| Oracle® Database SQL Reference 10g Release 2 (10.2) Part Number B14200-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
| Oracle® Database SQL Reference 10g Release 2 (10.2) Part Number B14200-02 |
|
|
View PDF |
Purpose
Use the CREATE TRIGGER statement to create and enable a database trigger, which is:
A stored PL/SQL block associated with a table, a schema, or the database or
An anonymous PL/SQL block or a call to a procedure implemented in PL/SQL or Java
Oracle Database automatically executes a trigger when specified conditions occur.
When you create a trigger, the database enables it automatically. You can subsequently disable and enable a trigger with the DISABLE and ENABLE clause of the ALTER TRIGGER or ALTER TABLE statement.
|
See Also:
|
Before a trigger can be created, the user SYS must run a SQL script commonly called DBMSSTDX.SQL. The exact name and location of this script depend on your operating system.
To create a trigger in your own schema on a table in your own schema or on your own schema (SCHEMA), you must have the CREATE TRIGGER system privilege.
To create a trigger in any schema on a table in any schema, or on another user's schema (schema.SCHEMA), you must have the CREATE ANY TRIGGER system privilege.
In addition to the preceding privileges, to create a trigger on DATABASE, you must have the ADMINISTER DATABASE TRIGGER system privilege.
If the trigger issues SQL statements or calls procedures or functions, then the owner of the trigger must have the privileges necessary to perform these operations. These privileges must be granted directly to the owner rather than acquired through roles.
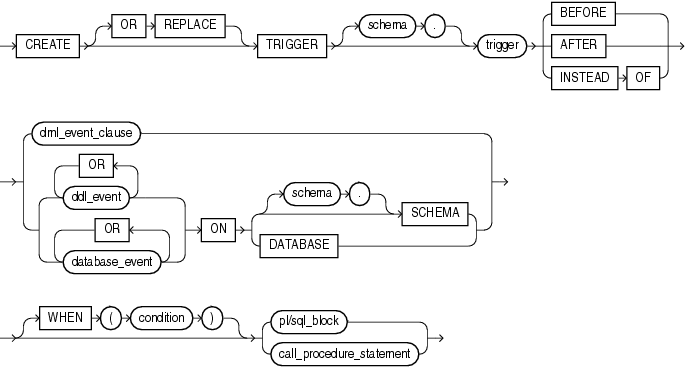
Syntax
create_trigger::=
DML_event_clause ::=
Semantics
Specify OR REPLACE to re-create the trigger if it already exists. Use this clause to change the definition of an existing trigger without first dropping it.
schema
Specify the schema to contain the trigger. If you omit schema, then Oracle Database creates the trigger in your own schema.
trigger
Specify the name of the trigger to be created.
If a trigger produces compilation errors, then it is still created, but it fails on execution. This means it effectively blocks all triggering DML statements until it is disabled, replaced by a version without compilation errors, or dropped. You can see the associated compiler error messages with the SQL*Plus command SHOW ERRORS.
|
Note: If you create a trigger on a base table of a materialized view, then you must ensure that the trigger does not fire during a refresh of the materialized view. During refresh, theDBMS_MVIEW procedure I_AM_A_REFRESH returns TRUE. |
Specify BEFORE to cause the database to fire the trigger before executing the triggering event. For row triggers, the trigger is fired before each affected row is changed.
Restrictions on BEFORE Triggers BEFORE triggers are subject to the following restrictions:
You cannot specify a BEFORE trigger on a view or an object view.
You can write to the :NEW value but not to the :OLD value.
Specify AFTER to cause the database to fire the trigger after executing the triggering event. For row triggers, the trigger is fired after each affected row is changed.
Restrictions on AFTER Triggers AFTER triggers are subject to the following restrictions:
You cannot specify an AFTER trigger on a view or an object view.
You cannot write either the :OLD or the :NEW value.
|
Note: When you create a materialized view log for a table, Oracle Database implicitly creates anAFTER ROW trigger on the table. This trigger inserts a row into the materialized view log whenever an INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE statement modifies data in the master table. You cannot control the order in which multiple row triggers fire. Therefore, you should not write triggers intended to affect the content of the materialized view. |
Specify INSTEAD OF to cause Oracle Database to fire the trigger instead of executing the triggering event. INSTEAD OF triggers are valid for DML events on views. They are not valid for DDL or database events.
