| Oracle9i Streams Release 2 (9.2) Part Number A96571-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle9i Streams Release 2 (9.2) Part Number A96571-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
This chapter illustrates an example of a single database that captures changes to a table, uses a DML handler during apply to re-enqueue the captured changes into a queue, and then applies a subset of the changes to a different table.
This chapter contains these topics:
The example in this chapter illustrates using Streams to capture and apply data manipulation language (DML) changes at a single database named cpap.net. Specifically, this example captures DML changes to the employees table in the hr schema, placing row logical change records (LCRs) into a queue named streams_queue. Then, an apply process dequeues these row LCRs from the same queue and sends them to a DML handler. The DML handler performs the following actions on the captured row LCRs:
emp_del table in the hr schema. This example assumes that the emp_del table is used to retain the records of all deleted employees. The DML handler is used to determine if each row LCR contains a DELETE statement. When the DML handler finds a row LCR containing a DELETE statement, it converts the DELETE into an INSERT on the emp_del table.Figure 20-1 provides an overview of the environment.
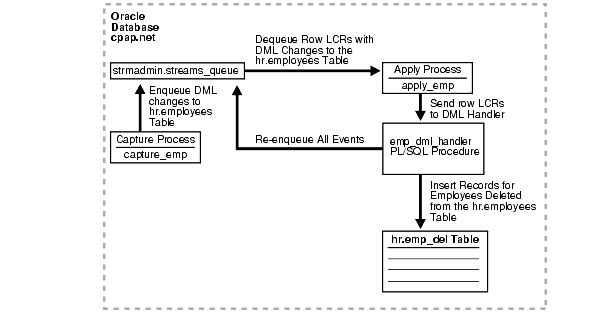
See Also:
|
The following prerequisites must be completed before you begin the example in this chapter.
AQ_TM_PROCESSES: This parameter establishes queue monitor processes. Values from 1 to 10 specify the number of queue monitor processes created to monitor the messages. If AQ_TM_PROCESSES is not specified or is set to 0, then the queue monitor processes are not created. In this example, AQ_TM_PROCESSES should be set to at least 1.
Setting the parameter to 1 or more starts the specified number of queue monitor processes. These queue monitor processes are responsible for managing time-based operations of messages such as delay and expiration, cleaning up retained messages after the specified retention time, and cleaning up consumed messages if the retention time is 0.
COMPATIBLE: This parameter must be set to 9.2.0 or higher.LOG_PARALLELISM: This parameter must be set to 1 because the database will capture events.
| See Also:
"Setting Initialization Parameters Relevant to Streams" for information about other initialization parameters that are important in a Streams environment |
ARCHIVELOG mode. Any database producing changes that will be captured must run in ARCHIVELOG mode.
| See Also:
Oracle9i Database Administrator's Guide for information about running a database in |
strmadmin) and prompts you for the tablespace you want to use for this user's data. Before you start this example, either create a new tablespace or identify an existing tablespace for the Streams administrator to use. The Streams administrator should not use the SYSTEM tablespace.Complete the following steps to create the hr.emp_del table, set up Streams administrator, and create the queue.
/************************* BEGINNING OF SCRIPT ******************************
Run SET ECHO ON and specify the spool file for the script. Check the spool file for errors after you run this script.
*/ SET ECHO ON SPOOL streams_setup_catapp.out /*
Connect to cpap.net as the hr user.
*/ CONNECT hr/hr@cpap.net /*
Create the hr.emp_del table. The shape of the emp_del table is the same as the employees table, except for one added timestamp column that will record the date when a row is inserted into the emp_del table.
*/ CREATE TABLE emp_del( employee_id NUMBER(6), first_name VARCHAR2(20), last_name VARCHAR2(25), email VARCHAR2(25), phone_number VARCHAR2(20), hire_date DATE, job_id VARCHAR2(10), salary NUMBER(8,2), commission_pct NUMBER(2,2), manager_id NUMBER(6), department_id NUMBER(4), timestamp DATE); CREATE UNIQUE INDEX emp_del_id_pk ON emp_del (employee_id); ALTER TABLE emp_del ADD (CONSTRAINT emp_del_id_pk PRIMARY KEY (employee_id)); /*
Connect to cpap.net as SYS user.
