Release 2 (9.2)
Part Number A96621-01
Home |
Book List |
Contents |
Index |
 Master Index |
 Feedback |
| Oracle9i XML Developer's Kits Guide - XDK Release 2 (9.2) Part Number A96621-01 |
|
This chapter contains the following sections:
XDK for Java contains the basic building blocks for reading, manipulating, transforming and viewing XML documents.
Oracle XDK for Java consists of the following components:
.xsd).XDK for Java comes with the Oracle database and with the application server. Or, you can download the latest beta or production version of XDK for Java from OTN.
If you installed XDK with Oracle database or iAS, you can skip the following steps and change into the XDK home directory ($XDK_HOME).
If you need to download the XDK from OTN, follow these steps:
Go to the URL:
http://otn.oracle.com/tech/xml/xdk_java/content.html
Click on the `Software' icon at the left side of the page.
Oracle XML Developer's Kit for Java on Sun SolarisTM Operating Environment- 9i Download the Complete File xdk_java_9_0_1_1_0A.tar.gz Directions Install GNU gzip. Download the Oracle XDK for Java in .tar format Extract the distribution package into a directory. (Ex: #gzip -dc xdk_java.tar | tar xvf -) The result should be the following files and directories: /bin - xdk executables and utilities /lib - directory for libraries /xdk - top xdk directory /xdk/demo - directory for demo files /xdk/doc - directory for documentation /xdk/admin - direcory for dband config files /xdk/*html. - doc navigation files /xdk/license.html - copy of license agreement
C:\ on NT), change the directory to C:\ then extract the files using the WinZip visual tool.After installing the XDK, the directory structure is:
-$XDK_HOME | - bin: executable files and setup script/batch files. | - lib: library files. | - xdk: | - admin: (Administration): XSU PL/SQL API setup SQL script and XSL Servlet Configuration file(XSQLConfig.xml). | - demo: demonstration code | - doc: documents including release notes and javadocs.
All the packages in XDK for Java are certified and supported with JDK 1.2 or JDK 1.1.8, so make sure that your CLASSPATH includes all the necessary libraries:
In addition, XML SQL Utility, XSQL Servlet and TransX Utility all depend on JDBC, which is listed in the following table:
| Component | Library | Notes |
|---|---|---|
|
JDBC |
classes111.zip |
JDBC for JDK 1.1.8 |
|
Globalization |
nls_charset111.jar |
Globalization support for JDK 1.2 and above Globalization support for JDK 1.1.8 |
These files will set up the environment:
UNIX: $XDK_HOME/bin/env.csh
NT: $XDK_HOME/bin/env.bat
The following tables list the environment variables, with the ones that must be customized marked with "Y":
The following table shows the UNIX environment variables (the ones that must be customized are marked with "Y"):
XSU installation is discussed in "Installation of XDK for PL/SQL".
The XSQL Servlet is designed to run on any Java VM, using any JDBC driver, against any database. In practice, we are able to test it against only the most popular configurations; we document the supported configurations that have been tested in the Oracle labs.
XSQL Pages and XSQL Servlet have been successfully tested only with:
These are the only three JDK versions that we know work correctly.
This XSQL Servlet has been tested with the following servlet engines:
JavaServer Pages can use <jsp:forward> and/or <jsp:include> to collaborate with XSQL Pages as part of an application. The following JSP platforms have been tested:
In general, it should work with any servlet engine supporting the Servlet 2.1 Specification or higher, and the Oracle JSP 1.0 reference implementation or functional equivalent from another vendor.