If a view is inherently updatable and has INSTEAD OF triggers, then the triggers take preference. In other words, the database fires the triggers instead of performing DML on the view.
If the view belongs to a hierarchy, then the trigger is not inherited by subviews.
|
Note: Oracle Database fine-grained access control lets you define row-level security policies on views. These policies enforce specified rules in response to DML operations. If anINSTEAD OF trigger is also defined on the view, then the database will not enforce the row-level security policies, because the database fires the INSTEAD OF trigger instead of executing the DML on the view. |
INSTEAD OF Triggers
INSTEAD OF triggers are valid only for views. You cannot specify an INSTEAD OF trigger on a table.
You can read both the :OLD and the :NEW value, but you cannot write either the :OLD or the :NEW value.
You can create multiple triggers of the same type (BEFORE, AFTER, or INSTEAD OF) that fire for the same statement on the same table. The order in which Oracle Database fires these triggers is indeterminate. If your application requires that one trigger be fired before another of the same type for the same statement, then combine these triggers into a single trigger whose trigger action performs the trigger actions of the original triggers in the appropriate order. |
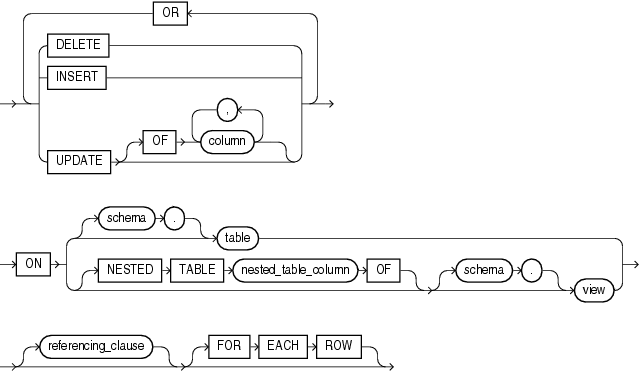
The DML_event_clause lets you specify one of three DML statements that can cause the trigger to fire. Oracle Database fires the trigger in the existing user transaction.
You cannot specify the MERGE keyword in the DML_event_clause. If you want a trigger to fire in relation to a MERGE operation, you must create triggers on the INSERT and UPDATE operations to which the MERGE operation decomposes.
DELETE
Specify DELETE if you want the database to fire the trigger whenever a DELETE statement removes a row from the table or removes an element from a nested table.
INSERT
Specify INSERT if you want the database to fire the trigger whenever an INSERT statement adds a row to a table or adds an element to a nested table.
UPDATE
Specify UPDATE if you want the database to fire the trigger whenever an UPDATE statement changes a value in one of the columns specified after OF. If you omit OF, then the database fires the trigger whenever an UPDATE statement changes a value in any column of the table or nested table.
For an UPDATE trigger, you can specify object type, varray, and REF columns after OF to indicate that the trigger should be fired whenever an UPDATE statement changes a value in one of the columns. However, you cannot change the values of these columns in the body of the trigger itself.
|
Note: Using OCI functions or theDBMS_LOB package to update LOB values or LOB attributes of object columns does not cause Oracle Database to fire triggers defined on the table containing the columns or the attributes. |
Restrictions on Triggers on UPDATE Operations The UPDATE clause is subject to the following restrictions:
You cannot specify UPDATE OF for an INSTEAD OF trigger. Oracle Database fires INSTEAD OF triggers whenever an UPDATE changes a value in any column of the view.
You cannot specify a nested table or LOB column in the UPDATE OF clause.
|
See Also: AS subquery clause of CREATE VIEW for a list of constructs that prevent inserts, updates, or deletes on a view |
Performing DML operations directly on nested table columns does not cause Oracle Database to fire triggers defined on the table containing the nested table column.
Specify one or more types of DDL statements that can cause the trigger to fire. You can create triggers for these events on DATABASE or SCHEMA unless otherwise noted. You can create BEFORE and AFTER triggers for these events. Oracle Database fires the trigger in the existing user transaction.
