Release 2 (9.2) for Windows
Part Number A95491-01
Home |
Book List |
Contents |
Index |
 Master Index |
 Feedback |
| Oracle9i Database Administrator's Guide Release 2 (9.2) for Windows Part Number A95491-01 |
|
This chapter describes how to create a database after installing Oracle, using either Database Configuration Assistant or command-line tools.
This chapter contains these topics:
Before you create a database, consider the following requirements:
All mounted Oracle databases in a network must have unique database names. When a database is created, a name is associated with it and stored in its control files. If you provide the database keyword, either in the CREATE DATABASE statement or when prompted by Database Configuration Assistant, then that value becomes the name for that database.
If you attempt to mount two Oracle9i databases with the same database name, then you receive the following error during mounting of the second database:
ORA-01102: cannot mount database in EXCLUSIVE mode
If there are two or more Oracle9i databases on the same computer, but located in different Oracle homes, then the following rules apply:
To change the name of an existing database, you must use the CREATE CONTROLFILE statement to re-create your control files and specify a new database name. This restriction exists only for Oracle8i and later versions. Any Oracle7 instances running simultaneously with an Oracle9i instance are not subject to this restriction.
|
Note: Directory path examples in this chapter follow Optimal Flexible Architecture (OFA) guidelines. An example of an OFA path is |
Oracle can access database files on a remote computer using Universal Naming Convention (UNC), but it may degrade database performance and network reliability. UNC is a PC format for specifying locations of resources on a local area network. UNC uses the following format:
\\server-name\shared-resource-path-name
For example, UNC specification for file system01.dbf in directory C:\oracle\oradata\orcl on shared server argon would be:
\\argon\oracle\oradata\orcl\system01.dbf
Locations of archive log files cannot be specified using UNC. Always set initialization parameter LOG_ARCHIVE_DEST_n to a mapped drive. If you set it to a UNC specification, then Oracle9i database does not start and you receive the following errors:
ORA-00256: error occurred in translating archive text string '\meldell\rmdrive' ORA-09291: sksachk: invalid device specified for archive destination OSD-04018: Unable to access the specified directory or device O/S-Error: (OS 2) The system cannot find the file specified
An ORA-00256 error also occurs if you enter \\\meldell\rmdrive or \\\meldell\\rmdrive. Control files required the additional backslashes for Oracle8 release 8.0.4, but redo log files and datafiles did not.
Oracle Corporation recommends you use Database Configuration Assistant to create a database, because it is easier.
Use Database Configuration Assistant (DBCA) to register a database running in a member server or workstation in Active Directory on a Windows 2000 domain from a member server or workstation.
If the database service is running on a server, then make sure everyone is a member of Pre Windows 2000 Compatible domain group. If everyone is not a member of this group, then add the username/computer name (LocalSystem) that the database service is running to the Pre Windows 2000 Compatible domain group. If this is not done, then the database on the member server will randomly get ACCESS DENIED errors when accessing Active Directory.
For Database Configuration Assistant to successfully register the database with Active Directory, the database service on the server is required to be running as a LocalSystem or domain user. If the database is running as a local user, then trying to register the database with Active Directory using Database Configuration Assistant fails, because this user cannot log on to Active Directory.
After successfully registering with the directory using Database Configuration Assistant, you must manually add a name to Access Control List of OracleDBSecurity container (in Active Directory) with read permissions on OracleDBSecurity container. If the database service is running as a LocalSystem, then manually add the computer name. If the database service is running as a domain user, then manually add the username. If this is not done, then you may not be able to use Active Directory to grant an enterprise role.
Database Configuration Assistant enables you to:
The Database Configuration Assistant Welcome page appears.
|
Note: You must have the Windows Administrator privilege to create an Oracle9i database. If Database Configuration Assistant is run from a user account that is not part of the Administrator's group, then it displays a warning stating that you do not have administrative privileges to create the database. |
A window appears prompting you to select an operation to perform.