The Oracle XSQL Page processor has been designed to exploit the maximum set of features against the Oracle JDBC drivers, but gracefully works against any database with a reasonable JDBC driver. While numerous users have reported successfully using XSQL Pages with many other JDBC drivers, the ones that we have tested in-house are:
The demos are set up to use the SCOTT schema on a database on your local machine (the machine where the web server is running). If you are running a local database and have a SCOTT account whose password is TIGER, then you are all set. Otherwise, you need to edit the .\xdk\admin\XSQLConfig.xml file to correspond to your appropriate values for username, password, dburl, and driver values for the connection named demo:
<?xml version="1.0" ?> <XSQLConfig> : <connectiondefs> <connection name="demo"> <username>scott</username> <password>tiger</password> <dburl>jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:ORCL</dburl> <driver>oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver</driver> </connection> <connection name="lite"> <username>system</username> <password>manager</password> <dburl>jdbc:Polite:POlite</dburl> <driver>oracle.lite.poljdbc.POLJDBCDriver</driver> </connection> </connectiondefs> : </XSQLConfig>
UNIX users and any user wanting to install the XSQL Servlet on other Web servers should continue with the instructions below depending on the Web server you're trying to use. In every case, there are these basic steps:
xsu12.jar - Oracle XML SQL Utilityxmlparserv2.jar - Oracle XML Parser for Java V2oraclexsql.jar- Oracle XSQL Pagesxsqlserializers.jar - Oracle XSQL Serializers for FOP/PDF Integrationclasses12.jar - Oracle JDBC Driver or the JAR file for the JDBC driver you will be using instead./xdk/admin) in the server CLASSPATH..xsql file extension to the oracle.xml.xsql.XSQLServlet servlet class./xsql to the directory where you extracted the XSQL files (to access the online help and demos).Oracle IAS release 1.0 and higher comes preconfigured to run XSQL Servlet. By default its Apache JServ servlet engine contains all of the wrapper.classpath entries in jserv.conf to include the necessary Java archives to run XSQL. The XSQLConfig.xml file is found in the ./xdk/admin subdirectory of the IAS installation home.
The easiest way to install XSQL Servlet in the Oracle9iAS OC4J servlet container is to install it as a global application. Assuming your OC4J installation home is C:\j2ee\home, and that you've extracted the XDK distribution into the C:\xdk902 directory, here are the setup steps:
C:\j2ee\home\lib directory (they should come pre-installed):
C:\xdk902\lib to C:\j2ee\home\lib.
C:\xdk\admin\XSQLConfig.xml configuration file to the C:\j2ee\home\default-web-app\WEB-INF\classes directory.C:\j2ee\home\config\global-web-application.xml server configuration file to add a <servlet> and <servlet-mapping> entry as child elements of the <web-app> element as follows:
<orion-web-app ...and so on... > : etc : <web-app> <servlet> <servlet-name>xsql</servlet-name> <servlet-class>oracle.xml.xsql.XSQLServlet</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>xsql</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/*.xsql</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> : etc : </web-app> </web-app>
At this point, you can refer to any XSQL page in any virtual path and it will be processed by the XSQL Servlet. If you want to try the XSQL built-in samples, demos, and online help, then you need to perform the following additional step to map a virtual path of /xsql/ to the C:\xdk\demo\java\xsql directory.
Edit the file:
c:\j2ee\home\application-deployments\default\defaultWebApp\orion-web.xml
to add the following <virtual-directory> entry:
<orion-web-app ...and so on...> : etc : <virtual-directory virtual-path="/xsql" real-path="/c:/xdk/xdk/demo/java/xsql/" /> : etc : </orion-web-app>