Restriction on Triggers on DDL Events You cannot specify as a triggering event any DDL operation performed through a PL/SQL procedure.
The following ddl_event values are valid:
ALTER Specify ALTER to fire the trigger whenever an ALTER statement modifies a database object in the data dictionary.
Restriction on Triggers on ALTER Operations The trigger will not be fired by an ALTER DATABASE statement.
ANALYZE Specify ANALYZE to fire the trigger whenever the database collects or deletes statistics or validates the structure of a database object.
ASSOCIATE STATISTICS Specify ASSOCIATE STATISTICS to fire the trigger whenever the database associates a statistics type with a database object.
AUDIT Specify AUDIT to fire the trigger whenever the database tracks the occurrence of a SQL statement or tracks operations on a schema object.
COMMENT Specify COMMENT to fire the trigger whenever a comment on a database object is added to the data dictionary.
CREATE Specify CREATE to fire the trigger whenever a CREATE statement adds a new database object to the data dictionary.
Restriction on Triggers on CREATE Operations The trigger will not be fired by a CREATE DATABASE or CREATE CONTROLFILE statement.
DISASSOCIATE STATISTICS Specify DISASSOCIATE STATISTICS to fire the trigger whenever the database disassociates a statistics type from a database object.
DROP Specify DROP to fire the trigger whenever a DROP statement removes a database object from the data dictionary.
GRANT Specify GRANT to fire the trigger whenever a user grants system privileges or roles or object privileges to another user or to a role.
NOAUDIT Specify NOAUDIT to fire the trigger whenever a NOAUDIT statement instructs the database to stop tracking a SQL statement or operations on a schema object.
RENAME Specify RENAME to fire the trigger whenever a RENAME statement changes the name of a database object.
REVOKE Specify REVOKE to fire the trigger whenever a REVOKE statement removes system privileges or roles or object privileges from a user or role.
TRUNCATE Specify TRUNCATE to fire the trigger whenever a TRUNCATE statement removes the rows from a table or cluster and resets its storage characteristics.
DDL Specify DDL to fire the trigger whenever any of the preceding DDL statements is issued.
Specify one or more particular states of the database that can cause the trigger to fire. You can create triggers for these events on DATABASE or SCHEMA unless otherwise noted. For each of these triggering events, Oracle Database opens an autonomous transaction scope, fires the trigger, and commits any separate transaction (regardless of any existing user transaction).
SERVERERROR Specify SERVERERROR to fire the trigger whenever a server error message is logged.
The following errors do not cause a SERVERERROR trigger to fire:
ORA-01403: no data found
ORA-01422: exact fetch returns more than requested number of rows
ORA-01423: error encountered while checking for extra rows in exact fetch
ORA-01034: ORACLE not available
ORA-04030: out of process memory when trying to allocate string bytes (string, string)
LOGON Specify LOGON to fire the trigger whenever a client application logs onto the database.
LOGOFF Specify LOGOFF to fire the trigger whenever a client application logs off the database.
STARTUP Specify STARTUP to fire the trigger whenever the database is opened.
SHUTDOWN Specify SHUTDOWN to fire the trigger whenever an instance of the database is shut down.
SUSPEND Specify SUSPEND to fire the trigger whenever a server error causes a transaction to be suspended.
DB_ROLE_CHANGE In a Data Guard configuration, specify DB_ROLE_CHANGE to fire the trigger whenever a role change occurs from standby to primary or from primary to standby.
|
Notes:
|
The ON clause lets you determine the database object on which the trigger is to be created. Specify the schema and table or view name of one of the following on which the trigger is to be created:
Table or view
Object table or object view
A column of nested-table type
If you omit schema, then Oracle Database assumes the table is in your own schema. You can create triggers on index-organized tables.
Restriction on Schema You cannot create a trigger on a table in the schema SYS.
Specify the nested_table_column of a view upon which the trigger is being defined. Such a trigger will fire only if the DML operates on the elements of the nested table.
Restriction on Triggers on Nested Tables You can specify NESTED TABLE only for INSTEAD OF triggers.
