| Oracle® Database SQL Reference 10g Release 2 (10.2) Part Number B14200-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Database SQL Reference 10g Release 2 (10.2) Part Number B14200-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
Purpose
Use the CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW statement to create a materialized view. A materialized view is a database object that contains the results of a query. The FROM clause of the query can name tables, views, and other materialized views. Collectively these objects are called master tables (a replication term) or detail tables (a data warehousing term). This reference uses "master tables" for consistency. The databases containing the master tables are called the master databases.
|
Note: The keywordSNAPSHOT is supported in place of MATERIALIZED VIEW for backward compatibility. |
For replication purposes, materialized views allow you to maintain copies of remote data on your local node. The copies can be updatable with the Advanced Replication feature and are read-only without this feature. You can select data from a materialized view as you would from a table or view. In replication environments, the materialized views commonly created are primary key, rowid, object, and subquery materialized views.
|
See Also: Oracle Database Advanced Replication for information on the types of materialized views used to support replication |
For data warehousing purposes, the materialized views commonly created are materialized aggregate views, single-table materialized aggregate views, and materialized join views. All three types of materialized views can be used by query rewrite, an optimization technique that transforms a user request written in terms of master tables into a semantically equivalent request that includes one or more materialized views.
|
See Also:
|
Additional Topics
Prerequisites
The privileges required to create a materialized view should be granted directly rather than through a role.
To create a materialized view in your own schema:
You must have been granted the CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW system privilege and either the CREATE TABLE or CREATE ANY TABLE system privilege.
You must also have access to any master tables of the materialized view that you do not own, either through a SELECT object privilege on each of the tables or through the SELECT ANY TABLE system privilege.
To create a materialized view in another user's schema:
You must have the CREATE ANY MATERIALIZED VIEW system privilege.
The owner of the materialized view must have the CREATE TABLE system privilege. The owner must also have access to any master tables of the materialized view that the schema owner does not own (for example, if the master tables are on a remote database) and to any materialized view logs defined on those master tables, either through a SELECT object privilege on each of the tables or through the SELECT ANY TABLE system privilege.
To create a refresh-on-commit materialized view (ON COMMIT REFRESH clause), in addition to the preceding privileges, you must have the ON COMMIT REFRESH object privilege on any master tables that you do not own or you must have the ON COMMIT REFRESH system privilege.
To create the materialized view with query rewrite enabled, in addition to the preceding privileges:
If the schema owner does not own the master tables, then the schema owner must have the GLOBAL QUERY REWRITE privilege or the QUERY REWRITE object privilege on each table outside the schema.
If you are defining the materialized view on a prebuilt container (ON PREBUILT TABLE clause), then you must have the SELECT privilege WITH GRANT OPTION on the container table.
The user whose schema contains the materialized view must have sufficient quota in the target tablespace to store the master table and index of the materialized view or must have the UNLIMITED TABLESPACE system privilege.
When you create a materialized view, Oracle Database creates one internal table and at least one index, and may create one view, all in the schema of the materialized view. Oracle Database uses these objects to maintain the materialized view data. You must have the privileges necessary to create these objects.