Then, you can browse the demos using the URL:
http://yoursever:yourport/xsql/index.html
Setup the server CLASSPATH correctly for the XSQL Servlet. This is done by editing the JServ configuration file named jserv.properties. Assuming you installed the XSQL Servlet files into C:\, you need to add the following entries to use the Oracle JDBC 1.x Driver:
# Oracle XML SQL Utility (XSU) wrapper.classpath=C:\xdk902\lib\xsu111.jar # Oracle XSQL Servlet wrapper.classpath=C:\xdk902\lib\oraclexsql.jar # Oracle JDBC (8.1.6) -- JDBC 1.x driver wrapper.classpath=directory_where_JDBC_Driver_resides\classes111.zip # Oracle XML Parser V2 (with XSLT Engine) wrapper.classpath=C:\xdk902\lib\xmlparserv2.jar # XSQLConfig.xml File location wrapper.classpath=directory_where_XSQLConfig.xml_resides # FOR Apache FOP Generation, Add # wrapper.classpath=C:\xdk902\lib\xsqlserializers.jar # wrapper.classpath=FOPHOME/fop.jar # wrapper.classpath=FOPHOME/lib/batik.jar
To use the Oracle JDBC 2.0 Driver, the list looks like:
# Oracle XML SQL Utility (XSU) wrapper.classpath=C:\xdk902\lib\xsu12.jar # Oracle XSQL Servlet wrapper.classpath=C:\xdk902\lib\oraclexsql.jar # Oracle JDBC (8.1.6) -- JDBC 2.0 driver wrapper.classpath=directory_where_JDBC_Driver_resides\classes12.zip # Oracle XML Parser V2 (with XSLT Engine) wrapper.classpath=C:\xdk902\lib\xmlparserv2.jar # XSQLConfig.xml File location wrapper.classpath=directory_where_XSQLConfig.xml_resides # FOR Apache FOP Generation, Add # wrapper.classpath=C:\xdk902\lib\xsqlserializers.jar # wrapper.classpath=FOPHOME/fop.jar # wrapper.classpath=FOPHOME/lib/w3c.jar
To do this, you need to edit the JServ configuration file named jserv.conf (in JServ 1.0 this was named mod_jserv.conf on some platforms). Add the following lines:
# Executes a servlet passing filename with proper extension in PATH_TRANSLATED # property of servlet request. # Syntax: ApJServAction [extension] [servlet-uri] # Defaults: NONE ApJServAction .xsql /servlets/oracle.xml.xsql.XSQLServlet
In this step, we want to map the virtual path \xsql\ to C:\xdk902\xdk\demo\java\xsql\ (or wherever you installed the XSQL Servlet files). To do this, you need to edit the Apache configuration file named httpd.conf and add the following line:
Alias /xsql/ "C:\xdk902\xdk\demo\java\xsql\"
Restart the Apache server and browse the URL:
http://localhost/xsql/index.html
This is done by editing the Tomcat startup script named tomcat.bat in ./jakarta-tomcat/bin and adding five lines to append the appropriate entries onto the system CLASSPATH before the Tomcat server is started as shown below:
For Oracle JDBC 1.x Driver:
rem Set up the CLASSPATH that we need set cp=%CLASSPATH% set CLASSPATH=. set CLASSPATH=%TOMCAT_HOME%\classes set CLASSPATH=%CLASSPATH%;%TOMCAT_HOME%\lib\webserver.jar set CLASSPATH=%CLASSPATH%;%TOMCAT_HOME%\lib\jasper.jar set CLASSPATH=%CLASSPATH%;%TOMCAT_HOME%\lib\xml.jar set CLASSPATH=%CLASSPATH%;%TOMCAT_HOME%\lib\servlet.jar set CLASSPATH=%CLASSPATH%;%JAVA_HOME%\lib\tools.jar REM Added for Oracle XSQL Servlet REM ----------------------------- set CLASSPATH=%CLASSPATH%;C:\xdk902\lib\xsu111.jar set CLASSPATH=%CLASSPATH%;C:\xdk902\lib\oraclexsql.jar set CLASSPATH=%CLASSPATH%;C:\xdk902\lib\xmlparserv2.jar set CLASSPATH=%CLASSPATH%;directory_where_JDBC_Driver_resides\classes111.zip set CLASSPATH=%CLASSPATH%;directory_where_XSQLConfig.xml_resides REM FOR Apache FOP Generation, Add REM set CLASSPATH=%CLASSPATH%;C:\xdk902\lib\xsqlserializers.jar REM set CLASSPATH=%CLASSPATH%;FOPHOME/fop.jar REM set CLASSPATH=%CLASSPATH%;FOPHOME/lib/batik.jar
For Oracle JDBC 2.0 Driver:
rem Set up the CLASSPATH that we need set cp=%CLASSPATH% set CLASSPATH=. set CLASSPATH=%TOMCAT_HOME%\classes set CLASSPATH=%CLASSPATH%;%TOMCAT_HOME%\lib\webserver.jar set CLASSPATH=%CLASSPATH%;%TOMCAT_HOME%\lib\jasper.jar set CLASSPATH=%CLASSPATH%;%TOMCAT_HOME%\lib\xml.jar set CLASSPATH=%CLASSPATH%;%TOMCAT_HOME%\lib\servlet.jar set CLASSPATH=%CLASSPATH%;%JAVA_HOME%\lib\tools.jar REM Added for Oracle XSQL Servlet REM ----------------------------- set CLASSPATH=%CLASSPATH%;C:\xdk902\lib\xsu12.jar set CLASSPATH=%CLASSPATH%;C:\xdk902\lib\oraclexsql.jar set CLASSPATH=%CLASSPATH%;C:\xdk902\lib\xmlparserv2.jar set CLASSPATH=%CLASSPATH%;directory_where_JDBC_Driver_resides\classes12.zip set CLASSPATH=%CLASSPATH%;directory_where_XSQLConfig.xml_resides REM FOR Apache FOP Generation, Add REM set CLASSPATH=%CLASSPATH%;C:\xdk902\lib\xsqlserializers.jar REM set CLASSPATH=%CLASSPATH%;FOPHOME/fop.jar REM set CLASSPATH=%CLASSPATH%;FOPHOME/lib/batik.jar
Tomcat supports creating any number of configuration contexts to better organize the web applications your site needs to support. Each context is mapped to a virtual directory path, and has its own separate servlet configuration information. XSQL Servlet comes with a preconfigured context file to make XSQL Servlet setup easier.
By default, Tomcat 3.1 and 3.2 come preconfigured with the following contexts (defined by <Context> entries in the ./jakarta-tomcat/conf/server.xml file).
We could install XSQL Servlet into one of these, but for simplicity we'll create a new context just for the XSQL Servlet that maps to the directory where you installed the XSQL Servlet distribution.
Edit the ./jakarta-tomcat/conf/server.xml file to add the following <Context> entry with path= "/xsql".
<Context path="/test" docBase="webapps/test" debug="0" reloadable="true" /> <!-- | Define a Servlet context for the XSQL Servlet | | The XSQL Servlet ships with a .\WEB-INF directory | with its web.xml file preconfigured for C:\xdk902\xdk\demo\java\xsql | installation. +--> <Context path="/xsql" docBase="C:\xdk902\xdk\demo\java\xsql"/>
Note that the docBase= "C:\xsql" points to the physical directory where you installed the XSQL Servlet distribution. You then need to create a WEB-INF subdirectory in the C:\xdk902\xdk\demo\java\xsql directory and save the following ./WEB-INF/web.xml file in it:
<?xml version = '1.0' encoding = 'UTF-8'?> <!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC "-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.2//EN" "http://java.sun.com/j2ee/dtds/web-app_2_2.dtd"> <web-app> <servlet> <servlet-name>oracle-xsql-servlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>oracle.xml.xsql.XSQLServlet</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>oracle-xsql-servlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern> *.xsql </url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
|
Note: To add the XSQL Servlet to an existing context, add the servlet and servlet-mapping entries that you find in the |
This is already achieved by creating the /xsql context preceding.
Restart the Tomcat server and browse the URL:
http://localhost:8080/xsql/index.html
If you use Tomcat with an XML Parser (such as the Sun Crimson Parser) that only supports DOM Level 1 interfaces, then you must edit tomcat.bat to insure that the Oracle XML Parser's archive xmlparser.jar comes before the DOM Level 1 parser's archive in the CLASSPATH. For example, you could edit tomcat.bat to add the following lines:
REM NEED TO PUT xmlparserv2.jar FIRST before parser.jar set CP=C:\xdk902\lib\xmlparserv2.jar;%CP%
just before the lines:
echo Using CLASSPATH: %CP% echo. set CLASSPATH=%CP%
Here is a summary on the setting that related to Globalization Support.
xmlmesg.jar: If you are using the language other than English you would need to set the xmlmesg.jar into your CLASSPATH to let the parser get correct messages in your language.nls_charset12.jar: If you are using a multibyte character set other than one of the following,
then you must set this JAR file into your Java CLASSPATH so that JDBC can convert the character set of the input file to the database character set during the loading of XML files using either XSU, TransX or XSQL Servlet.
