| Oracle® Database SQL Reference 10g Release 2 (10.2) Part Number B14200-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Database SQL Reference 10g Release 2 (10.2) Part Number B14200-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
Purpose
Use the ALTER TABLESPACE statement to alter an existing tablespace or one or more of its datafiles or tempfiles.
You cannot use this statement to convert a dictionary-managed tablespace to a locally managed tablespace. For that purpose, use the DBMS_SPACE_ADMIN package, which is documented in PL/SQL Packages and Types Reference.
|
See Also: Oracle Database Administrator's Guide and CREATE TABLESPACE for information on creating a tablespace |
Prerequisites
To alter the SYSAUX tablespace, you must have the SYSDBA system privilege.
If you have ALTER TABLESPACE system privilege, then you can perform any ALTER TABLESPACE operation. If you have MANAGE TABLESPACE system privilege, then you can only perform the following operations:
Take the tablespace online or offline
Begin or end a backup
Make the tablespace read only or read write
Before you can make a tablespace read only, the following conditions must be met:
The tablespace must be online.
The tablespace must not contain any active rollback segments. For this reason, the SYSTEM tablespace can never be made read only, because it contains the SYSTEM rollback segment. Additionally, because the rollback segments of a read-only tablespace are not accessible, Oracle recommends that you drop the rollback segments before you make a tablespace read only.
The tablespace must not be involved in an open backup, because the end of a backup updates the header file of all datafiles in the tablespace.
Performing this function in restricted mode may help you meet these restrictions, because only users with RESTRICTED SESSION system privilege can be logged on.
Syntax
alter_tablespace::=

(table_compression ::=--part of ALTER TABLE, storage_clause::=, size_clause::=, datafile_tempfile_clauses ::=, tablespace_logging_clauses ::=, tablespace_group_clause::=, tablespace_state_clauses::=, autoextend_clause ::=, flashback_mode_clause ::=, tablespace_retention_clause::=)

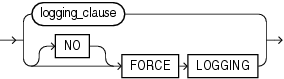
tablespace_logging_clauses ::=
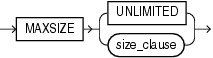
maxsize_clause::=
tablespace_retention_clause::=
Semantics
tablespace
Specify the name of the tablespace to be altered.
Restrictions on Altering Tablespaces Altering tablespaces is subject to the following restrictions:
If tablespace is an undo tablespace, then the only other clauses you can specify in this statement are ADD DATAFILE, RENAME DATAFILE, RENAME TO (renaming the tablespace), DATAFILE ... ONLINE, DATAFILE ... OFFLINE, BEGIN BACKUP, and END BACKUP.
You cannot make the SYSTEM tablespace read only or temporary and you cannot take it offline.
For locally managed temporary tablespaces, the only clause you can specify in this statement is the ADD clause.
|
See Also: Oracle Database Administrator's Guide for information on automatic undo management and undo tablespaces |
DEFAULT storage_clause lets you specify the new default storage parameters for objects subsequently created in the tablespace. For a dictionary-managed temporary table, Oracle Database considers only the NEXT parameter of the storage_clause.
Please refer to the storage_clause for more information.
Restriction on Default Tablespace Storage You cannot specify this clause for a locally managed tablespace.
This clause is valid only for permanent dictionary-managed tablespaces. The MINIMUM EXTENT clause lets you control free space fragmentation in the tablespace by ensuring that every used or free extent in a tablespace is at least as large as, and is a multiple of, the value specified in the size_clause.
Restriction on MINIMUM EXTENT You cannot specify this clause for a locally managed tablespace or for a dictionary-managed temporary tablespace.
|
See Also: size_clause for information about that clause, Oracle Database Administrator's Guide for more information about usingMINIMUM EXTENT to control space fragmentation |
This clause is valid only for bigfile tablespaces. It lets you increase or decrease the size of the single datafile to an absolute size. Use K, M, G, or T to specify the size in kilobytes, megabytes, gigabytes, or terabytes, respectively.
To change the size of a newly added datafile or tempfile in smallfile tablespaces, use the ALTER DATABASE ... autoextend_clause (see database_file_clauses ).
For each datafile in the tablespace, this clause combines all contiguous free extents into larger contiguous extents.
Use this clause to rename tablespace. This clause is valid only if tablespace and all its datafiles are online and the COMPATIBLE parameter is set to 10.0.0 or greater. You can rename both permanent and temporary tablespaces.