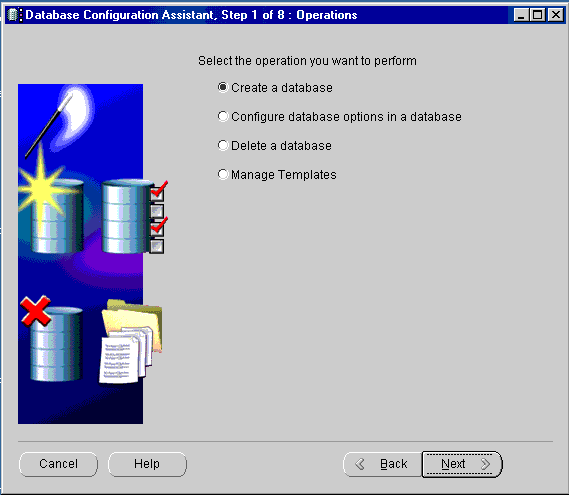
A window appears prompting you to select a database template.

The name is typically of the form name.domain, and the SID must be 64 characters or less.
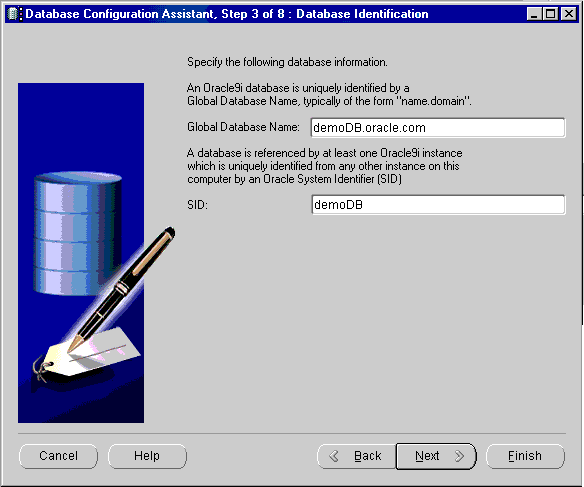
|
Note: If you use Database Configuration Assistant to create a new database in a new Oracle home, then file listener.ora is updated with the SID information, and a new TNS entry is generated in file tnsnames.ora. Both files are located in |
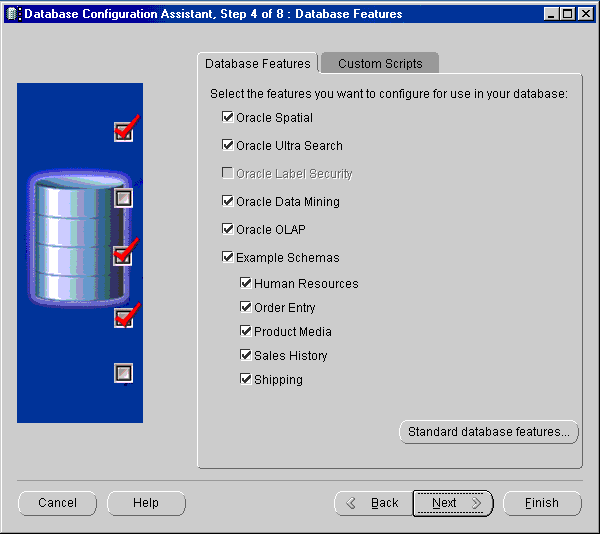
Text description of the illustration dbfeat.gif
|
Note: Oracle Label Security is available only through the database Custom installation type. For more information, see Oracle9i Database Installation Guide for Windows. |
Additional features become available if you click Standard Edition Features...
The Database Connection Options window appears.
Typical lets you set percentage of physical memory for Oracle and database type. Custom lets you specify initialization parameter values and other options including:
The Database Storage page appears.
