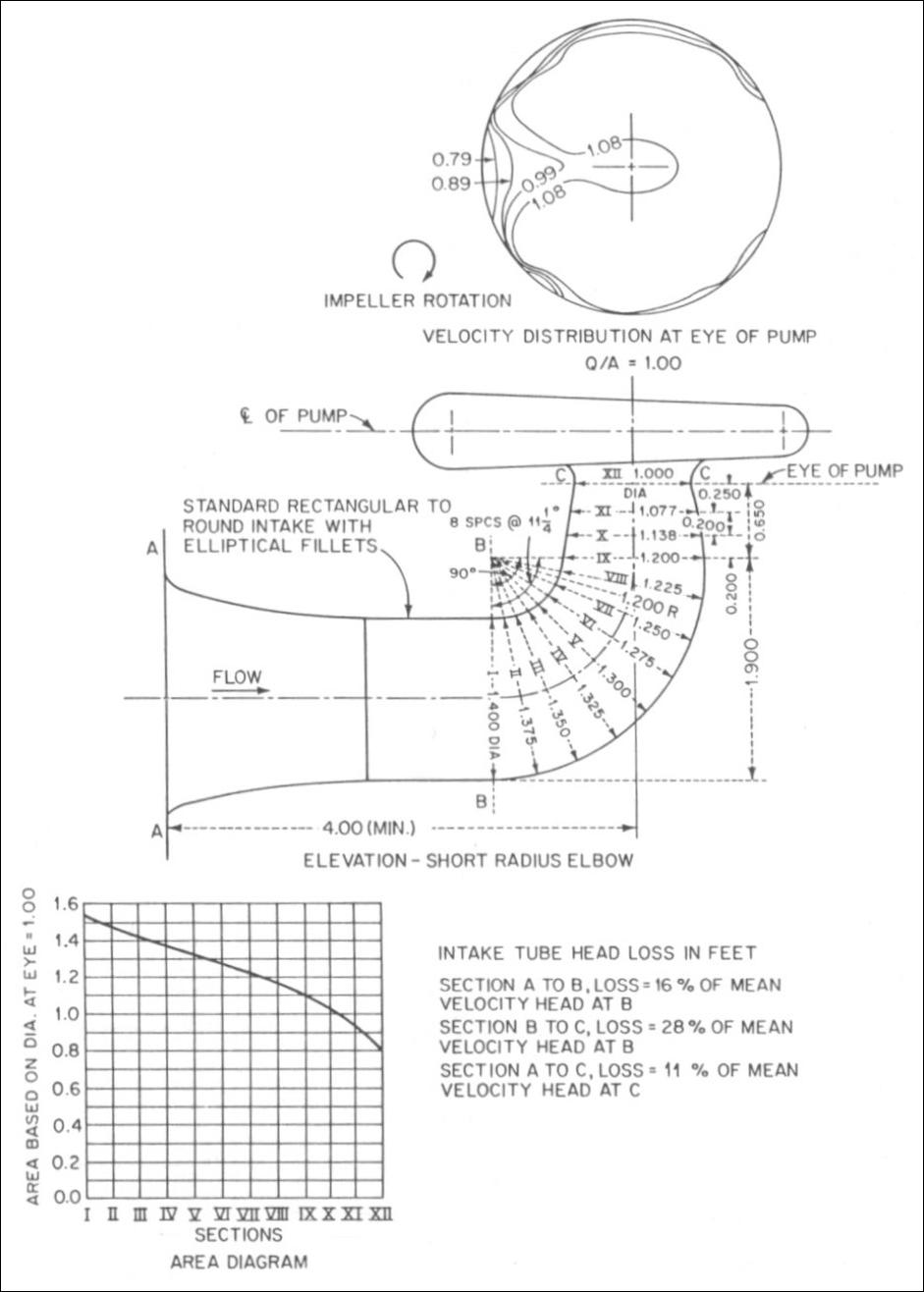
Pump Suction Elbows :
Figures given below illustrate two typical rectangular to round reducing suction elbows. Elbows of this configuration
are sometimes used under dry pit vertical volute pumps. These elbows are formed in concrete and are designed to require
a minimum height, thus permitting a higher pump setting with reduced excavation. Figure (first) shows a long - radius
elbow and figure (second) shows a short - radius elbow. The resulting velocity distribution into the impeller eye and the
loss of head are shown for these selected two designs.