|
See Also:
|
Syntax
create_materialized_view::=
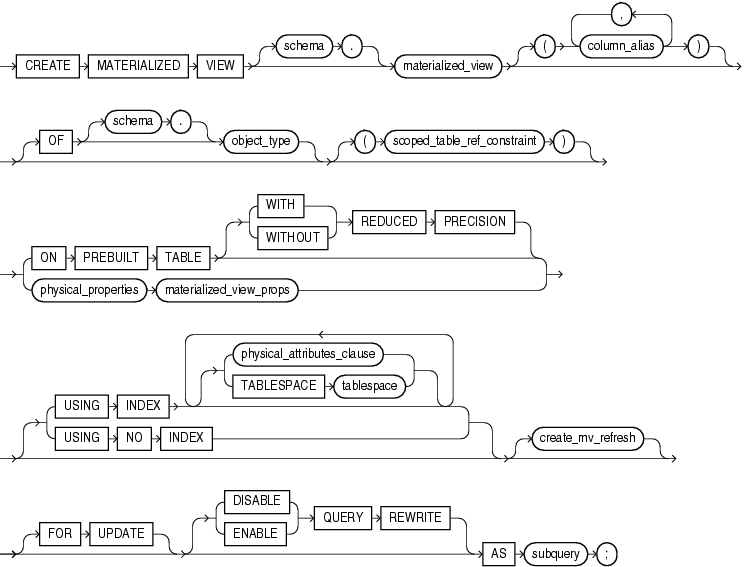
(physical_properties::=, scoped_table_ref_constraint ::=, materialized_view_props::=, physical_attributes_clause::=, create_mv_refresh::=, subquery::=)
physical_properties::=
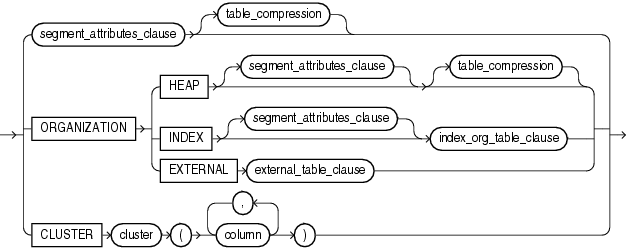
(segment_attributes_clause::=, table_compression ::=, index_org_table_clause::=)

(column_properties ::=, table_partitioning_clauses ::=--part of CREATE TABLE syntax, parallel_clause::=, build_clause::=)
scoped_table_ref_constraint ::=

(mapping_table_clause: not supported with materialized views, key_compression::=, index_org_overflow_clause::=)
key_compression::=
index_org_overflow_clause::=

(segment_attributes_clause::=)

(physical_attributes_clause::=, logging_clause::=)
physical_attributes_clause::=
logging_clause::=



(object_type_col_properties::=, nested_table_col_properties::=, varray_col_properties::=, LOB_partition_storage::=, LOB_storage_clause::=, XMLType_column_properties: not supported for materialized views)

(substitutable_column_clause::=)
substitutable_column_clause::=
nested_table_col_properties::=
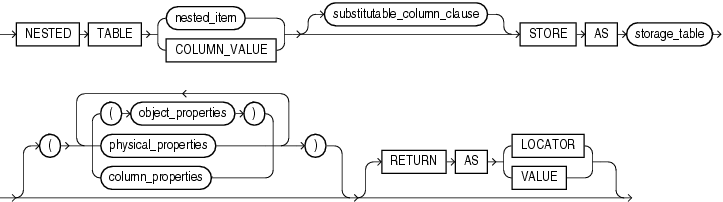
(substitutable_column_clause::=, object_properties::=, physical_properties::=--part of CREATE TABLE syntax, column_properties ::=)
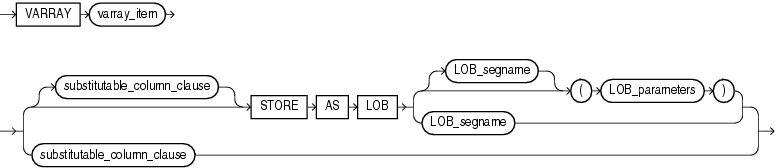
(substitutable_column_clause::=, LOB_parameters::=)

LOB_parameters::=
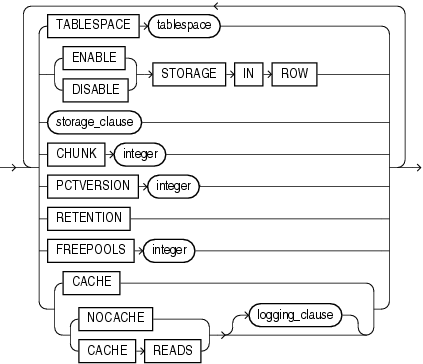
(storage_clause::=, logging_clause::=)
LOB_partition_storage::=
(LOB_storage_clause::=, varray_col_properties::=)

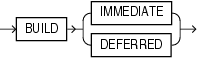
build_clause::=
Semantics
schema
Specify the schema to contain the materialized view. If you omit schema, then Oracle Database creates the materialized view in your schema.
materialized_view
Specify the name of the materialized view to be created. Oracle Database generates names for the table and indexes used to maintain the materialized view by adding a prefix or suffix to the materialized view name.
column_alias
You can specify a column alias for each column of the materialized view. The column alias list explicitly resolves any column name conflict, eliminating the need to specify aliases in the SELECT clause of the materialized view. If you specify any column alias in this clause, you must specify an alias for each data source referenced in the SELECT clause.