*/ CONNECT SYS/CHANGE_ON_INSTALL@cpap.net AS SYSDBA /*
Create the Streams administrator named strmadmin and grant this user the necessary privileges. These privileges enable the user to manage queues, execute subprograms in packages related to Streams, create rule sets, create rules, and monitor the Streams environment by querying data dictionary views and queue tables. You may choose a different name for this user.
In this example, the Streams administrator will be the apply user for the apply process and must be able to apply changes to the hr.emp_del table. Therefore, the Streams administrator is granted ALL privileges on this table.
*/ GRANT CONNECT, RESOURCE, SELECT_CATALOG_ROLE TO strmadmin IDENTIFIED BY strmadminpw; ACCEPT streams_tbs PROMPT 'Enter Streams administrator tablespace on cpap.net: ' ALTER USER strmadmin DEFAULT TABLESPACE &streams_tbs QUOTA UNLIMITED ON &streams_tbs; GRANT ALL ON hr.emp_del TO strmadmin; GRANT EXECUTE ON DBMS_APPLY_ADM TO strmadmin; GRANT EXECUTE ON DBMS_AQ TO strmadmin; GRANT EXECUTE ON DBMS_AQADM TO strmadmin; GRANT EXECUTE ON DBMS_CAPTURE_ADM TO strmadmin; GRANT EXECUTE ON DBMS_FLASHBACK TO strmadmin; GRANT EXECUTE ON DBMS_STREAMS_ADM TO strmadmin; BEGIN DBMS_RULE_ADM.GRANT_SYSTEM_PRIVILEGE( privilege => DBMS_RULE_ADM.CREATE_RULE_SET_OBJ, grantee => 'strmadmin', grant_option => FALSE); END; / BEGIN DBMS_RULE_ADM.GRANT_SYSTEM_PRIVILEGE( privilege => DBMS_RULE_ADM.CREATE_RULE_OBJ, grantee => 'strmadmin', grant_option => FALSE); END; /
/*
Connect to cpap.net as the strmadmin user.
*/ CONNECT strmadmin/strmadminpw@cpap.net /*
Run the SET_UP_QUEUE procedure to create a queue named streams_queue at cpap.net. This queue will function as the Streams queue by holding the captured changes that will be dequeued by an apply process.
Running the SET_UP_QUEUE procedure performs the following actions:
streams_queue_table. This queue table is owned by the Streams administrator (strmadmin) and uses the default storage of this user.streams_queue owned by the Streams administrator (strmadmin).*/ EXEC DBMS_STREAMS_ADM.SET_UP_QUEUE(); /*
Check the streams_setup_catapp.out spool file to ensure that all actions finished successfully after this script is completed.
*/ SET ECHO OFF SPOOL OFF /*************************** END OF SCRIPT ******************************/
Complete the following steps to capture changes to the hr.employees table and apply these changes on single database in a customized way using a DML handler.
/************************* BEGINNING OF SCRIPT ******************************
Run SET ECHO ON and specify the spool file for the script. Check the spool file for errors after you run this script.
*/ SET ECHO ON SPOOL streams_config_capapp.out /*
By default, the LogMiner tables are in the SYSTEM tablespace, but the SYSTEM tablespace may not have enough space for these tables once a capture process starts to capture changes. Therefore, you must create an alternate tablespace for the LogMiner tables.
Connect to cpap.net as SYS user.
*/ CONNECT SYS/CHANGE_ON_INSTALL@cpap.net AS SYSDBA /*
Create an alternate tablespace for the LogMiner tables.
*/ ACCEPT tspace_name DEFAULT 'logmnrts' PROMPT 'Enter tablespace name (for example, logmnrts): ' ACCEPT db_file_directory DEFAULT '' PROMPT 'Enter the complete path to the datafile directory (for example, /usr/oracle/dbs): ' ACCEPT db_file_name DEFAULT 'logmnrts.dbf' PROMPT 'Enter the name of the datafile (for example, logmnrts.dbf): ' CREATE TABLESPACE &tspace_name DATAFILE '&db_file_directory/&db_file_name' SIZE 25 M REUSE AUTOEXTEND ON MAXSIZE UNLIMITED; EXECUTE DBMS_LOGMNR_D.SET_TABLESPACE('&tspace_name'); /*
Supplemental logging places additional information in the redo log for changes made to tables. The apply process needs this extra information to perform certain operations, such as unique row identification.