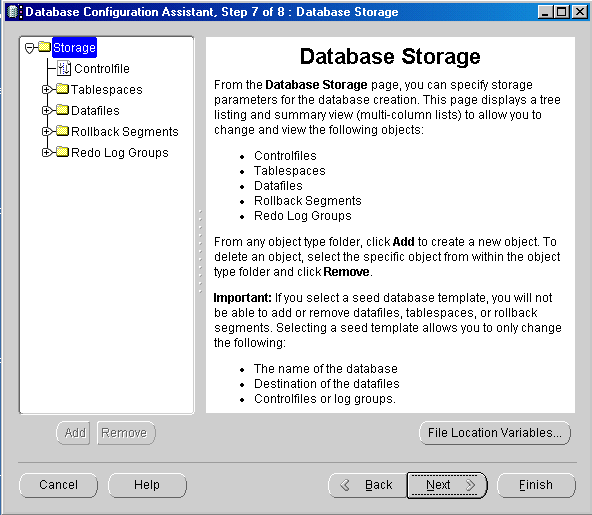
The Creation Options window appears.

After you finish creating your Oracle9i database with Database Configuration Assistant, you can import either or both of two sample schemas available on the CD-ROM:
To import an OLTP or data warehousing sample schema into your Oracle9i database:
C:\> sqlplus
Enter user-name: SYSTEM/password
SQL> CREATE USER sampleoltp IDENTIFIED BY password; SQL> GRANT RESOURCE TO sampleoltp; SQL> GRANT CONNECT TO sampleoltp;
For the data warehousing sample schema, enter:
SQL> CREATE USER samplestar IDENTIFIED BY password; SQL> GRANT RESOURCE TO samplestar; SQL> GRANT CONNECT TO samplestar;
SQL> EXIT
ORACLE_BASE\ORACLE_HOME\assistants\dbca\samples on your hard drive.imp sampleoltp/password FILE=source90.dmp FULL=y LOG=myimp.log
For the data warehousing sample schema, enter:
imp samplestar/password FILE=target90.dmp FULL=y LOG=myimp.log
The Delete a Database option of Database Configuration Assistant lets you quickly and easily delete all database files except the initialization parameter file.
This section describes how to create a new database manually. As part of its database software files, Oracle provides a sample database creation script and a sample initialization parameter file, both of which can be edited to suit your needs. Alternatively, if you have an existing script you can use it as-is to create a database manually or edit it using the sample database creation script as a guide.
Database creations are of three types:
Table 1-1 summarizes tasks involved in creating a new database for each of these database creation categories. Each step is explained in detail in the following subsections.
| Task | Copy existing database and delete old database | Copy existing database and keep old database | Create new database when no database exists on system |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
Yes |
MaybeFoot 1 |
Not applicable |
|
|
Yes |
No |
Not applicable |
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
No |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
Yes |
MaybeFoot 2 |
Not applicable |
|
|
No |
Only if you change the default |
Yes |
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
| 1 Yes if you copy data from the existing database to the new database; no otherwise. 2 Yes if you import tables and other objects exported from the existing database; no otherwise. |
We use an example in the following sections to demonstrate how to create a database. In this example, the existing database is the starter database with a SID of orcl located in directory C:\oracle\oradata\orcl. You will copy orcl to a new database with a database name and SID of prod located in directory C:\oracle\oradata\prod. You will then delete starter database orcl.
|
Note: In this example, |
Create the following directories in which to put administration and database files for new database prod:
C:\oracle\admin\prodC:\oracle\admin\prod\bdumpC:\oracle\admin\prod\pfileC:\oracle\admin\prod\udumpC:\oracle\oradata\prodYou are required to export an existing database only if you intend to copy its contents to a new database. You will use Export utility for this task. Although you can start Export utility in either parameter mode or interactive mode, Oracle Corporation recommends parameter mode. Interactive mode provides less functionality than parameter mode and exists for backward compatibility only.