The OF object_type clause lets you explicitly create an object materialized view of type object_type.
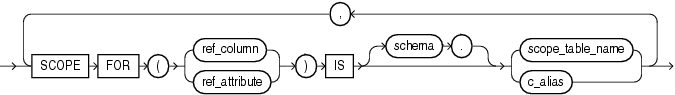
Use the SCOPE FOR clause to restrict the scope of references to a single object table. You can refer either to the table name with scope_table_name or to a column alias. The values in the REF column or attribute point to objects in scope_table_name or c_alias, in which object instances of the same type as the REF column are stored. If you specify aliases, then they must have a one-to-one correspondence with the columns in the SELECT list of the defining query of the materialized view.
The ON PREBUILT TABLE clause lets you register an existing table as a preinitialized materialized view. This clause is particularly useful for registering large materialized views in a data warehousing environment. The table must have the same name and be in the same schema as the resulting materialized view.
If the materialized view is dropped, then the preexisting table reverts to its identity as a table.
|
Caution: This clause assumes that the table object reflects the materialization of a subquery. Oracle strongly recommends that you ensure that this assumption is true in order to ensure that the materialized view correctly reflects the data in its master tables. |
WITH REDUCED PRECISION Specify WITH REDUCED PRECISION to authorize the loss of precision that will result if the precision of the table or materialized view columns do not exactly match the precision returned by subquery.
WITHOUT REDUCED PRECISION Specify WITHOUT REDUCED PRECISION to require that the precision of the table or materialized view columns match exactly the precision returned by subquery, or the create operation will fail. This is the default.
Restrictions on Using Prebuilt Tables Prebuilt tables are subject to the following restrictions:
Each column alias in subquery must correspond to a column in the prebuilt table, and corresponding columns must have matching datatypes.
If you specify this clause, then you cannot specify a NOT NULL constraint for any column that is not referenced in subquery unless you also specify a default value for that column.
physical_properties_clause
The components of the physical_properties_clause have the same semantics for materialized views that they have for tables, with exceptions and additions described in the sections that follow.
Restriction on the physical_properties_clause You cannot specify ORGANIZATION EXTERNAL for a materialized view.
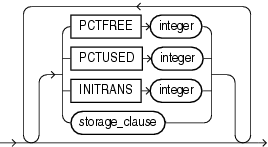
Use the segment_attributes_clause to establish values for the PCTFREE, PCTUSED, and INITRANS parameters, the storage characteristics for the materialized view, to assign a tablespace, and to specify whether logging is to occur. In the USING INDEX clause, you cannot specify PCTFREE or PCTUSED.
TABLESPACE Clause Specify the tablespace in which the materialized view is to be created. If you omit this clause, then Oracle Database creates the materialized view in the default tablespace of the schema containing the materialized view.
|
See Also: physical_attributes_clause and storage_clause for a complete description of these clauses, including default values |
logging_clause Specify LOGGING or NOLOGGING to establish the logging characteristics for the materialized view. The default is the logging characteristic of the tablespace in which the materialized view resides.
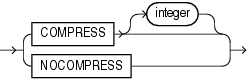
Use the table_compression clause to instruct the database whether to compress data segments to reduce disk and memory use. The COMPRESS keyword enables table compression. The NOCOMPRESS keyword disables table compression.
index_org_table_clause
The ORGANIZATION INDEX clause lets you create an index-organized materialized view. In such a materialized view, data rows are stored in an index defined on the primary key of the materialized view. You can specify index organization for the following types of materialized views:
Read-only and updatable object materialized views. You must ensure that the master table has a primary key.
Read-only and updatable primary key materialized views.
Read-only rowid materialized views.
The keywords and parameters of the index_org_table_clause have the same semantics as described in CREATE TABLE, with the restrictions that follow.