The following statement specifies an unconditional supplemental log group for the primary key column in the hr.employees table.
*/ ALTER TABLE hr.employees ADD SUPPLEMENTAL LOG GROUP log_group_employees_pk (employee_id) ALWAYS; /*
Connect to cpap.net as the strmadmin user.
*/ CONNECT strmadmin/strmadminpw@cpap.net /*
Configure the capture process to capture DML changes to the hr.employees table at cpap.net. This step specifies that DML changes to this table are captured by the capture process and enqueued into the specified queue.
*/ BEGIN DBMS_STREAMS_ADM.ADD_TABLE_RULES( table_name => 'hr.employees', streams_type => 'capture', streams_name => 'capture_emp', queue_name => 'strmadmin.streams_queue', include_dml => true, include_ddl => false); END; / /*
Because this example captures and applies changes in a single database, no instantiation is necessary. However, the apply process at the cpap.net database still must be instructed to apply changes that were made to the hr.employees table after a certain system change number (SCN).
This example uses the GET_SYSTEM_CHANGE_NUMBER function in the DBMS_FLASHBACK package to obtain the current SCN for the database. This SCN is used to run the SET_TABLE_INSTANTIATION_SCN procedure in the DBMS_APPLY_ADM package.
The SET_TABLE_INSTANTIATION_SCN procedure controls which LCRs for a table are ignored by an apply process and which LCRs for a table are applied by an apply process. If the commit SCN of an LCR for a table from a source database is less than or equal to the instantiation SCN for that table at a destination database, then the apply process at the destination database discards the LCR. Otherwise, the apply process applies the LCR. In this example, the cpap.net database is both the source database and the destination database.
The apply process will apply transactions to the hr.employees table with SCNs that were committed after SCN obtained in this step.
|
Note: The |
*/ DECLARE iscn NUMBER; -- Variable to hold instantiation SCN value BEGIN iscn := DBMS_FLASHBACK.GET_SYSTEM_CHANGE_NUMBER(); DBMS_APPLY_ADM.SET_TABLE_INSTANTIATION_SCN( source_object_name => 'hr.employees', source_database_name => 'cpap.net', instantiation_scn => iscn); END; / /*
This example uses an agent named emp_agent for explicit enqueue into and dequeue from the streams_queue. Because the strmadmin user owns the queue table for this queue, the strmadmin user is a secure user of the queue. This step creates the agent named emp_agent and associates this agent with the strmadmin user, which allows the agent to be used for enqueues into and dequeues from the secure queue.
*/ BEGIN DBMS_AQADM.CREATE_AQ_AGENT( agent_name => 'emp_agent'); DBMS_AQADM.ENABLE_DB_ACCESS( agent_name => 'emp_agent', db_username => 'strmadmin'); END; / /*
Create a subscriber that can be used by an application to dequeue the re-enqueued events. At least one subscriber must be specified before the events can be re-enqueued into the queue.
*/ DECLARE subscriber SYS.AQ$_AGENT; BEGIN subscriber := SYS.AQ$_AGENT('emp_agent', NULL, NULL); SYS.DBMS_AQADM.ADD_SUBSCRIBER( queue_name => 'strmadmin.streams_queue', subscriber => subscriber, rule => NULL, transformation => NULL); END; / /*
This step creates the enq_row_lcr procedure. This procedure will be used in the DML handler procedure created in Step 9 to enqueue row LCRs that contain changes to the hr.employees table.