If tablespace is read only, then Oracle Database does not update the datafile headers to reflect the new name. The alert log will indicate that the datafile headers have not been updated.
|
Note: If you re-create the control file, and if the datafiles that Oracle Database uses for this purpose are restored backups whose headers reflect the old tablespace name, then the re-created control file will also reflect the old tablespace name. However, after the database is fully recovered, the control file will reflect the new name. |
If tablespace has been designated as the undo tablespace for any instance in a Real Application Clusters environment, and if a server parameter file was used to start up the database, then Oracle Database changes the value of the UNDO_TABLESPACE parameter for that instance in the server parameter file (SPFILE) to reflect the new tablespace name. If a single-instance database is using a parameter file (pfile) instead of an spfile, then the database puts a message in the alert log advising the database administrator to change the value manually in the pfile.
Restriction on Renaming Tablespaces You cannot rename the SYSTEM or SYSAUX tablespaces.
BACKUP Clauses
Use these clauses to move all datafiles in a tablespace into or out of online (sometimes called hot) backup mode.
|
See Also:
|
Specify BEGIN BACKUP to indicate that an open backup is to be performed on the datafiles that make up this tablespace. This clause does not prevent users from accessing the tablespace. You must use this clause before beginning an open backup.
Restrictions on Beginning Tablespace Backup Beginning tablespace backup is subject to the following restrictions:
You cannot specify this clause for a read-only tablespace or for a temporary locally managed tablespace.
While the backup is in progress, you cannot take the tablespace offline normally, shut down the instance, or begin another backup of the tablespace.
Specify END BACKUP to indicate that an online backup of the tablespace is complete. Use this clause as soon as possible after completing an online backup. Otherwise, if an instance failure or SHUTDOWN ABORT occurs, then Oracle Database assumes that media recovery (possibly requiring archived redo log) is necessary at the next instance startup.
Restriction on Ending Tablespace Backup You cannot use this clause on a read-only tablespace.
The tablespace file clauses let you add or modify a datafile or tempfile.
ADD Clause
Specify ADD to add to the tablespace a datafile or tempfile specified by file_specification. Use the datafile_tempfile_spec form of file_specification (see file_specification) to list regular datafiles and tempfiles in an operating system file system or to list Automatic Storage Management disk group files.
For locally managed temporary tablespaces, this is the only clause you can specify at any time.
If you omit file_specification, then Oracle Database creates an Oracle-managed file of 100M with AUTOEXTEND enabled.
You can add a datafile or tempfile to a locally managed tablespace that is online or to a dictionary managed tablespace that is online or offline. Ensure the file is not in use by another database.
Restriction on Adding Datafiles and Tempfiles You cannot specify this clause for a bigfile (single-file) tablespace, as such a tablespace has only one datafile or tempfile.
|
Note: On some operating systems, Oracle does not allocate space for a tempfile until the tempfile blocks are actually accessed. This delay in space allocation results in faster creation and resizing of tempfiles, but it requires that sufficient disk space is available when the tempfiles are later used. To avoid potential problems, before you create or resize a tempfile, ensure that the available disk space exceeds the size of the new tempfile or the increased size of a resized tempfile. The excess space should allow for anticipated increases in disk space use by unrelated operations as well. Then proceed with the creation or resizing operation. |
Specify DROP to drop from the tablespace an empty datafile or tempfile specified by filename or file_number. This clause causes the datafile or tempfile to be removed from the data dictionary and deleted from the operating system. The database must be open at the time this clause is specified.
The ALTER TABLESPACE ... DROP TEMPFILE statement is equivalent to specifying the ALTER DATABASE TEMPFILE ... DROP INCLUDING DATAFILES.
Restrictions on Dropping Files To drop a datafile or tempfile, the datafile or tempfile:
Must be empty.
Cannot be the first file that was created in the tablespace. In such cases, drop the tablespace instead.
Cannot be in a read-only tablespace.
|
See Also:
|
RENAME DATAFILE Clause
Specify RENAME DATAFILE to rename one or more of the tablespace datafiles. The database must be open, and you must take the tablespace offline before renaming it. Each filename must fully specify a datafile using the conventions for filenames on your operating system.
This clause merely associates the tablespace with the new file rather than the old one. This clause does not actually change the name of the operating system file. You must change the name of the file through your operating system.
ONLINE | OFFLINE Clauses
Use these clauses to take all datafiles or tempfiles in the tablespace offline or put them online. These clauses have no effect on the ONLINE or OFFLINE status of the tablespace itself.
The database must be mounted. If tablespace is SYSTEM, or an undo tablespace, or the default temporary tablespace, then the database must not be open.
tablespace_logging_clauses
Use these clauses to set or change the logging characteristics of the tablespace.
Specify LOGGING if you want logging of all tables, indexes, and partitions within the tablespace. The tablespace-level logging attribute can be overridden by logging specifications at the table, index, and partition levels.
