| Oracle9i OLAP User's Guide Release 2 (9.2.0.2) Part Number A95295-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle9i OLAP User's Guide Release 2 (9.2.0.2) Part Number A95295-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
SQL-based applications can access multidimensional data, which is stored in analytic workspaces. Two mechanisms in the database's object technology make this possible:
CREATE TYPE statement, you create an abstract template that corresponds to a real-world object.
In OLAP, these "real-world objects" are measures, dimensions, hierarchies, attributes, and so forth. By defining object types for the objects in an analytic workspace, you can describe the format of multidimensional data to SQL as rows and columns.
FROM clause of a query. A table function can take a collection of rows as input.
You can use table functions to fetch data from objects in an analytic workspace. The table functions require arguments that are passed to the OLAP engine, which selects, manipulates, and returns the data. By incorporating table functions into your application, you have the most power and flexibility in selecting and manipulating data in the analytic workspace.
If you overlay the table functions with relational views, then you can make the table functions (and thus the source of the data) transparent to SQL-based applications. Your applications can use standard SQL to run against these views of multidimensional data, the same way that they access other relational tables and views in the database.
| See Also:
PL/SQL User's Guide and Reference for detailed information about object types and table functions. |
Figure 3-1 shows how a SQL application can access multidimensional data (using table functions and views) as well as relational data.
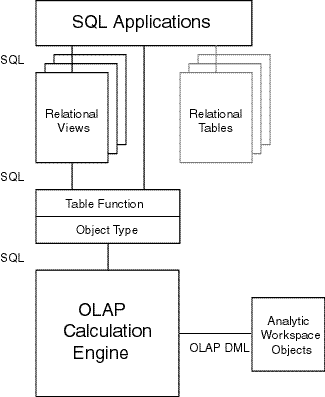
Text description of the illustration sqltodml.gif
There are several ways that SQL can access the multidimensional data of an analytic workspace. An abstract data type and the table functions underlie all of them. The method that you choose depends on how you want to use the data.
CWM2_OLAP_AW_CREATE package to create the analytic workspace from a star schema. Use other procedures in this package to define a star schema of dimension views and fact views, which represent the measures, dimensions, hierarchies, and attributes in the analytic workspace. You can then query these views using standard SQL SELECT statements. You can use other CWM2 APIs to create OLAP Catalog metadata based on these views.AW_CREATE process, you can use the CWM2_OLAP_AW_ACCESS PL/SQL package to generate views of the workspace.OLAP_TABLE function in SQL SELECT statements. This method is more complex than using CWM2_OLAP_AW_CREATE or CWM2_OLAP_AW_ACCESS, but it provides more flexibility and power in an application than using predefined views.
Using the procedures and functions in the DBMS_AW package, SQL programmers can issue OLAP DML commands directly against analytic workspace data. They can move data from relational tables into an analytic workspace, perform advanced analysis of the data (for example, forecasting), and copy data from the analytic workspace back into relational tables.
While the data is in the analytic workspace, SQL programmers can also issue SELECT statements against the data in the analytic workspace using the OLAP_TABLE function.