*/ CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE enq_row_lcr(in_any IN SYS.ANYDATA) IS enqopt DBMS_AQ.ENQUEUE_OPTIONS_T; mprop DBMS_AQ.MESSAGE_PROPERTIES_T; recipients DBMS_AQ.AQ$_RECIPIENT_LIST_T; enq_eventid RAW(16); BEGIN mprop.SENDER_ID := SYS.AQ$_AGENT( name => 'emp_agent', address => NULL, protocol => NULL); recipients(1) := SYS.AQ$_AGENT( name => 'emp_agent', address => NULL, protocol => NULL); mprop.RECIPIENT_LIST := recipients; DBMS_AQ.ENQUEUE( queue_name => 'strmadmin.streams_queue', enqueue_options => enqopt, message_properties => mprop, payload => in_any, msgid => enq_eventid); END; / /*
This step creates the emp_dml_handler procedure. This procedure will be the DML handler for DML changes to the hr.employees table. It performs the following actions:
streams_queue using the enq_row_lcr procedure created in Step 8.DELETE command type into an INSERT row LCR and then inserts the converted row LCR into the hr.emp_del table by executing the row LCR.*/ CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE emp_dml_handler(in_any IN SYS.ANYDATA) IS lcr SYS.LCR$_ROW_RECORD; rc PLS_INTEGER; command VARCHAR2(10); old_values SYS.LCR$_ROW_LIST; BEGIN -- Re-enqueue the row LCR for explicit dequeue by another application enq_row_lcr(in_any); -- Access the LCR rc := in_any.GETOBJECT(lcr); -- Get the object command type command := lcr.GET_COMMAND_TYPE(); -- Check for DELETE command on the hr.employees table IF command = 'DELETE' THEN -- Set the command_type in the row LCR to INSERT lcr.SET_COMMAND_TYPE('INSERT'); -- Set the object_name in the row LCR to EMP_DEL lcr.SET_OBJECT_NAME('EMP_DEL'); -- Get the old values in the row LCR old_values := lcr.GET_VALUES('old'); -- Set the old values in the row LCR to the new values in the row LCR lcr.SET_VALUES('new', old_values); -- Set the old values in the row LCR to NULL lcr.SET_VALUES('old', NULL); -- Add a SYSDATE value for the timestamp column lcr.ADD_COLUMN('new', 'TIMESTAMP', SYS.AnyData.ConvertDate(SYSDATE)); -- Apply the row LCR as an INSERT into the EMP_DEL table lcr.EXECUTE(true); END IF; END; / /*
Set the DML handler for the hr.employees table to the procedure created in Step 9. Notice that the DML handler must be set separately for each possible operation on the table: INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE.
*/ BEGIN DBMS_APPLY_ADM.SET_DML_HANDLER( object_name => 'hr.employees', object_type => 'TABLE', operation_name => 'INSERT', error_handler => false, user_procedure => 'strmadmin.emp_dml_handler', apply_database_link => NULL); END; / BEGIN DBMS_APPLY_ADM.SET_DML_HANDLER( object_name => 'hr.employees', object_type => 'TABLE', operation_name => 'UPDATE', error_handler => false, user_procedure => 'strmadmin.emp_dml_handler', apply_database_link => NULL); END; / BEGIN DBMS_APPLY_ADM.SET_DML_HANDLER( object_name => 'hr.employees', object_type => 'TABLE', operation_name => 'DELETE', error_handler => false, user_procedure => 'strmadmin.emp_dml_handler', apply_database_link => NULL); END; / /*
The emp_dq procedure creates in this step can be used to dequeue the events that are re-enqueued by the DML handler created in Step 9. When the emp_dq procedure is executed, it dequeues each row LCR in the queue and displays the type of command in the row LCR, either INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE. Any information in the row LCRs can be accessed and displayed, not just the command type.