When an existing tablespace logging attribute is changed by an ALTER TABLESPACE statement, all tables, indexes, and partitions created after the statement will have the new default logging attribute (which you can still subsequently override). The logging attribute of existing objects is not changed.
If the tablespace is in FORCE LOGGING mode, then you can specify NOLOGGING in this statement to set the default logging mode of the tablespace to NOLOGGING, but this will not take the tablespace out of FORCE LOGGING mode.
Use this clause to put the tablespace in force logging mode or take it out of force logging mode. The database must be open and in READ WRITE mode. Neither of these settings changes the default LOGGING or NOLOGGING mode of the tablespace.
Restriction on Force Logging Mode You cannot specify FORCE LOGGING for an undo or a temporary tablespace.
|
See Also: Oracle Database Administrator's Guide for information on when to useFORCE LOGGING mode and "Changing Tablespace Logging Attributes: Example" |
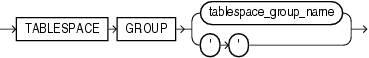
tablespace_group_clause
This clause is valid only for locally managed temporary tablespaces. Use this clause to add tablespace to or remove it from the tablespace_group_name tablespace group.
Specify a group name to indicate that tablespace is a member of this tablespace group. If tablespace_group_name does not already exist, then Oracle Database implicitly creates it when you alter tablespace to be a member of it.
Specify an empty string (' ') to remove tablespace from the tablespace_group_name tablespace group.
Restriction on Tablespace Groups You cannot specify a tablespace group for a permanent tablespace or for a dictionary-managed temporary tablespace.
|
See Also: Oracle Database Administrator's Guide for more information on tablespace groups and "Assigning a Tablespace Group: Example" |
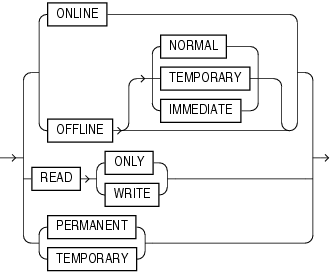
tablespace_state_clauses
Use these clauses to set or change the state of the tablespace.
Specify ONLINE to bring the tablespace online. Specify OFFLINE to take the tablespace offline and prevent further access to its segments. When you take a tablespace offline, all of its datafiles are also offline.
|
Suggestion: Before taking a tablespace offline for a long time, consider changing the tablespace allocation of any users who have been assigned the tablespace as either a default or temporary tablespace. While the tablespace is offline, such users cannot allocate space for objects or sort areas in the tablespace. See ALTER USER for more information on allocating tablespace quota to users. |
Restriction on Taking Tablespaces Offline You cannot take a temporary tablespace offline.
OFFLINE NORMAL Specify NORMAL to flush all blocks in all datafiles in the tablespace out of the system global area (SGA). You need not perform media recovery on this tablespace before bringing it back online. This is the default.
OFFLINE TEMPORARY If you specify TEMPORARY, then Oracle Database performs a checkpoint for all online datafiles in the tablespace but does not ensure that all files can be written. Files that are offline when you issue this statement may require media recovery before you bring the tablespace back online.
OFFLINE IMMEDIATE If you specify IMMEDIATE, then Oracle Database does not ensure that tablespace files are available and does not perform a checkpoint. You must perform media recovery on the tablespace before bringing it back online.
|
Note: TheFOR RECOVER setting for ALTER TABLESPACE ... OFFLINE has been deprecated. The syntax is supported for backward compatibility. However, Oracle recommends that you use the transportable tablespaces feature for tablespace recovery. |
|
See Also: Oracle Database Backup and Recovery Advanced User's Guide for information on using transportable tablespaces to perform media recovery |
Specify READ ONLY to place the tablespace in transition read-only mode. In this state, existing transactions can complete (commit or roll back), but no further DML operations are allowed to the tablespace except for rollback of existing transactions that previously modified blocks in the tablespace. You cannot make the SYSAUX tablespace READ ONLY.
When a tablespace is read only, you can copy its files to read-only media. You must then rename the datafiles in the control file to point to the new location by using the SQL statement ALTER DATABASE ... RENAME.
Specify READ WRITE to indicate that write operations are allowed on a previously read-only tablespace.
Specify PERMANENT to indicate that the tablespace is to be converted from a temporary to a permanent tablespace. A permanent tablespace is one in which permanent database objects can be stored. This is the default when a tablespace is created.
Specify TEMPORARY to indicate that the tablespace is to be converted from a permanent to a temporary tablespace. A temporary tablespace is one in which no permanent database objects can be stored. Objects in a temporary tablespace persist only for the duration of the session.
Restrictions on Temporary Tablespaces Temporary tablespaces are subject to the following restrictions:
You cannot specify TEMPORARY for the SYSAUX tablespace.