C:\> exp SYSTEM/password FILE=myexp.dmp FULL=y LOG=myexp.log
C:\> exp SYSTEM/password
Enter only the command exp SYSTEM/password to begin an interactive session and let Export utility prompt you for information it needs.
| See Also:
Oracle9i Database Utilities for more information on using Export utility. |
To export all data from an existing database to a new database:
ORACLE_SID to the database service of the database whose contents you intend to export. For example, if the database you intend to export is starter database orcl, then enter the following at the command prompt. Note that there are no spaces around the equal sign (=) character.C:\> set ORACLE_SID=orcl
C:\> exp SYSTEM/password FILE=myexp.dmp FULL=y LOG=myexp.log
You now have a full database export of starter database orcl in file myexp.dmp. All messages from Export utility are logged in file myexp.log.
Deleting database files is required only when you copy an existing database to a new database to replace the old database. In the following example, you delete the database files of starter database orcl.
To delete database files:
orcl at the command prompt:C:\> oradim -SHUTDOWN -SID orcl -USRPWD password -SHUTTYPE inst -SHUTMODE i
C:\oracle\oradata\orcl:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
If you are using starter database orcl as the basis for your new database, then copy the initialization parameter file from
C:\ORACLE_BASE\admin\orcl\pfile\init.ora
to
C:\ORACLE_BASE\admin\prod\pfile\init.ora
and modify the file as described in this section.
If you do not have an existing database on your system, then you cannot copy an existing initialization parameter file to use as the basis for your new initialization parameter file. However, you can use the sample initialization parameter file initsmpl.ora provided in
ORACLE_BASE\ORACLE_HOME\admin\sample\pfile
as the basis for the initialization parameter file for database prod.
If you use initsmpl.ora as the basis for the initialization parameter file, then you must set the following parameters to the indicated values, or you will not be able to start database prod:
DB_NAME=prod.domain
Parameter DB_NAME indicates the database name and must match the name used in the CREATE DATABASE statement in "Putting the CREATE DATABASE Statement in a Script". You give a unique database name to each database. You can use up to eight characters for a database name. The name is not required to match the SID of the database service.
INSTANCE_NAME=prod.domainSERVICE_NAMES=prod.domainCONTROL_FILES = ("C:\oracle\oradata\prod\control01.ctl", "C:\oracle\oradata\prod\control02.ctl", "C:\oracle\oradata\prod\control03.ctl")
Parameter CONTROL_FILES lists database control files. You do not have control files on your file system at this point, because control files are created when you run the CREATE DATABASE statement. Ensure that you specify the complete path and filename, including drive letter.
BACKGROUND_DUMP_DEST = C:\oracle\admin\prod\bdumpUSER_DUMP_DEST = C:\oracle\admin\prod\udumpDB_FILES=100
Modifying initialization parameter DB_FILES is not required, but it is recommended to optimize performance. Set this parameter to the same number as the value of the MAXDATAFILES option of the CREATE DATABASE statement. The value of 100 is used for this example.
| See Also:
Oracle9i Database Reference for information on other initialization parameters that you can add or modify |
You are required to create and start an Oracle service only if you do one of the following:
Before you create the database, first create a Windows service to run the database. This service is the Oracle9i database process, oracle.exe, installed in the form of a Windows NT service.
Use ORADIM utility to create the service. After it has been created, the service starts automatically. See "Using ORADIM Utility to Administer an Oracle Instance" for information on how to use ORADIM utility.
To create and start an Oracle service:
C:\> oradim -NEW -SID prod -INTPWD password -STARTMODE manual -PFILE "C:\oracle\admin\prod\pfile\init.ora"
Note that the previously created initialization parameter file is specified, with complete path, including drive name. You can check if the service is started in the Services window of the Control Panel.
ORACLE_SID to equal prod. Note that there are no spaces around the equal sign (=) character:C:\> set ORACLE_SID=prod
The CREATE DATABASE statement is a SQL statement that creates the database. A script containing this statement can be used anytime you create a database.