| See Also:
"Displaying Detailed Information About Apply Errors" for more information about displaying information in LCRs |
*/ CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE emp_dq (consumer IN VARCHAR2) AS deqopt DBMS_AQ.DEQUEUE_OPTIONS_T; mprop DBMS_AQ.MESSAGE_PROPERTIES_T; msgid RAW(16); payload SYS.AnyData; new_messages BOOLEAN := TRUE; row_lcr SYS.LCR$_ROW_RECORD; tc pls_integer; next_trans EXCEPTION; no_messages EXCEPTION; pragma exception_init (next_trans, -25235); pragma exception_init (no_messages, -25228); BEGIN deqopt.consumer_name := consumer; deqopt.wait := 1; WHILE (new_messages) LOOP BEGIN DBMS_AQ.DEQUEUE( queue_name => 'strmadmin.streams_queue', dequeue_options => deqopt, message_properties => mprop, payload => payload, msgid => msgid); COMMIT; deqopt.navigation := DBMS_AQ.NEXT; IF (payload.GetTypeName = 'SYS.LCR$_ROW_RECORD') THEN tc := payload.GetObject(row_lcr); DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(row_lcr.GET_COMMAND_TYPE || ' row LCR dequeued'); END IF; EXCEPTION WHEN next_trans THEN deqopt.navigation := DBMS_AQ.NEXT_TRANSACTION; WHEN no_messages THEN new_messages := FALSE; DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('No more events'); END; END LOOP; END; / /*
Configure an apply process to apply DML changes to the hr.employees table. Although the DML handler for the apply process causes deleted employees to be inserted into the emp_del table, this rule specifies the employees table, because the row LCRs in the queue contain changes to the employees table, not the emp_del table.
*/ BEGIN DBMS_STREAMS_ADM.ADD_TABLE_RULES( table_name => 'hr.employees', streams_type => 'apply', streams_name => 'apply_emp', queue_name => 'strmadmin.streams_queue', include_dml => true, include_ddl => false, source_database => 'cpap.net'); END; / /*
Set the disable_on_error parameter to n so that the apply process will not be disabled if it encounters an error, and start the apply process at cpap.net.
*/ BEGIN DBMS_APPLY_ADM.SET_PARAMETER( apply_name => 'apply_emp', parameter => 'disable_on_error', value => 'n'); END; / BEGIN DBMS_APPLY_ADM.START_APPLY( apply_name => 'apply_emp'); END; / /*
Start the capture process at cpap.net.
*/ BEGIN DBMS_CAPTURE_ADM.START_CAPTURE( capture_name => 'capture_emp'); END; / /*
Check the streams_config_catapp.out spool file to ensure that all actions finished successfully after this script is completed.
*/ SET ECHO OFF SPOOL OFF /*************************** END OF SCRIPT ******************************/
Complete the following steps to make DML changes to the hr.employees table, query for the resulting inserts into the hr.emp_del table and the re-enqueued events in the streams_queue_table, and dequeue the events that were re-enqueued by the DML handler.
Make the following DML changes to the hr.employees table.
CONNECT hr/hr@cpap.net INSERT INTO hr.employees values(207, 'JOHN', 'SMITH', 'JSMITH@MYCOMPANY.COM', NULL, '07-JUN-94', 'AC_ACCOUNT', 777, NULL, NULL, 110); COMMIT; UPDATE hr.employees SET salary=5999 WHERE employee_id=206; COMMIT; DELETE FROM hr.employees WHERE employee_id=207; COMMIT;
After some time passes to allow for capture and apply of the changes performed in the previous step, run the following queries to see the results:
CONNECT strmadmin/strmadminpw@cpap.net SELECT * FROM hr.emp_del; SELECT MSG_ID, MSG_STATE, CONSUMER_NAME FROM AQ$STREAMS_QUEUE_TABLE;
When you run the first query, you should see a record for the employee with an employee_id of 207. This employee was deleted in the previous step. When you run the second query, you should see the re-enqueued events resulting from all of the changes in the previous step, and the MSG_STATE should be READY for these events.
Use the emp_dq procedure to dequeue the events that were re-enqueued by the DML handler.
SET SERVEROUTPUT ON SIZE 100000 EXEC emp_dq('emp_agent');
For each row changed by a DML statement, one line is returned, and each line states the command type of the change (either INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE). If you repeat the query on the queue table in Step 2 after the events are dequeued, then the dequeued events should have been consumed. That is, the MSG_STATE should be PROCESSED for these events.
SELECT MSG_ID, MSG_STATE, CONSUMER_NAME FROM AQ$STREAMS_QUEUE_TABLE;