| Oracle9i Net Services Administrator's Guide Release 2 (9.2) Part Number A96580-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle9i Net Services Administrator's Guide Release 2 (9.2) Part Number A96580-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
This chapter describes how to configure Oracle Connection Manager features.
This chapter contains these topics:
See Also:
|
Oracle Connection Manager is a proxy server, an intermediate server that forwards connection requests to the database server or to other proxy servers. It has three primary functions:
Session multiplexing--You can quickly configure Oracle Connection Manager to funnel multiple client sessions through a network connection to a shared server destination.
Access control--You can use rule-based configuration to filter out certain client requests and accept others.
Protocol conversion--Oracle Connection Manager accepts connection requests in any protocol that Oracle supports.
Configuring Oracle Connection Manager is a three-part process:
cman.ora file on the Oracle Connection Manager computer. This file specifies listening endpoints for the server, the route path for Oracle Connection Manager, access control rules, and Oracle Connection Manager performance parameters.This section contains these topics:
|
Note: Oracle Net Manager does not support configuration of the |
To configure the Oracle Connection Manager computer, you can define four types of parameters in the cman.ora file:
The cman.ora file is located in the $ORACLE_HOME/network/admin directory on UNIX and in the ORACLE_HOME\network\admin directory on Windows NT. Figure 13-1 shows an example cman.ora file.
CMAN=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcp)(HOST=proxysvr)(PORT=1630))(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcps)(HOST=144.25.22.217)(PORT=2484))CMAN_ADMIN=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcp)(HOST=proxysvr)(PORT=1830))CMAN_RULES=(RULE=(SRC=206.62.226.32/27)(DST=sales-server)(SRV=*)(ACT=accept)))CMAN_PROFILE=(PARAMETER_LIST=(LOG_LEVEL=2)(TRACING=on))
The listening endpoint list specifies protocol addresses for the gateway and administrative processes. The gateway process, CMGW, uses the CMAN parameter and the administrative process, CMADMIN, uses the CMAN_ADMIN parameter.
Both processes can be configured with multiple protocol addresses. In Figure 13-1, the CMGW process has two protocol addresses. The first address shown is the default listening protocol address of TCP/IP, port 1630:
(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcp)(HOST=proxysvr)(PORT=1630))
The second is the protocol address of Oracle Connection Manager if TCP/IP with Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) is used:
(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcps)(HOST=144.25.22.217)(PORT=2484))
The access control rule list specifies which connections are accepted, rejected, or dropped.
(RULE=(SRC=206.62.226.32/27)(DST=sales-server)(SRV=*)(ACT=accept)
In the previous example, src=206.62.226.32/27 designates the IP address of the client, or source. DST=sales-server designates the destination host name. The abbreviation ACT stands for "action"--that is, accept, reject, or drop.
|
Note: Enter at least one rule; otherwise the default option "reject" is overridden and all connections are accepted. |
The parameter list set attributes for an Oracle Connection Manager.
| See Also:
Oracle9i Net Services Reference Guide for a complete list of parameters and their default and allowed values |
To route clients to the database server through Oracle Connection Manager, configure either the tnsnames.ora file or the directory server with a connect descriptor that specifies protocol addresses of Oracle Connection Manager and the listener. Take note of the following:
USE_CMAN=true must be set in the sqlnet.ora file on computers where each Oracle Names server resides. To set this parameter, follow the procedure in "Routing Connection Requests".tnsnames.ora file or a directory, the protocol addresses and the SOURCE_ROUTE parameter must be set. To configure the local or directory naming methods for Oracle Connection Manager, perform these tasks:
"Task 1: Configure an Oracle Connection Manager Protocol Address"
To configure a protocol address for Oracle Connection Manager:
The Welcome page of the Net Service Name Wizard appears.
The Protocol page appears.
The Protocol Settings page appears.
| See Also:
Oracle9i Net Services Reference Guide for protocol parameter settings |
The Service page appears.
If the destination service is and Oracle9i or Oracle8i database, select Oracle8i or later, and enter a service name in the Service Name field. If destination service is an Oracle release 8.0 database, select Oracle8 or Previous, and enter an Oracle System Identifier (SID) for an instance in the Database SID field.
| See Also:
"About Connect Descriptors" for further information about setting the service name string |
The new net service name and the Oracle Connection Manager protocol address is added to the Service Naming folder.
After the Oracle Connection Manager protocol address is specified, create an address for the listener, so that the Oracle Connection Manager can connect to the server.
To configure the protocol address for the listener:
Notice that the Oracle Connection Manager protocol address is displayed in the Address 1 tab:
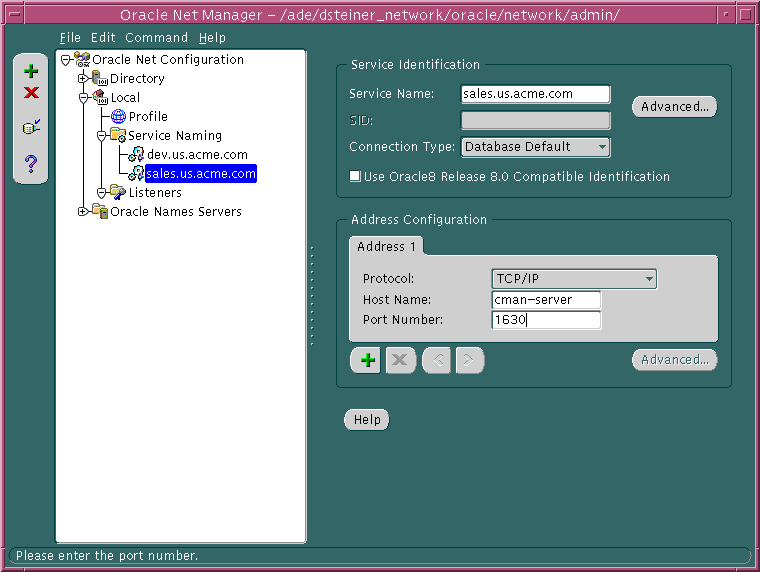
A new Address tab displays.