The CREATE DATABASE statement may have the following parameters:
MAXDATAFILES - default value: 32, maximum value: 65534MAXLOGFILES - default value: 32, maximum value: 255When you run a CREATE DATABASE statement, Oracle performs several operations depending upon clauses that you specified in the CREATE DATABASE statement or initialization parameters that you have set.
|
Note: Oracle Managed Files is a feature that works with the CREATE DATABASE statement to simplify administration of an Oracle database. Oracle Managed Files eliminates the requirement to directly manage operating system files comprising an Oracle database, because you specify operations in terms of database objects rather than filenames. For more information on using Oracle Managed Files see Oracle9i Database Administrator's Guide. |
To create database prod, copy and save the following statement in a file named script_name.sql:
CREATE DATABASE prod MAXLOGFILES 5 MAXDATAFILES 100 DATAFILE 'oracle\oradata\prod\system01.dbf' SIZE 325M REUSE AUTOEXTEND ON NEXT 10240K MAXSIZE UNLIMITED UNDO TABLESPACE "UNDOTBS" DATAFILE 'oracle\oradata\prod\undotbs01.dbf' SIZE 200M REUSE AUTOEXTEND ON NEXT 5120K MAXSIZE UNLIMITED CHARACTER SET WE8MSWIN1252 logfile 'C:\oracle\oradata\prod\redo01.log' size 100M reuse, 'C:\oracle\oradata\prod\redo02.log' size 100M reuse, 'C:\oracle\oradata\prod\redo03.log' size 100M reuse;
To use the SQL script to create a database:
OracleServicePROD, and its status column must display Started. If not, then select the service name and choose Start.
You can also check the status of the service by entering the following at the command prompt:
C:\> net START
A list of all Windows services currently running on the system appears. If OracleServicePROD is missing from the list, then enter:
C:\> net START OracleServicePROD
PROD the current SID:C:\> set ORACLE_SID=PROD
C:\> sqlplus / NOLOG SQL> CONNECT / AS SYSDBA
The message connected appears.
SQL> SPOOL script_name.log
script_name.sql that you created in "Putting the CREATE DATABASE Statement in a Script":SQL> @C:\oracle\ora92\rdbms\admin\script_name.sql;
If the database is successfully created, then the instance is started and the following message appears numerous times: Statement processed
You can use Import utility to import the full export created in "Exporting an Existing Database" into the new database. Although you can start Import utility using either parameter mode or interactive mode, Oracle Corporation recommends parameter mode because it provides more functionality. Interactive mode exists solely for backward compatibility.
C:\> imp SYSTEM/password FILE=myexp.dmp FULL=y LOG=myexp.log
C:\> imp SYSTEM/password
Enter only imp SYSTEM/password to begin an interactive session and let Import utility prompt you for information it needs.
See Oracle9i Database Utilities for more information on using Import utility.
To import a database:
C:\> imp SYSTEM/password FILE=myexp.dmp FULL=y LOG=myimp.log
|
IMPORTANT: If the original database from which the export file was generated contains tablespaces that are not in the new database, then Import utility tries to create those tablespaces with associated datafiles. The easy solution is to ensure that both databases contain the same tablespaces. Datafiles are not required to be identical. Only tablespace names are important. |
If this is the first database on the system or if you intend to make the new database the default database, then you must make a change in the registry.
C:\> regedt32
The Registry Editor window appears.
\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\ORACLE\HOME0 for the first Oracle home on your computer. For subsequent installations to different Oracle homes on the same computer, the path is \HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\ORACLE\HOMEID where ID is the unique number identifying the Oracle home.
| See Also:
"Configuration Parameters and the Registry" in Oracle9i Database Getting Started for Windows for more information on subkey locations for multiple Oracle homes |
ORACLE_SID on the right side of the Registry Editor window.prod in this example.If you do not yet have parameter ORACLE_SID, because this is the first database on your system, then you must create it.
To create parameter ORACLE_SID:
The Add Value dialog box appears:
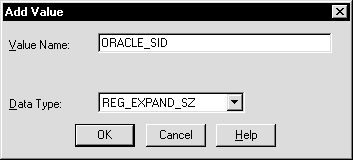
ORACLE_SID in the Value Name text box.REG_EXPAND_SZ (for an expandable string) in the Data Type list box.A string editor dialog box appropriate for the data type appears:
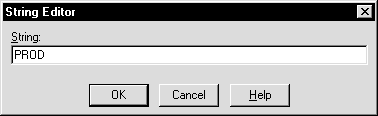
prod in the String Editor dialog box.Registry Editor adds parameter ORACLE_SID.
