 Description of object_hierarchy.jpg
Description of object_hierarchy.jpg
|
Oracle® OLAP Analytic Workspace Java API Reference 10g Release 2 (10.2) B14351-02 |
Object Hierarchy
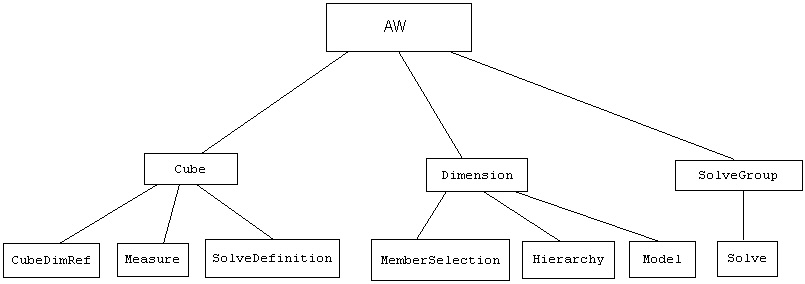
The Oracle OLAP Analytic Workspace Java API object model defines a set of hierarchical relationships between objects in the API. The top-level object is an AW, which represents the analytic workspace. The AW exists within the name space of a relational schema. The second-level objects in the hierarchy, which are Cube, Dimension, and SolveGroup, are owned by the AW. Other objects are owned by the second-level objects, and so on.
The following diagram illustrates the primary ownership relationships between the objects at the highest levels in the model.
 Description of object_hierarchy.jpg
Description of object_hierarchy.jpg
In most cases, dependent objects are optional. For example, a SolveGroup can own several Solve objects or none. In some cases, an AW requires at least one instance of a dependent object. For example, a Cube must have at least one Measure. The UML diagrams available with the some of the class descriptions indicate the associations of the classes.
A Cube specifies a unit of multidimensional data. All of the data in the Cube shares the same multidimensional structure. A Cube has at least one Measure, which identifies a type of data, and at least one reference to a Dimension. A Cube can own one or more SolveDefinition objects. A SolveDefinition is a set of instructions for aggregating or allocating the data of the Cube or generating a forecast based on the data. A SolveDefinition is used by a Solve.
A Dimension specifies a list of values (dimension members) that can be used as an index to the data in a Cube. A Dimension can own Hierarchy and MemberSelection objects, which represent one or more groups of dimension members. A Dimension can also own one or more Model objects.
MemberSelection is a Level, which represents the members of a Dimension that are at the same level in a hierarchy of the Dimension. For example, a time dimension typically has a hierarchy with a Month level and a Year level.Hierarchy defines an ordered set of relationships between members in a dimension. There are two types of hierarchies: level-based hierarchies and value-based. A level-based hierarchy defines parent-child relationships between dimension members in an ordered set of levels. A value-based hierarchy has only one level and defines the parent-child relationships by dimension member value rather than by level.Model represents a set of dimension members and a set of calculations that an aggregation operation can use to produce customized values for a Measure.A SolveGroup is a collection of Solve objects. Each Solve uses a SolveDefinition to specify the aggregation, allocation, or forecasting of multidimensional data. Solves are ordered within a SolveGroup. The order determines when the calculations are performed during an analytic workspace build.
Data Mapping and Object Attributes
The subclasses of AWObject are Cube, Dimension, MemberSelection, HierarchyLevelAssociation, and Hierarchy.
An AWObject can have mappings to sources of data in the relational schema. An AWObject that has a mapping to data from relational tables is the target object of a data load. The mapping is represented by a MappingGroup object.
An AWObject can own attributes. Attributes represent a quality or description of an object. Attributes can be used to restrict the current set of dimension members associated with an object. In the object model, attributes are represented by Attribute and AttributeProjection objects. In the current release, only a Dimension can support an Attribute. An AttributeProjection associates an attribute to a Level or Hierarchy that is owned by a Dimension.
The AWObject owns the MappingGroup and Attribute objects associated with it. The following diagram shows the objects that can be owned by any AWObject.

Description of objhierattrmap.jpg.
Analytic Workspace standard form naming conventions specify a full name for each logical object in an analytic workspace. The full name includes the parent of the object, the simple logical name of the object, and the object type.
In the Oracle OLAP Analytic Workspace Java API, the full name is the object identifier. The BaseObject class and the subclasses of it have a getID method that returns a String that contains the following components.
The identifier is in the format owner.name.type. The owner is the parent of the object.
For objects at the top levels of the object model, the identifier does not include the owning object. The identifier of an AW, Cube, Dimension, or SolveGroup object is in the format name.type.
For example, the identifier of an AW with the name GLOBALAW is GLOBALAW.AW. The identifier of a Dimension with the name PRODUCT_AW that is owned by the AW is PRODUCT_AW.DIMENSION. The identifier of a Hierarchy with the name PRODUCT_ROLLUP_AW that is owned by PRODUCT_AW is PRODUCT_AW.PRODUCT_ROLLUP_AW.HIERARCHY.
For more information on database standard form naming conventions, see the Oracle OLAP Application Developer's Guide.