Text description of the illustration cman2.gif
| See Also:
Oracle9i Net Services Reference Guide for further information about protocol addresses and parameters |
The Address List Options dialog box appears:
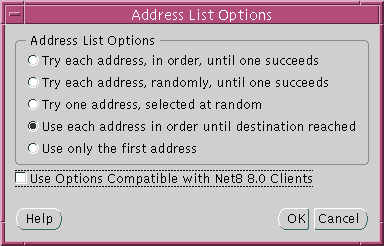
This option sets SOURCE_ROUTE=on. It tells the client to connect to the first protocol address, the Oracle Connection Manager, and from the first protocol address to the second protocol address, the listener.
|
Note: If you specify the addresses of two or more Oracle Connection Managers in the connect descriptor, you can manually include parameters for load balancing and connect-time failover. See the Oracle9i Net Services Reference Guide for examples of how to configure multiple listeners for load balancing and failover. |
Figure 13-2 shows a comparison of a typical tnsnames.ora file and a tnsnames.ora file with an entry to use Oracle Connection Manager. Oracle Connection Manager entries are shown in boldface text.
Figure 13-3 depicts a client using TCP/IP to connect to Oracle Connection Manager, and Oracle Connection Manager using TCP/IP with SSL to connect to a database server.
sales= (DESCRIPTION= (SOURCE_ROUTE=yes) (ADDRESS= (PROTOCOL=tcp) (HOST=cman-server) (PORT=1521)) (ADDRESS= (PROTOCOL=tcps) (HOST=sales-server) (PORT=1521)) (CONNECT_DATA= (SERVICE_NAME=sales.com)))
Configuring the database server involves optionally configuring the server for session multiplexing.
To enable Connection Manager to take advantage of session multiplexing, set the DISPATCHERS parameter in the initialization parameter file with the attributes PROTOCOL and MULTIPLEX.
DISPATCHERS="(PROTOCOL=tcp)(MULTIPLEX=on)"
See Also:
|
This section contains these topics:
The first feature is enabled using the parameter DISPATCHERS in the initialization parameter file, the second and third using the parameters RULE_LIST and CMAN parameters in the cman.ora file.
Once the attributes PROTOCOL and MULTIPLEX have been added to the parameter DISPATCHERS in the initialization parameter file, enabling session multiplexing is simply a matter of ensuring that MULTIPLEX is set to on or to an equivalent value.
You can set different levels of multiplexing, as Table 13-1 shows.
|
Note: You can configure the |
Oracle Connection Manager includes a feature that enables you to control client access to designated database servers in a TCP/IP environment. By specifying certain filtering rules, you can allow or restrict specific clients access to a database server.
To configure access control:
cman.ora file, if one does not already exist.CMAN_RULES with the following subparameters:
(CMAN_RULES= (RULE_LIST= (RULE=(SRC=source_host) (DST=destination_host) (SRV=service) (ACT=accept | reject | drop))))
| See Also:
Oracle9i Net Services Reference Guide for default values and allowed values of Oracle Connection Manager parameters |
You can define multiple rules in the RULE_LIST. The action (ACT) in the first matched RULE is applied to the connection request. If no rules are defined, all connections are accepted.
In the following example, client computer client1-pc is denied access to the service sales.us.acme.com, but client 144.25.23.45 is granted access to the service db1.
(RULE_LIST= (RULE=(SRC=client1-pc)(DST=sales-server)(SRV=sales.us.acme.com)(ACT=reject)) (RULE=(SRC=144.25.23.45)(DST=144.25.187.200)(SRV=db1)(ACT=accept)))
Oracle Connection Manager provides support for protocol conversion, enabling clients and a database server configured with different network protocols to communicate with each other. An Oracle Connection Manager can listen on any protocol that Oracle supports.
Without this kind of support, a client that uses Named Pipes cannot connect to a database server that uses TCP/IP. If Oracle Connection Manager is configured for TCP/IP, the client can connect to Oracle Connection Manager using Named Pipes, and Oracle Connection Manager can connect to the database server using TCP/IP.
As the following example shows, the cman.ora must be configured with a protocol address for each protocol that the client uses. Sample addresses for three protocols are shown--TCP/IP, Named Pipes, and TCP/IP with SSL.
(CMAN= (ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcp)(HOST=proxysvr1)(PORT=1630))) (ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=nmp)(SERVER=proxysvr_pc)(PIPE=cmanpipe))) (ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcps)(HOST=144.25.22.217)(PORT=2484)))
By default, Oracle Connection Manager accepts client connection requests at the following default protocol address:
CMAN=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcp)(HOST=anyhost)(PORT=1630))
To configure protocol conversion:
cman.ora file, if one does not already exist.CMAN parameter:
CMAN= (ADDRESS=(protocol_address_information)) (ADDRESS=(protocol_address_information))
| See Also:
Oracle9i Net Services Reference Guide for further information about protocol addresses and parameters |