Registry Editor exits.
|
Caution: If anything goes wrong while operating the new database without a backup, then you must repeat the database creation procedure. Back up your database now to prevent loss of data. |
To back up the new database:
C:\> oradim -SHUTDOWN -SID prod -USRPWD password -SHUTTYPE srvc,inst -SHUTMODE i
|
Caution: Although ORADIM utility returns the prompt immediately, you must wait for the database and the service to stop completely before continuing to Step 2. Wait until the Control Panel indicates service |
Database files consist of the initialization parameter file, control files, online redo log files, and datafiles.
When the backup is complete, you can start the database again, create users and objects, if necessary, make any other changes, and use the database.
Be sure to back up the database after making any significant changes, such as switching archiving mode or adding a tablespace or datafile.
| See Also:
Chapter 6, "Backing Up and Recovering Database Files", Oracle9i Database Concepts, Oracle9i User-Managed Backup and Recovery Guide, and Oracle9i Database Administrator's Guide for more information on archiving and backup and recovery. |
ORADIM utility is a command-line tool that is available with Oracle9i database. You are required to use ORADIM utility only if you are manually creating, deleting, or modifying databases. Database Configuration Assistant is an easier tool to use for this purpose.
The following sections describe ORADIM utility commands and parameters. Note that each command is preceded by a dash (-). To get a list of ORADIM utility parameters, enter:
oradim -? | -H | -HELP
|
Note: Specifying oradim without any options also returns a list of oradim parameters and descriptions. |
When you use ORADIM utility, a log file called oradim.log opens in ORACLE_BASE\ORACLE_HOME\database, or in the directory specified by registry parameter ORA_CWD. All operations, whether successful or failed, are logged in this file. You must check this file to verify success of an operation.
If you have installed an Oracle database service on Windows 2000, then when logging in as SYSTEM user (LocalSystem), with startup mode set to Automatic, it is possible that the Oracle database service starts but the database does not start automatically. The following error message is written to file ORADIM.LOG in directory ORACLE_BASE\ORACLE_HOME\database:
ORA-12640: Authentication adapter initialization failed
Oracle Enterprise Management Agent, Oracle Enterprise Manager Management Server and Oracle Internet Directory may also fail, because they cannot connect to the database for the same reason.
The workarounds are to modify SQLNET.ORA, start the database with SQL*Plus after the service is started, or start the service as a specific user.
Modify SQLNET.ORA, either by removing the line
sqlnet.authentication_services=(NTS)
or by changing it to
sqlnet.authentication_services=(NONE)
Start the database manually after the Oracle database service has started, using SQL*Plus and connecting as SYSDBA.
The Services dialog box appears.
The Service Control dialog box appears.