The following figure shows the dependencies of XDK when using JDK 1.2 and higher:
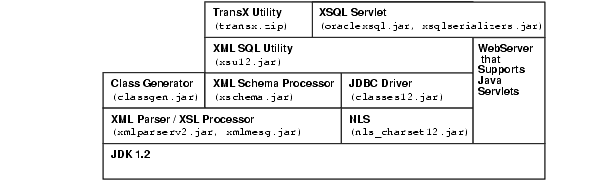
After you correctly setup the environment, include all the necessary JAR files in your CLASSPATH. You can then start writing your Java programs and compiling them with the javac command:
javac your_program.java
If the compilation finishes without errors, then you can just test your program using the command line or the Web Server.
| See Also:
Chapter 4, "XML Parser for Java" for further discussion of the XDK for Java components |
The XDK for JavaBeans permit easily adding visual or non-visual interfaces to XML applications. The bean encapsulation includes documentation and descriptors that can be accessed directly from Java Integrated Development Environments like JDeveloper.
Oracle XDK for JavaBeans consists of the following components:
XMLType.XDK for JavaBeans comes with Oracle Database or iAS application server. You can also download the latest versions of XDK for JavaBeans from OTN.
If you installed XDK with Oracle Database or iAS application server, you can skip the following steps and direct to refer to the XDK home directory (we will refer to this directory as $XDK_HOME).
If you need to download the XDK from OTN, follow these steps:
Use this URL in your browser:
http://otn.oracle.com/tech/xml/xdk_jbeans/index.html
Click on the Software icon at the left-hand side of the page.
Oracle XML Developer's Kit for Java on Sun SolarisTM Operating Environment- 9i Download the Complete File xdk_java_9_0_2_0_0C.tar.gz Directions Install GNU gzip. Download the Oracle XDK for JavaBeans in .tar format Extract the distribution package into a directory. (Ex: #gzip -dc xdk_java.tar | tar xvf -) The result should be the following files and directories: /bin - xdk executables and utilities /lib - directory for libraries /xdk - top xdk directory /xdk/demo - directory for demo files /xdk/doc - directory for documentation /xdk/admin - direcory for dband config files /xdk/*html - doc navigation files /xdk/license.html - copy of license agreement
\C: on NT), change the directory to \C: then extract the files using the WinZip visual tool.After installing the XDK, the directory structure is:
-$XDK_HOME | - bin: executable files and setup script/batch files. | - lib: library files. | - xdk | - admin (Administration): XSU PL/SQL API setup SQL script and XSL Servlet Configuration file (XSQLConfig.xml). | - demo: demonstration code | - doc: documents including release notes and javadocs.
All the packages in XDK for JavaBeans are certified and supported with JDK 1.2 or 1.1.8, so make sure that your CLASSPATH includes all the necessary libraries.
For JDK versions lower that JDK 1.2, you will need to include the JDK library in your CLASSPATH, as well as the Swing library, swingall.jar at "Java Foundation Classes (JFC)/Swing 1.0.3" in page
http://java.sun.com/products/archive/index.html
The following table lists the libraries of XDK for JavaBeans:
In addition, XML SQL Utility, XSQL Servlet and TransX Utility all depend on other components, whose libraries are listed in the following table:
Use this script file provided on UNIX:
$XDK_HOME/bin/env.csh
For Windows, use this provided batch file:
%XDK_HOME/bin/env.bat
The following tables list the environment variables needed during XDK setup. Variables that must be customized before running the script or batch file are marked as "Y" in the column "Customize".
For Windows NT see the following table for the settings:
Here is a summary of the settings that are related to Globalization Support.
xmlmesg.jar into your Java CLASSPATH to let the parser obtain the correct messages in your language.then set nls_charset12.jar into your Java CLASSPATH so that JDBC can convert the character set of the input file to the database character set during loading of XML files.
| See Also:
Chapter 10, "XDK JavaBeans" for further discussion of the XDK for JavaBeans components |
|
 Copyright © 2001, 2002 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|