Release 2 (9.2) for Windows
Part Number A95490-01
Home |
Book List |
Contents |
Index |
 Master Index |
 Feedback |
| Oracle9i Database Getting Started Release 2 (9.2) for Windows Part Number A95490-01 |
|
This chapter describes Windows services in general and Oracle9i Database Windows services in particular.
This chapter contains these topics:
Oracle9i starts each instance as a service on Windows. A service is an executable process registered in the Windows registry and administered by Windows. The registry automatically tracks and records security information for each service created.
Oracle also uses services, similar to Windows services, to provide support for its operations. Oracle services are created during the database creation process and are associated with the Oracle database. They are used to create, connect to, and use an Oracle instance.
Services simplify the process of starting up the database. The database can be configured to come up automatically when the computer is restarted, with no user interaction. Another advantage of services is that they can start with a specified user privilege.
Services start background processes, similar to daemon processes on UNIX. When the Oracle database service starts, there is no typical Oracle thread running in the process. Instead, the process waits for the first connection from SQL*Plus. This causes a foreground thread to start and creates background threads of the System Global Area.
When Oracle9i database is shut down, all threads that were created are terminated. But the process itself continues, waiting for the next connection request and startup command.
Finally, Oracle Net Listener is a service. This service needs to run before users can connect to Oracle9i database. This process does not affect how clients connect to or use Oracle9i database.
Services are started manually or they can be set to start automatically when the computer is restarted. By default, services run under the system user. However, system is not a user that can create a logon session; rather, it is an operating system session for running system services.
The following are some of the services available on Windows. You may have additional services, depending on components you installed.
Used by Oracle Object Link Manager to synchronize symbolic link naming to logical volume mapping automatically on all nodes in a cluster.
Back end for Oracle OLAP Instance Manager. Performs tasks specified in Instance Manager, such as starting and stopping an OLAP service or changing its configuration settings. Oracle OLAP Agent also returns information from the operating system, such as success or failure of a startup attempt.
Default OLAP service. Supports a calculation engine and multidimensional analytic workspaces for analytical applications. Performs complex statistical, mathematical, and financial calculations along with predictive analysis functions such as forecasting, modeling, consolidations, allocations, and scenario management.
Used for Cluster Manager for Oracle Real Application Clusters.
Responsible for starting and shutting down all Oracle Internet Directory (OID) servers (oidldapd, oidrepld, and oidmetad). Also monitors all OID servers once they are up and running. If an OID server goes down, then OracleDirectoryService_SID restarts it.
Used for external naming methods (Novell Directory Services and Network Information Service).
Global Services Daemon (GSD) receives requests from SRVCTL to execute an administrative job task, such as startup or shutdown. The task is executed locally on all nodes, and results are sent back to SRVCTL. This service is installed with Real Application Clusters.
Part of Oracle Enterprise Manager product suite. Intelligent Agent is required for execution of jobs and performance monitoring of Oracle services or targets such as listeners, databases, Oracle HTTP Server, and Oracle Applications. Intelligent Agent also collects statistical data for Capacity Planner and Performance Manager, which are data-collecting applications available in Oracle Diagnostics Pack.
Used for Client Cache Service, a networking product.
Performs administrative functions, including answering requests sent from Oracle Connection Manager Control utility, monitoring registered listeners, and communicating address information to Oracle Names servers.
Listens for incoming client connection requests. It also provides session multiplexing, access control, and protocol conversion functions.
Starts Oracle HTTP Server. Used as Web server with browser-based Oracle Enterprise Manager.
Management Server is the middle tier of Oracle Enterprise Manager. It maintains centralized intelligence and distributed control between clients and managed nodes.
Oracle Enterprise Manager Paging Server allows Enterprise Manager administrators to receive paging notifications concerning registered events and scheduled jobs.
Listens for and accepts incoming connection requests from client applications. Automatically starts when the Windows computer restarts. If it is not started, then the following error message appears when attempting to connect with username/password@net_service_name:
ORA-12541 TNS: no listener
Created and configured during installation of Oracle Fail Safe and Oracle Real Application Clusters Guard. Required on all Windows clusters nodes where these components are installed. OracleMSCSService is under the control of Microsoft Cluster Server and should be set to manual startup.
Helps Oracle databases recover in-doubt Oracle transactions that were started on behalf of Microsoft Transaction Server (MTS) transactions originating from Windows NT and Windows 2000 computers. There is only one such service for each Windows NT or Windows 2000 computer having Oracle Services for MTS installed.
Used for the distributed naming service developed for Oracle environments.
Created for the database instance system identifier, where SID is the value you entered for the database name during Oracle9i installation. This service is mandatory. If is it not started, then the following ORA-12560 error message appears when you attempt to use any Oracle9i Utilities, such as SQL*Plus:
ORA-12560 TNS: protocol adapter error
See OracleSNMPPeerMasterAgent. Encapsulator is only required when you have more than one SNMP sub-agent installed and configured on the system.
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is a standard internet protocol enabling certain nodes in a network to query other network components or applications for information concerning their status and activities. All requests sent to a given network node are handled by the same Master Agent, which redirects requests to appropriate managed elements on the node, in some cases using subagents.
A kernel mode service to provide I/O fencing. Restarts a node in case the node hangs in kernel mode for a defined amount of time. The service is installed on all nodes with OracleCMService9i.
Oracle services appear in the Services dialog box of the Control Panel:
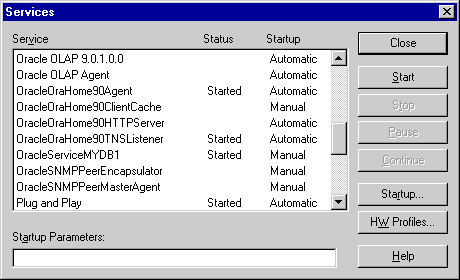
Text description of the illustration capture.gif
All Oracle services begin with "Ora". Use the Services dialog box to start or stop each of the Oracle services available on the computer.
Services are found in the registry under:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CURRENTCONTROLSET\SERVICES.
See Also:
|
|
 Copyright © 1996, 2002 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|