DATABASE
Specify DATABASE to define the trigger on the entire database. The trigger fires whenever any database user initiates the triggering event.
SCHEMA
Specify SCHEMA to define the trigger on the current schema. The trigger fires whenever any user connected as schema initiates the triggering event.
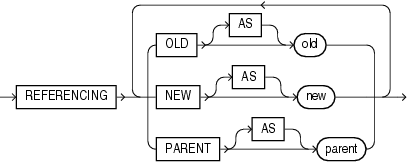
The referencing_clause lets you specify correlation names. You can use correlation names in the PL/SQL block and WHEN condition of a row trigger to refer specifically to old and new values of the current row. The default correlation names are OLD and NEW. If your row trigger is associated with a table named OLD or NEW, use this clause to specify different correlation names to avoid confusion between the table name and the correlation name.
If the trigger is defined on a nested table, then OLD and NEW refer to the row of the nested table, and PARENT refers to the current row of the parent table.
If the trigger is defined on an object table or view, then OLD and NEW refer to object instances.
Restriction on the referencing_clause The referencing_clause is not valid with INSTEAD OF triggers on CREATE DDL events.
Specify FOR EACH ROW to designate the trigger as a row trigger. Oracle Database fires a row trigger once for each row that is affected by the triggering statement and meets the optional trigger constraint defined in the WHEN condition.
Except for INSTEAD OF triggers, if you omit this clause, then the trigger is a statement trigger. Oracle Database fires a statement trigger only once when the triggering statement is issued if the optional trigger constraint is met.
INSTEAD OF trigger statements are implicitly activated for each row.
Restriction on Row Triggers This clause is valid only for DML event triggers, not for DDL or database event triggers.
Specify the trigger condition, which is a SQL condition that must be satisfied for the database to fire the trigger. See the syntax description of condition in Chapter 7, "Conditions". This condition must contain correlation names and cannot contain a query.
The NEW and OLD keywords, when specified in the WHEN clause, are not considered bind variables, so are not preceded by a colon (:). However, you must precede NEW and OLD with a colon in all references other than the WHEN clause.
Restrictions on Trigger Conditions Trigger conditions are subject to the following restrictions:
If you specify this clause for a DML event trigger, then you must also specify FOR EACH ROW. Oracle Database evaluates this condition for each row affected by the triggering statement.
You cannot specify trigger conditions for INSTEAD OF trigger statements.
You can reference object columns or their attributes, or varray, nested table, or LOB columns. You cannot invoke PL/SQL functions or methods in the trigger condition.
Specify the PL/SQL block that Oracle Database executes to fire the trigger.
The PL/SQL block of a database trigger can contain one of a series of built-in functions in the SYS schema designed solely to extract system event attributes. These functions can be used only in the PL/SQL block of a database trigger.
Restrictions on Trigger Implementation The implementation of a trigger is subject to the following restrictions:
The PL/SQL block of a trigger cannot contain transaction control SQL statements (COMMIT, ROLLBACK, SAVEPOINT, and SET CONSTRAINT) if the block is executed within the same transaction.
You can reference and use LOB columns in the trigger action inside the PL/SQL block. You can modify the :NEW values but not the :OLD values of LOB columns within the trigger action.
|
See Also:
|
The call_procedure_statement lets you call a stored procedure rather than specifying the trigger code inline as a PL/SQL block. The syntax of this statement is the same as that for CALL, with the following exceptions:
You cannot specify the INTO clause of CALL, because it applies only to functions.
You cannot specify bind variables in expr.
To reference columns of tables on which the trigger is being defined, you must specify :NEW and :OLD.
Creating a DML Trigger: Examples This example shows the basic syntax for a BEFORE statement trigger. You would write such a trigger to place restrictions on DML statements issued on a table, for example, when such statements could be issued.
CREATE TRIGGER schema.trigger_name BEFORE DELETE OR INSERT OR UPDATE ON schema.table_name pl/sql_block
Oracle Database fires such a trigger whenever a DML statement affects the table. This trigger is a BEFORE statement trigger, so the database fires it once before executing the triggering statement.