Restrictions on Index-Organized Materialized Views Index-organized materialized views are subject to the following restrictions:
You cannot specify the following CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW clauses: CACHE or NOCACHE, CLUSTER, or ON PREBUILT TABLE.
In the index_org_table_clause:
You cannot specify the mapping_table_clause.
You can specify COMPRESS only for a materialized view based on a composite primary key. You can specify NOCOMPRESS for a materialized view based on either a simple or composite primary key.
CLUSTER Clause
The CLUSTER clause lets you create the materialized view as part of the specified cluster. A cluster materialized view uses the space allocation of the cluster. Therefore, you do not specify physical attributes or the TABLESPACE clause with the CLUSTER clause.
Restriction on Cluster Materialized Views If you specify CLUSTER, then you cannot specify the table_partitioning_clauses in materialized_view_props.
materialized_view_props
Use these property clauses to describe a materialized view that is not based on an existing table. To create a materialized view that is based on an existing table, use the ON PREBUILT TABLE clause.
The column_properties clause lets you specify the storage characteristics of a LOB, nested table, varray, or XMLType column. The object_type_col_properties are not relevant for a materialized view.
The table_partitioning_clauses let you specify that the materialized view is partitioned on specified ranges of values or on a hash function. Partitioning of materialized views is the same as partitioning of tables.
For data that will be accessed frequently, CACHE specifies that the blocks retrieved for this table are placed at the most recently used end of the least recently used (LRU) list in the buffer cache when a full table scan is performed. This attribute is useful for small lookup tables. NOCACHE specifies that the blocks are placed at the least recently used end of the LRU list.
|
Note: NOCACHE has no effect on materialized views for which you specify KEEP in the storage_clause. |
The parallel_clause lets you indicate whether parallel operations will be supported for the materialized view and sets the default degree of parallelism for queries and DML on the materialized view after creation.
For complete information on this clause, please refer to parallel_clause in the documentation on CREATE TABLE.
The build_clause lets you specify when to populate the materialized view.
IMMEDIATE Specify IMMEDIATE to indicate that the materialized view is to be populated immediately. This is the default.
DEFERRED Specify DEFERRED to indicate that the materialized view is to be populated by the next REFRESH operation. The first (deferred) refresh must always be a complete refresh. Until then, the materialized view has a staleness value of UNUSABLE, so it cannot be used for query rewrite.
The USING INDEX clause lets you establish the value of the INITRANS and STORAGE parameters for the default index Oracle Database uses to maintain the materialized view data. If USING INDEX is not specified, then default values are used for the index. Oracle Database uses the default index to speed up incremental (FAST) refresh of the materialized view.
Restriction on USING INDEX clause You cannot specify the PCTUSED parameter in this clause.
Specify USING NO INDEX to suppress the creation of the default index. You can create an alternative index explicitly by using the CREATE INDEX statement. You should create such an index if you specify USING NO INDEX and you are creating the materialized view with the incremental refresh method (REFRESH FAST).
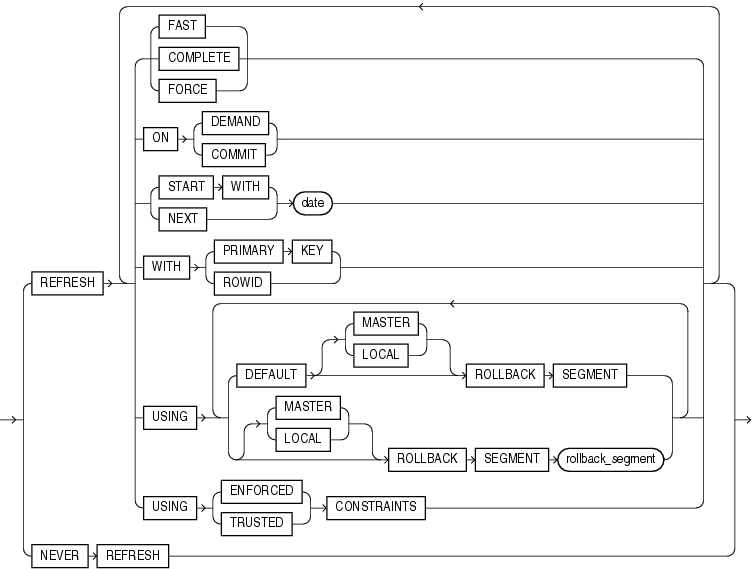
Use the create_mv_refresh clause to specify the default methods, modes, and times for the database to refresh the materialized view. If the master tables of a materialized view are modified, then the data in the materialized view must be updated to make the materialized view accurately reflect the data currently in its master tables. This clause lets you schedule the times and specify the method and mode for the database to refresh the materialized view.
