| Oracle® Database SQL Reference 10g Release 2 (10.2) Part Number B14200-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Database SQL Reference 10g Release 2 (10.2) Part Number B14200-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
|
Note: Oracle strongly recommends that you run your database in automatic undo management mode instead of using rollback segments. Do not use rollback segments unless you must do so for compatibility with earlier versions of Oracle Database. Please refer to Oracle Database Administrator's Guide for information on automatic undo management. |
Purpose
Use the CREATE ROLLBACK SEGMENT statement to create a rollback segment, which is an object that Oracle Database uses to store data necessary to reverse, or undo, changes made by transactions.
The information in this section assumes that your database is not running in automatic undo mode (the UNDO_MANAGEMENT initialization parameter is set to MANUAL or not set at all). If your database is running in automatic undo mode (the UNDO_MANAGEMENT initialization parameter is set to AUTO), then user-created rollback segments are irrelevant.
Further, if your database has a locally managed SYSTEM tablespace, then you cannot create rollback segments in any dictionary-managed tablespace. Instead, you must either use the automatic undo management feature or create locally managed tablespaces to hold the rollback segments.
|
Note: A tablespace can have multiple rollback segments. Generally, multiple rollback segments improve performance.
|
To use objects in a tablespace other than the SYSTEM tablespace:
If you are using rollback segments for undo, at least one rollback segment (other than the SYSTEM rollback segment) must be online.
If you are running the database in automatic undo mode, at least one UNDO tablespace must be online.
|
See Also:
|
Prerequisites
To create a rollback segment, you must have the CREATE ROLLBACK SEGMENT system privilege.
Syntax
create_rollback_segment::=
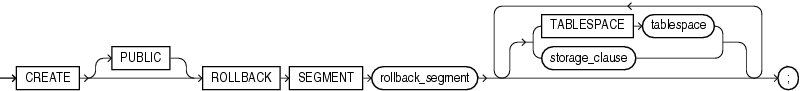
Semantics
PUBLIC
Specify PUBLIC to indicate that the rollback segment is public and is available to any instance. If you omit this clause, the rollback segment is private and is available only to the instance naming it in its initialization parameter ROLLBACK_SEGMENTS.
rollback_segment
Specify the name of the rollback segment to be created.
TABLESPACE
Use the TABLESPACE clause to identify the tablespace in which the rollback segment is created. If you omit this clause, then the database creates the rollback segment in the SYSTEM tablespace.
|
Note: Oracle Database must access rollback segments frequently. Therefore, Oracle strongly recommends that you do not create rollback segments in theSYSTEM tablespace, either explicitly or implicitly by omitting this clause. In addition, to avoid high contention for the tablespace containing the rollback segment, it should not contain other objects such as tables and indexes, and it should require minimal extent allocation and deallocation.
To achieve these goals, create rollback segments in locally managed tablespaces with autoallocation disabled--that is, in tablespaces created with the |
storage_clause
The storage_clause lets you specify storage characteristics for the rollback segment.
The OPTIMAL parameter of the storage_clause is of particular interest, because it applies only to rollback segments.
You cannot specify the PCTINCREASE parameter of the storage_clause with CREATE ROLLBACK SEGMENT.
Examples
Creating a Rollback Segment: Example The following statement creates a rollback segment with default storage values in an appropriately configured tablespace:
CREATE TABLESPACE rbs_ts DATAFILE 'rbs01.dbf' SIZE 10M EXTENT MANAGEMENT LOCAL UNIFORM SIZE 100K; /* This example and the next will fail if your database is in automatic undo mode. */ CREATE ROLLBACK SEGMENT rbs_one TABLESPACE rbs_ts;
The preceding statement is equivalent to the following:
CREATE ROLLBACK SEGMENT rbs_one
TABLESPACE rbs_ts
STORAGE
( INITIAL 10K
NEXT 10K
MAXEXTENTS UNLIMITED );