The next example shows a partial BEFORE row trigger. The PL/SQL block might specify, for example, that an employee's salary must fall within the established salary range for the employee's job:
CREATE TRIGGER hr.salary_check
BEFORE INSERT OR UPDATE OF salary, job_id ON hr.employees
FOR EACH ROW
WHEN (new.job_id <> 'AD_VP')
pl/sql_block
Oracle Database fires this trigger whenever one of the following statements is issued:
An INSERT statement that adds rows to the employees table
An UPDATE statement that changes values of the salary or job_id columns of the employees table
salary_check is a BEFORE row trigger, so the database fires it before changing each row that is updated by the UPDATE statement or before adding each row that is inserted by the INSERT statement.
salary_check has a trigger condition that prevents it from checking the salary of the administrative vice president (AD_VP).
Creating a DDL Trigger: Example This example creates an AFTER statement trigger on any DDL statement CREATE. Such a trigger can be used to audit the creation of new data dictionary objects in your schema.
CREATE TRIGGER audit_db_object AFTER CREATE
ON SCHEMA
pl/sql_block
Calling a Procedure in a Trigger Body: Example You could create the salary_check trigger described in the preceding example by calling a procedure instead of providing the trigger body in a PL/SQL block. Assume you have defined a procedure check_sal in the hr schema, which verifies that an employee's salary is in an appropriate range. Then you could create the trigger salary_check as follows:
CREATE TRIGGER salary_check BEFORE INSERT OR UPDATE OF salary, job_id ON employees FOR EACH ROW WHEN (new.job_id <> 'AD_VP') CALL check_sal(:new.job_id, :new.salary, :new.last_name)
The procedure check_sal could be implemented in PL/SQL, C, or Java. Also, you can specify :OLD values in the CALL clause instead of :NEW values.
Creating a Database Event Trigger: Example This example shows the basic syntax for a trigger to log all errors. The hypothetical PL/SQL block does some special processing for a particular error (invalid logon, error number 1017). This trigger is an AFTER statement trigger, so it is fired after an unsuccessful statement execution, such as unsuccessful logon.
CREATE TRIGGER log_errors AFTER SERVERERROR ON DATABASE BEGIN IF (IS_SERVERERROR (1017)) THEN <special processing of logon error> ELSE <log error number> END IF; END;
Creating an INSTEAD OF Trigger: Example In this example, an oe.order_info view is created to display information about customers and their orders:
CREATE VIEW order_info AS
SELECT c.customer_id, c.cust_last_name, c.cust_first_name,
o.order_id, o.order_date, o.order_status
FROM customers c, orders o
WHERE c.customer_id = o.customer_id;
Normally this view would not be updatable, because the primary key of the orders table (order_id) is not unique in the result set of the join view. To make this view updatable, create an INSTEAD OF trigger on the view to process INSERT statements directed to the view. The PL/SQL trigger implementation is shown in italics.
CREATE OR REPLACE TRIGGER order_info_insert INSTEAD OF INSERT ON order_info DECLARE duplicate_info EXCEPTION; PRAGMA EXCEPTION_INIT (duplicate_info, -00001); BEGIN INSERT INTO customers (customer_id, cust_last_name, cust_first_name) VALUES ( :new.customer_id, :new.cust_last_name, :new.cust_first_name); INSERT INTO orders (order_id, order_date, customer_id) VALUES ( :new.order_id, :new.order_date, :new.customer_id); EXCEPTION WHEN duplicate_info THEN RAISE_APPLICATION_ERROR ( num=> -20107, msg=> 'Duplicate customer or order ID'); END order_info_insert; /
You can now insert into both base tables through the view (as long as all NOT NULL columns receive values):
INSERT INTO order_info VALUES (999, 'Smith', 'John', 2500, '13-MAR-2001', 0);
Creating a SCHEMA Trigger: Example The following example creates a BEFORE statement trigger on the sample schema hr. When a user connected as hr attempts to drop a database object, the database fires the trigger before dropping the object:
CREATE OR REPLACE TRIGGER drop_trigger
BEFORE DROP ON hr.SCHEMA
BEGIN
RAISE_APPLICATION_ERROR (
num => -20000,
msg => 'Cannot drop object');
END;
/