To use ORADIM utility to create an instance, enter:
oradim -NEW -SID SID | -SRVC service_name [INTPWD password][-MAXUSERS number][-STARTMODE auto | manual][-PFILE filename] [-TIMEOUT secs]
where
-NEW indicates that you are creating a new instance. This is a mandatory parameter.-SID SID is the name of the instance to create. You must specify either this parameter or parameter -SRVC.-SRVC service_name is the name of the service to create (OracleServiceSID). You must specify either this parameter or parameter -SID.-INTPWD password is the password for the new instance. This is the password for the user logged in with SYSDBA privileges. Option -INTPWD is not required. If you do not specify it, then operating system authentication is used, and no password is required.-MAXUSERS number is the number of users defined in the password file. The default is 5.-STARTMODE auto, manual indicates whether to start the instance automatically or manually at startup. Default is manual.-PFILE filename is the initialization parameter file to be used with this instance. Ensure that you specify the complete path name of this file, including drive letter.-TIMEOUT secs sets the maximum time to wait (in seconds) before the service for a particular SID stops.To create an instance called PROD, for example, you might enter:
C:\> oradim -NEW -SID prod -INTPWD mypassword1 -STARTMODE auto -PFILE C:\oracle\admin\prod\pfile\init.ora
To use ORADIM utility to start an instance, enter
oradim -STARTUP -SID SID [-USRPWD user_pwd] [-STARTTYPE srvc | inst | srvc, inst] [-PFILE filename]
where
-STARTUP indicates that you are starting an instance that already exists. This is a mandatory parameter.-SID SID is the name of the instance to start. This is a mandatory parameter.-USERPWD user_pwd is the password.-STARTTYPE srvc, inst indicates whether to start the service or the instance. One or both values can be specified. If it is not specified, then the registry is checked for the current setting.-PFILE filename is the initialization parameter file to be used with this instance. Ensure that you specify the complete path name of this file, including drive letter.To start an instance called puma, for example, you might enter:
C:\> oradim -STARTUP -SID puma -STARTTYPE inst -PFILE C:\oracle\admin\prod\pfile\init.ora
To use ORADIM utility to stop an instance, enter:
oradim -SHUTDOWN -SID SID [-USRPWD user_pwd] [-SHUTTYPE srvc | inst | srvc, inst] [-SHUTMODE a | i | n]
where
-SHUTDOWN indicates that you are stopping an instance. This is a mandatory parameter.-SID SID specifies the name of the instance to stop. This is a mandatory parameter.-USERPWD user_pwd specifies the password.-SHUTTYPE srvc, inst indicates whether to stop the service or the instance. One or both values can be specified. If it is not specified, then the registry is checked for the current setting.-SHUTMODE a, i, n specifies how to stop an instance: a indicates abort mode, i indicates immediate mode, and n indicates normal mode. This is an optional parameter. If you do not specify how to stop an instance, then normal is the default mode.To stop an instance called puma, for example, you might enter:
C:\> oradim -SHUTDOWN -SID puma -SHUTTYPE srvc, inst
You can modify an existing instance to change such values as instance name, instance password, startup mode, shutdown mode, and shutdown type. To use ORADIM utility to modify an instance, enter:
oradim -EDIT -SID SID [-NEWSID NEWSID][INTPWD password][-STARTMODE a | m][-PFILE filename][SHUTMODE a | i | n][SHUTTYPE srvc | inst | srvc, inst]
where
-EDIT indicates that you are modifying an instance. This is a mandatory parameter.-SID SID specifies the name of the instance to modify. This is a mandatory parameter.-NEWSID NEWSID specifies the new instance name. This is an optional parameter.-STARTMODE a, m specifies how to start the instance at system startup: a specifies automatically and m specifies manually. Default is manual.-PFILE filename specifies the initialization parameter file to be used with this instance. Ensure that you specify the complete path name of this file, including drive letter.-SHUTMODE a, i, n specifies how to stop an instance: a indicates abort mode, i indicates immediate mode, and n indicates normal mode. This is an optional parameter. If you do not specify how to stop an instance, then normal is the default mode.-SHUTTYPE srvc, inst indicates whether to stop the service or the instance. One or both values can be specified. If it is not specified, then the registry is checked for the current setting.To change an instance name from prod to lynx, set a new instance password mycat123, and specify a new initialization parameter file, for example, you might enter:
C:\> oradim -EDIT -SID prod -NEWSID lynx -INTPWD mycat123 -STARTMODE a -PFILE C:\oracle\admin\lynx\pfile\init.ora
To use ORADIM utility to delete an instance, enter:
oradim -DELETE -SID SID | -SRVC service_name
where
-DELETE Indicates that you are deleting an instance or service. This is a mandatory parameter.-SID SID specifies the name of the SID to delete. You must specify either this parameter or parameter -SRVC.-SRVC service_name specifies the name of the service to delete. You must specify either this parameter or parameter -SID.To delete an instance called prod, for example, you might enter:
C:\> oradim -DELETE -SID prod
|
 Copyright © 1996, 2002 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|