If tablespace was not created with a standard block size, then you cannot change it from permanent to temporary.
You cannot specify TEMPORARY for a tablespace in FORCE LOGGING mode.
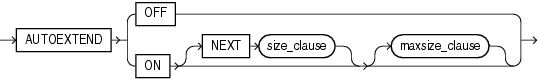
autoextend_clause
This clause is valid only for bigfile (single-file) tablespaces. Use this clause to enable or disable autoextension of the single datafile in the tablespace. To enable or disable autoextension of a newly added datafile or tempfile in smallfile tablespaces, use the autoextend_clause of the database_file_clauses in the ALTER DATABASE statement.
|
See Also:
|
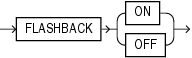
Use this clause to specify whether this tablespace should participate in any subsequent FLASHBACK DATABASE operation.
For you to turn FLASHBACK mode on, the database must be mounted, either open or closed
For you to turn FLASHBACK mode off, the database must be mounted and closed.
This clause is not valid for temporary tablespaces.
Please refer to CREATE TABLESPACE for more complete information on this clause.
|
See Also: Oracle Database Backup and Recovery Advanced User's Guide for more information about Flashback Database |
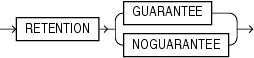
This clause has the same semantics in CREATE TABLESPACE and ALTER TABLESPACE statements. Please refer to tablespace_retention_clause in the documentation on CREATE TABLESPACE.
Examples
Backing Up Tablespaces: Examples The following statement signals to the database that a backup is about to begin:
ALTER TABLESPACE tbs_01
BEGIN BACKUP;
The following statement signals to the database that the backup is finished:
ALTER TABLESPACE tbs_01 END BACKUP;
Moving and Renaming Tablespaces: Example This example moves and renames a datafile associated with the tbs_02 tablespace, created in "Enabling Autoextend for a Tablespace: Example", from diskb:tbs_f5.dat to diska:tbs_f5.dat:
Take the tablespace offline using an ALTER TABLESPACE statement with the OFFLINE clause:
ALTER TABLESPACE tbs_02 OFFLINE NORMAL;
Copy the file from diskb:tbs_f5.dat to diska:tbs_f5.dat using your operating system commands.
Rename the datafile using an ALTER TABLESPACE statement with the RENAME DATAFILE clause:
ALTER TABLESPACE tbs_02 RENAME DATAFILE 'diskb:tbs_f5.dat' TO 'diska:tbs_f5.dat';
Bring the tablespace back online using an ALTER TABLESPACE statement with the ONLINE clause:
ALTER TABLESPACE tbs_02 ONLINE;
Adding and Dropping Datafiles and Tempfiles: Examples The following statement adds a datafile to the tablespace. When more space is needed, new 10-kilobytes extents will be added up to a maximum of 100 kilobytes:
ALTER TABLESPACE tbs_03
ADD DATAFILE 'tbs_f04.dbf'
SIZE 100K
AUTOEXTEND ON
NEXT 10K
MAXSIZE 100K;
The following statement drops the empty datafile:
ALTER TABLESPACE tbs_03
DROP DATAFILE 'tbs_f04.dbf';
The following statements add a tempfile to the temporary tablespace created in "Creating a Temporary Tablespace: Example" and then drops the tempfile:
ALTER TABLESPACE temp_demo ADD TEMPFILE 'temp05.dbf' SIZE 5 AUTOEXTEND ON; ALTER TABLESPACE temp_demo DROP TEMPFILE 'temp05.dbf';
Adding an Oracle-managed Datafile: Example The following example adds an Oracle-managed datafile to the omf_ts1 tablespace (see "Creating Oracle-managed Files: Examples" for the creation of this tablespace). The new datafile is 100M and is autoextensible with unlimited maximum size:
ALTER TABLESPACE omf_ts1 ADD DATAFILE;
Changing Tablespace Logging Attributes: Example The following example changes the default logging attribute of a tablespace to NOLOGGING:
ALTER TABLESPACE tbs_03 NOLOGGING;
Altering a tablespace logging attribute has no affect on the logging attributes of the existing schema objects within the tablespace. The tablespace-level logging attribute can be overridden by logging specifications at the table, index, and partition levels.
Changing Undo Data Retention: Examples The following statement changes the undo data retention for tablespace undots1 to normal undo data behavior:
ALTER TABLESPACE undots1 RETENTION NOGUARANTEE;
The following statement changes the undo data retention for tablespace undots1 to behavior that preserves unexpired undo data:
ALTER TABLESPACE undots1 RETENTION GUARANTEE;