|
Note: This clause only sets the default refresh options. For instructions on actually implementing the refresh, refer to Oracle Database Advanced Replication and Oracle Data Warehousing Guide. |
|
See Also:
|
Specify FAST to indicate the incremental refresh method, which performs the refresh according to the changes that have occurred to the master tables. The changes for conventional DML changes are stored in the materialized view log associated with the master table.The changes for direct-path INSERT operations are stored in the direct loader log.
If you specify REFRESH FAST, then the CREATE statement will fail unless materialized view logs already exist for the materialized view master tables. Oracle Database creates the direct loader log automatically when a direct-path INSERT takes place. No user intervention is needed.
For both conventional DML changes and for direct-path INSERT operations, other conditions may restrict the eligibility of a materialized view for fast refresh.
Materialized views are not eligible for fast refresh if the defining query contains an analytic function.
|
See Also:
|
Specify COMPLETE to indicate the complete refresh method, which is implemented by executing the defining query of the materialized view. If you request a complete refresh, then Oracle Database performs a complete refresh even if a fast refresh is possible.
Specify FORCE to indicate that when a refresh occurs, Oracle Database will perform a fast refresh if one is possible or a complete refresh if fast refresh is not possible. If you do not specify a refresh method (FAST, COMPLETE, or FORCE), then FORCE is the default.
Specify ON COMMIT to indicate that a fast refresh is to occur whenever the database commits a transaction that operates on a master table of the materialized view. This clause may increase the time taken to complete the commit, because the database performs the refresh operation as part of the commit process.
Restrictions on Refreshing ON COMMIT
This clause is not supported for materialized views containing object types.
If you specify this clause, you cannot subsequently execute a distributed transaction on any master table of this materialized view. For example, you cannot insert into the master by selecting from a remote table. The ON DEMAND clause does not impose this restriction on subsequent distributed transactions on master tables.
Specify ON DEMAND to indicate that the materialized view will be refreshed on demand by calling one of the three DBMS_MVIEW refresh procedures. If you omit both ON COMMIT and ON DEMAND, ON DEMAND is the default.
|
See Also:
|
If you specify ON COMMIT or ON DEMAND, then you cannot also specify START WITH or NEXT.
START WITH Clause
Specify a datetime expression for the first automatic refresh time.
NEXT Clause
Specify a datetime expression for calculating the interval between automatic refreshes.
Both the START WITH and NEXT values must evaluate to a time in the future. If you omit the START WITH value, then the database determines the first automatic refresh time by evaluating the NEXT expression with respect to the creation time of the materialized view. If you specify a START WITH value but omit the NEXT value, then the database refreshes the materialized view only once. If you omit both the START WITH and NEXT values, or if you omit the create_mv_refresh entirely, then the database does not automatically refresh the materialized view.
Specify WITH PRIMARY KEY to create a primary key materialized view. This is the default and should be used in all cases except those described for WITH ROWID. Primary key materialized views allow materialized view master tables to be reorganized without affecting the eligibility of the materialized view for fast refresh. The master table must contain an enabled primary key constraint, and the defining query of the materialized view must specify all of the primary key columns directly. That is, in the defining query, the primary key columns cannot be specified as the argument to a function such as UPPER.
Restriction on Primary Key Materialized Views You cannot specify this clause for an object materialized view. Oracle Database implicitly refreshes objects materialized WITH OBJECT ID.
|
See Also: Oracle Database Advanced Replication for detailed information about primary key materialized views and "Creating Primary Key Materialized Views: Example" |
Specify WITH ROWID to create a rowid materialized view. Rowid materialized views are useful if the materialized view does not include all primary key columns of the master tables. Rowid materialized views must be based on a single table and cannot contain any of the following:
Distinct or aggregate functions
GROUP BY or CONNECT BY clauses
Subqueries
Joins
Set operations
Rowid materialized views are not eligible for fast refresh after a master table reorganization until a complete refresh has been performed.