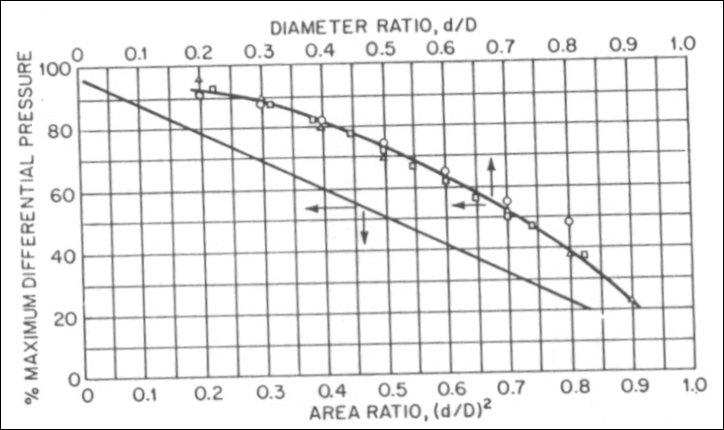
Meters :
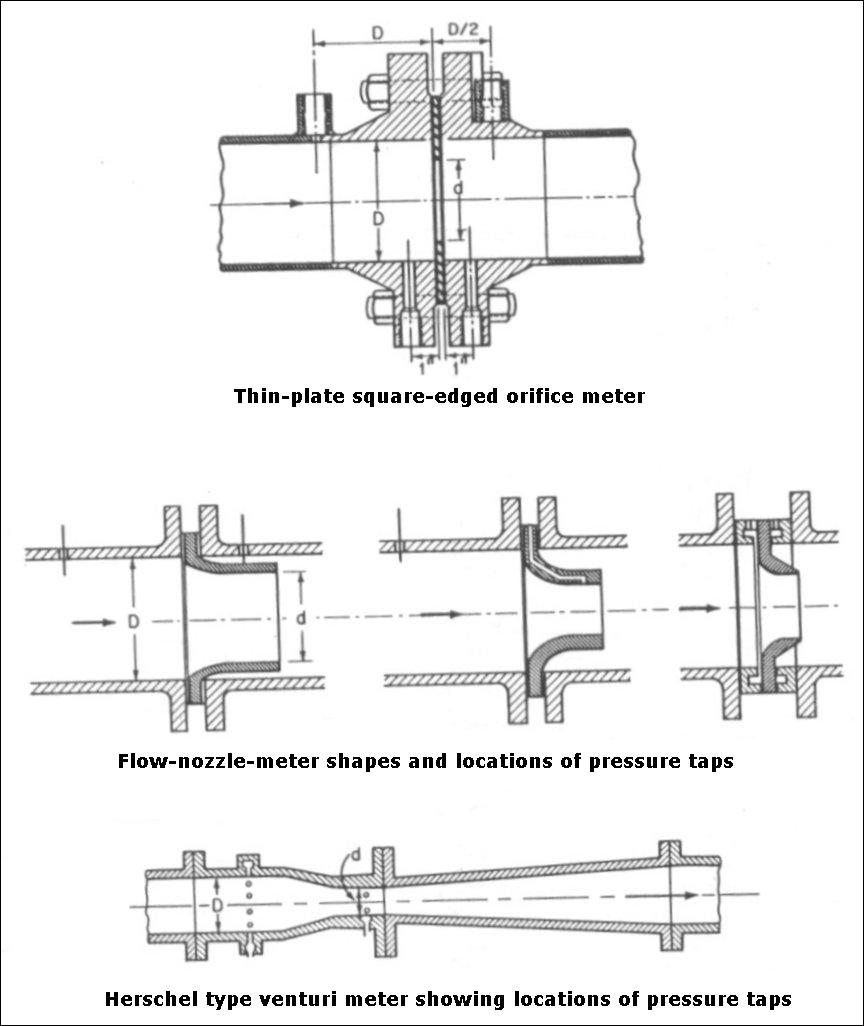
Orifices, nozzles, and venturi meters are used to measure rate of flow. These metering devices, however, introduce
additional loss of head into the pumping system. Each of these meters is designed to create a pressure differential through
the primary element. The magnitude of the pressure differential depends on the velocity and the density of the liquid
and the design of the element. The primary element restricts the area of flow, increases the velocity, and decreases the
pressure. An expanding section following the primary element provides pressure head recovery and determines the meter
efficiency. The pressure differential between inlet and throat taps measures rate of flow ; the pressure differential
between inlet and outlet taps measures the meter head loss (an outlet tap is not usually provided). The meters offering
the least resistance to flow are in the following decreasing order ; venturi, nozzle, and orifice. Figures given below
illustrate these different meter designs.
When meters are designed and pressure taps are located as recommended, figures given below may be used to estimate the
overall pressure loss. The loss of pressure is expressed as a percentage of the differential pressure measured at the
appropriate taps and values are given for various size meters.