| Oracle9i SQL Reference Release 2 (9.2) Part Number A96540-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle9i SQL Reference Release 2 (9.2) Part Number A96540-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
Use the MERGE statement to select rows from one table for update or insertion into another table. The decision whether to update or insert into the target table is based on a condition in the ON clause.
This statement is a convenient way to combine at least two operations. It lets you avoid multiple INSERT and UPDATE DML statements.
MERGE is a deterministic statement. That is, you cannot update the same row of the target table multiple times in the same MERGE statement.
You must have INSERT and UPDATE object privileges on the target table and SELECT privilege on the source table.
merge::=
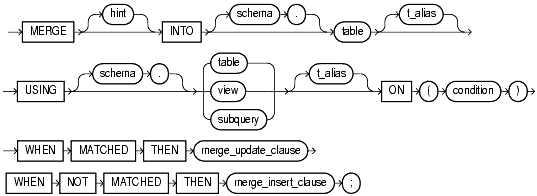
Use the INTO clause to specify the target table you are updating or inserting into.
Use the USING clause to specify the source of the data to be updated or inserted. The source can be a table, view, or the result of a subquery.
Use the ON clause to specify the condition upon which the MERGE operation either updates or inserts. For each row in the target table for which the search condition is true, Oracle updates the row based with corresponding data from the source table. If the condition is not true for any rows, then Oracle inserts into the target table based on the corresponding source table row.
Use these clauses to instruct Oracle how to respond to the results of the join condition in the ON clause. You can specify these two clauses in either order.
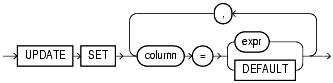
The merge_update_clause specifies the new column values of the target table. Oracle performs this update if the condition of the ON clause is true. If the update clause is executed, then all update triggers defined on the target table are activated.
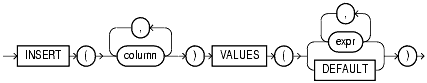
DEFAULT when updating a view.ON condition clause.The merge_insert_clause specifies values to insert into the column of the target table if the condition of the ON clause is false. If the insert clause is executed, then all insert triggers defined on the target table are activated.
You cannot specify DEFAULT when updating a view.
The following example creates a bonuses table in the sample schema oe with a default bonus of 100. It then inserts into the bonuses table all employees who made sales (based on the sales_rep_id column of the oe.orders table). Finally, the Human Resources manager decides that all employees should receive a bonus. Those who have not made sales get a bonus of 1% of their salary. Those who already made sales get an increase in their bonus equal to 1% of their salary. The MERGE statement implements these changes in one step:
CREATE TABLE bonuses (employee_id NUMBER, bonus NUMBER DEFAULT 100); INSERT INTO bonuses(employee_id) (SELECT e.employee_id FROM employees e, orders o WHERE e.employee_id = o.sales_rep_id GROUP BY e.employee_id); SELECT * FROM bonuses; EMPLOYEE_ID BONUS ----------- ---------- 153 100 154 100 155 100 156 100 158 100 159 100 160 100 161 100 163 100 MERGE INTO bonuses D USING (SELECT employee_id, salary, department_id FROM employees WHERE department_id = 80) S ON (D.employee_id = S.employee_id) WHEN MATCHED THEN UPDATE SET D.bonus = D.bonus + S.salary*.01 WHEN NOT MATCHED THEN INSERT (D.employee_id, D.bonus) VALUES (S.employee_id, S.salary*0.1); EMPLOYEE_ID BONUS ----------- ---------- 153 180 154 175 155 170 156 200 158 190 159 180 160 175 161 170 163 195 157 950 145 1400 170 960 179 620 152 900 169 1000 . . .