Restriction on Rowid Materialized Views You cannot specify this clause for an object materialized view. Oracle Database implicitly refreshes objects materialized WITH OBJECT ID.
This clause is not valid if your database is in automatic undo mode, because in that mode Oracle Database uses undo tablespaces instead of rollback segments. Oracle strongly recommends that you use automatic undo mode. This clause is supported for backward compatibility with replication environments containing older versions of Oracle Database that still use rollback segments.
For rollback_segment, specify the remote rollback segment to be used during materialized view refresh.
DEFAULT DEFAULT specifies that Oracle Database will choose automatically which rollback segment to use. If you specify DEFAULT, you cannot specify rollback_segment. DEFAULT is most useful when modifying, rather than creating, a materialized view.
MASTER MASTER specifies the remote rollback segment to be used at the remote master site for the individual materialized view.
LOCAL LOCAL specifies the remote rollback segment to be used for the local refresh group that contains the materialized view. This is the default.
|
See Also: Oracle Database Advanced Replication for information on specifying the local materialized view rollback segment using theDBMS_REFRESH package |
If you omit rollback_segment, then the database automatically chooses the rollback segment to be used. One master rollback segment is stored for each materialized view and is validated during materialized view creation and refresh. If the materialized view is complex, then the database ignores any master rollback segment you specify.
The USING ... CONSTRAINTS clause lets Oracle Database choose more rewrite options during the refresh operation, resulting in more efficient refresh execution. The clause lets Oracle Database use unenforced constraints, such as dimension relationships or constraints in the RELY state, rather than relying only on enforced constraints during the refresh operation.
|
Caution: TheUSING TRUSTED CONSTRAINTS clause lets Oracle Database use dimension and constraint information that has been declared trustworthy by the database administrator but that has not been validated by the database. If the dimension and constraint information is valid, then performance may improve. However, if this information is invalid, then the refresh procedure may corrupt the materialized view even though it returns a success status. |
If you omit this clause, then the default is USING ENFORCED CONSTRAINTS.
NEVER REFRESH Clause
Specify NEVER REFRESH to prevent the materialized view from being refreshed with any Oracle Database refresh mechanism or packaged procedure. Oracle Database will ignore any REFRESH statement on the materialized view issued from such a procedure. To reverse this clause, you must issue an ALTER MATERIALIZED VIEW ... REFRESH statement.
Specify FOR UPDATE to allow a subquery, primary key, object, or rowid materialized view to be updated. When used in conjunction with Advanced Replication, these updates will be propagated to the master.
The QUERY REWRITE clause lets you specify whether the materialized view is eligible to be used for query rewrite.
ENABLE Clause Specify ENABLE to enable the materialized view for query rewrite.
Restrictions on Enabling Query Rewrite Enabling of query rewrite is subject to the following restrictions:
You can enable query rewrite only if all user-defined functions in the materialized view are DETERMINISTIC.
You can enable query rewrite only if expressions in the statement are repeatable. For example, you cannot include CURRENT_TIME or USER, sequence values (such as the CURRVAL or NEXTVAL pseudocolumns), or the SAMPLE clause (which may sample different rows as the contents of the materialized view change).
|
Notes:
|
|
See Also:
|
DISABLE Clause Specify DISABLE to indicate that the materialized view is not eligible for use by query rewrite. A disabled materialized view can be refreshed.
Specify the defining query of the materialized view. When you create the materialized view, Oracle Database executes this subquery and places the results in the materialized view. This subquery is any valid SQL subquery. However, not all subqueries are fast refreshable, nor are all subqueries eligible for query rewrite. The length of the subquery is limited to 64K bytes.
Notes on the Defining Query of a Materialized View The following notes apply to materialized views:
Oracle Database does not execute the defining query immediately if you specify BUILD DEFERRED.
Oracle recommends that you qualify each table and view in the FROM clause of the defining query of the materialized view with the schema containing it.
Restrictions on the Defining Query of a Materialized View The materialized view query is subject to the following restrictions:
The defining query of a materialized view can select from tables, views, or materialized views owned by the user SYS, but you cannot enable QUERY REWRITE on such a materialized view.
You cannot define a materialized view with a subquery in the select list of the defining query. You can, however, include subqueries elsewhere in the defining query, such as in the WHERE clause.
Materialized join views and materialized aggregate views with a GROUP BY clause cannot select from an index-organized table.
Materialized views cannot contain columns of datatype LONG.
You cannot create a materialized view log on a temporary table. Therefore, if the defining query references a temporary table, then this materialized view will not be eligible for FAST refresh, nor can you specify the QUERY REWRITE clause in this statement.
If the FROM clause of the defining query references another materialized view, then you must always refresh the materialized view referenced in the defining query before refreshing the materialized view you are creating in this statement.
If you are creating a materialized view enabled for query rewrite, then:
The defining query cannot contain, either directly or through a view, references to ROWNUM, USER, SYSDATE, remote tables, sequences, or PL/SQL functions that write or read database or package state.
Neither the materialized view nor the master tables of the materialized view can be remote.
If you want the materialized view to be eligible for fast refresh using a materialized view log, then some additional restrictions may apply.
|
See Also:
|
The following examples require the materialized logs that are created in the "Examples" section of CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW.
Creating Materialized Aggregate Views: Example The following statement creates and populates a materialized aggregate view on the sample sh.sales table and specifies the default refresh method, mode, and time. It uses the materialized view log created in "Creating a Materialized View Log: Examples", as well as the two additional logs shown here:
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW LOG ON times
WITH ROWID, SEQUENCE (time_id, calendar_year)
INCLUDING NEW VALUES;
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW LOG ON products
WITH ROWID, SEQUENCE (prod_id)
INCLUDING NEW VALUES;
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW sales_mv
BUILD IMMEDIATE
REFRESH FAST ON COMMIT
AS SELECT t.calendar_year, p.prod_id,
SUM(s.amount_sold) AS sum_sales
FROM times t, products p, sales s
WHERE t.time_id = s.time_id AND p.prod_id = s.prod_id
GROUP BY t.calendar_year, p.prod_id;
Creating Materialized Join Views: Example The following statement creates and populates the materialized aggregate view sales_by_month_by_state using tables in the sample sh schema. The materialized view will be populated with data as soon as the statement executes successfully. By default, subsequent refreshes will be accomplished by reexecuting the defining query of the materialized view:
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW sales_by_month_by_state
TABLESPACE example
PARALLEL 4
BUILD IMMEDIATE
REFRESH COMPLETE
ENABLE QUERY REWRITE
AS SELECT t.calendar_month_desc, c.cust_state_province,
SUM(s.amount_sold) AS sum_sales
FROM times t, sales s, customers c
WHERE s.time_id = t.time_id AND s.cust_id = c.cust_id
GROUP BY t.calendar_month_desc, c.cust_state_province;
Creating Prebuilt Materialized Views: Example The following statement creates a materialized aggregate view for the preexisting summary table, sales_sum_table:
CREATE TABLE sales_sum_table
(month VARCHAR2(8), state VARCHAR2(40), sales NUMBER(10,2));
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW sales_sum_table
ON PREBUILT TABLE WITH REDUCED PRECISION
ENABLE QUERY REWRITE
AS SELECT t.calendar_month_desc AS month,
c.cust_state_province AS state,
SUM(s.amount_sold) AS sales
FROM times t, customers c, sales s
WHERE s.time_id = t.time_id AND s.cust_id = c.cust_id
GROUP BY t.calendar_month_desc, c.cust_state_province;
In this example, the materialized view has the same name and also has the same number of columns with the same datatypes as the prebuilt table. The WITH REDUCED PRECISION clause allows for differences between the precision of the materialized view columns and the precision of the values returned by the subquery.
Creating Subquery Materialized Views: Example The following statement creates a subquery materialized view based on the customers and countries tables in the sh schema at the remote database:
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW foreign_customers FOR UPDATE
AS SELECT * FROM sh.customers@remote cu
WHERE EXISTS
(SELECT * FROM sh.countries@remote co
WHERE co.country_id = cu.country_id);
Creating Primary Key Materialized Views: Example The following statement creates the primary key materialized view catalog on the sample table oe.product_information:
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW catalog REFRESH FAST START WITH SYSDATE NEXT SYSDATE + 1/4096 WITH PRIMARY KEY AS SELECT * FROM product_information;
Creating Rowid Materialized Views: Example The following statement creates a rowid materialized view on the sample table oe.orders:
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW order_data REFRESH WITH ROWID AS SELECT * FROM orders;
Periodic Refresh of Materialized Views: Example The following statement creates the primary key materialized view emp_data and populates it with data from the sample table hr.employees:
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW LOG ON employees WITH PRIMARY KEY INCLUDING NEW VALUES; CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW emp_data PCTFREE 5 PCTUSED 60 TABLESPACE example STORAGE (INITIAL 50K NEXT 50K) REFRESH FAST NEXT sysdate + 7 AS SELECT * FROM employees;
The statement does not include a START WITH parameter, so Oracle Database determines the first automatic refresh time by evaluating the NEXT value using the current SYSDATE. A materialized view log was created for the employee table, so Oracle Database performs a fast refresh of the materialized view every 7 days, beginning 7 days after the materialized view is created.
Because the materialized view conforms to the conditions for fast refresh, the database will perform a fast refresh. The preceding statement also establishes storage characteristics that the database uses to maintain the materialized view.
Automatic Refresh Times for Materialized Views: Example The following statement creates the complex materialized view all_customers that queries the employee tables on the remote and local databases:
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW all_customers
PCTFREE 5 PCTUSED 60
TABLESPACE example
STORAGE (INITIAL 50K NEXT 50K)
USING INDEX STORAGE (INITIAL 25K NEXT 25K)
REFRESH START WITH ROUND(SYSDATE + 1) + 11/24
NEXT NEXT_DAY(TRUNC(SYSDATE), 'MONDAY') + 15/24
AS SELECT * FROM sh.customers@remote
UNION
SELECT * FROM sh.customers@local;
Oracle Database automatically refreshes this materialized view tomorrow at 11:00 a.m. and subsequently every Monday at 3:00 p.m. The default refresh method is FORCE. The defining query contains a UNION operator, which is not supported for fast refresh, so the database will automatically perform a complete refresh.
The preceding statement also establishes storage characteristics for both the materialized view and the index that the database uses to maintain it:
The first STORAGE clause establishes the sizes of the first and second extents of the materialized view as 50 kilobytes each.
The second STORAGE clause, appearing with the USING INDEX clause, establishes the sizes of the first and second extents of the index as 25 kilobytes each.
Creating a Fast Refreshable Materialized View: Example The following statement creates a fast-refreshable materialized view that selects columns from the order_items table in the sample oe schema, using the UNION set operator to restrict the rows returned from the product_information and inventories tables using WHERE conditions. The materialized view logs for order_items and product_information were created in the "Examples" section of CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW LOG. This example also requires a materialized view log on oe.inventories.
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW LOG ON inventories
WITH (quantity_on_hand);
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW warranty_orders REFRESH FAST AS
SELECT order_id, line_item_id, product_id FROM order_items o
WHERE EXISTS
(SELECT * FROM inventories i WHERE o.product_id = i.product_id
AND i.quantity_on_hand IS NOT NULL)
UNION
SELECT order_id, line_item_id, product_id FROM order_items
WHERE quantity > 5;
This materialized view requires that materialized view logs be defined on order_items (with product_id as a join column) and on inventories (with quantity_on_hand as a filter column). See "Specifying Filter Columns for Materialized View Logs: Example" and "Specifying Join Columns for Materialized View Logs: Example".
Creating a Nested Materialized View: Example The following example uses the materialized view from the preceding example as a master table to create a materialized view tailored for a particular sales representative in the sample oe schema:
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW my_warranty_orders AS SELECT w.order_id, w.line_item_id, o.order_date FROM warranty_orders w, orders o WHERE o.order_id = o.order_id AND o.sales_rep_id = 165;