|
Oracle® Business Intelligence Discoverer Administration Guide
10g Release 2 (10.1.2.1) B13916-04 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
|
Oracle® Business Intelligence Discoverer Administration Guide
10g Release 2 (10.1.2.1) B13916-04 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
This chapter provides additional information about Discoverer summary folders and contains the following topics:
"What is the context and future for Discoverer's use of summary tables/materialized views?"
"About viewing the SQL and execution plan for query rewrite in Discoverer"
"About configuring how Discoverer displays SQL in the SQL Inspector dialog"
"Examples of execution plan (in Discoverer) using/not using a materialized view"
"Example of the SQL (in Discoverer) where Discoverer rewrites the query"
"Example illustrating the advantages of rewriting a query to use a summary table"
"What is different about summary folders that are based on external summary tables?"
"About refresh options for Oracle Enterprise Edition databases"
"About refreshing summary folders following import between Oracle databases"
Discoverer created the concept of rewriting a query to use a summary table. The idea of creating a summary table and having the SQL automatically rewritten was patented by Oracle.
It became clear that this functionality would be useful for all database users, so Oracle moved the functionality to the database. Discoverer uses materialized views and query rewrite whenever possible and still supports its original query rewrite to Discoverer summary tables if not.
The long term direction is to work with the server query rewrite mechanism and gradually remove the Discoverer-specific mechanism.
Discoverer uses query rewrite under the following database conditions:
With Oracle Enterprise Edition databases Discoverer sends a query to the database and the database decides whether a suitable materialized view exists for the query rather than accessing the detail data tables. If one does exist, the database rewrites the query to use the materialized view.
With Oracle Standard Edition databases. Discoverer rewrites the query to use a suitable summary table rather than accessing the detail data tables.
With Oracle Enterprise Edition databases, when mapping a view to items in the EUL, Discoverer rewrites the query to use a suitable summary table.
Query rewrite is transparent to the Discoverer end user and provides exactly the same results as queries that run against the detail tables but returns the results in far less time.
Note: Before query rewrite can be used, the option to use summary folders must be set in Discoverer Plus (for further information, see the Oracle Business Intelligence Discoverer Plus User's Guide).
For more information about the rules regarding Oracle Enterprise Edition database rewrite scenarios, see the Oracle Database Data Warehousing Guide.
Discoverer rewrites a query to use a summary table instead of the detail data when all of the following conditions are met:
All the items specified in a query must either:
exist in a single summary combination
For more information, see "What are summary combinations?".
be able to be joined to a summary table via foreign keys that exist in a summary combination
Where derived items are used, you must include in the summary combination:
the derived items
the components used to create the derived items
For more information about derived items, see "What are derived items?".
Where items are from complex folders, create another summary folder using the same combination of items, but from the source (simple) folders.
For more information about complex folders, see "What are complex folders?".
Join paths specified in the query must match those specified in the summary combination that satisfies the query. This ensures that the summary result set data matches that in the detail data tables.
However, you can define queries using fewer joins than specified in the summary table, provided that you select the Detail item values always exist in the master folder radio button in the "Edit Join dialog: Options tab".
The summary folder must have the Available for Queries property set to Yes
For more information about summary folder properties, see "How to edit the properties of summary folders".
The conditions specified on the Query Governor tab of the Options dialog in Discoverer Plus must be met.
For more information, see the Oracle Business Intelligence Discoverer Plus User's Guide.
The Discoverer end user running the query must have database SELECT access to the summary table.
For more information about the privileges required to create summary folders, see "What are the prerequisites for creating summary folders manually in Discoverer?".
To view the SQL sent to the database server and the execution plan that the database server uses to return the results data from a query, you use the SQL Inspector dialog in Discoverer Plus. The SQL Inspector dialog displays the SQL and includes the name of the materialized view or the summary table used. For more information about the SQL Inspector dialog, see the Oracle Business Intelligence Discoverer Plus User's Guide.
In Oracle Business Intelligence Discoverer Plus and Oracle Business Intelligence Discoverer Desktop, end users can look at SQL being generated by Discoverer to create worksheets. The SQL that is shown in the SQL Inspector is not necessarily the same as that which is sent to the RDBMS.
Discoverer always sends SQL that contains inline views to the RDBMS. Because inline views can be difficult for end users to read, you can configure Discoverer to reformat SQL to make it easier to read. Reformatted SQL is also known as 'flattened' SQL.
To configure how Discoverer displays SQL, edit the SQLType registry setting (for more information, see Chapter 21, "Discoverer registry settings" and "How to edit Discoverer Administrator and Discoverer Desktop registry settings").
Note that although the inline view SQL is passed to the RDBMS, it is not all executed in the database. The RDBMS optimizer strips the SQL from all columns of inline views. The only columns that are returned by the database are those in the outer select statement. For example, in the following SQL statement:
select dname from
(select dname, deptno, manager_id, manager_name, location, address, phone, zip from departments)
the RDBMS optimizer converts the SQL to:
select dname from departments
In the above SQL statement, the only column returned to Discoverer is the dname column.
To see the SQL that is executed in the database, look at the flattened SQL in the SQL Inspector dialog in Discoverer Plus or Discoverer Desktop.
You can tell whether a query is subject to query rewrite by invoking the SQL Inspector dialog in Discoverer Plus. The table below illustrates how the server execution plan might be displayed when used in a query for which no suitable materialized view exists. In this example the server completes a full table scan of three VIDEO5 data tables to return the result set.
| A SQL statement that Discoverer displays in the SQL Inspector dialog: Plan tab |
|---|
SELECT STATEMENT SORT GROUP BY TABLE ACCESS FULL VIDEO5.Sales TABLE ACCESS FULL VIDEO5.Product TABLE ACCESS FULL VIDEO5.Time |
The table below illustrates how the server execution plan might be displayed when used in a query for which a suitable materialized view exists. In this example the server uses the materialized view to return the result set.
| An execution plan that Discoverer displays in the SQL Inspector dialog: Plan tab |
|---|
SELECT STATEMENT SORT GROUP BY TABLE ACCESS FULL NICK.EUL5_MV101510 |
The SQL statement in the table above illustrates how the server can rewrite a query to use a suitable materialized view.
The materialized view is identified in the execution plan by the table name EUL5_MV{identifier}
When Discoverer runs against an Oracle Standard Edition database, Discoverer controls query rewrite to use a suitable summary table. Discoverer displays the SQL sent to the database server in the SQL Inspector dialog: SQL tab.
The table below displays the SQL statement used for a Discoverer worksheet using items from the Video Analysis folder (for more information, see Chapter 27, "Installing the Discoverer sample data EUL, data, and workbook"). The SQL statement shows that the summary table EUL5_SUM100750 is referenced.
| A SQL statement that Discoverer Plus might display in the SQL Inspector dialog: SQL tab |
|---|
SELECT EUL5_SUM100750,"Department", EUL5_SUM100750, "Region", EUL5_SUM100750,"Calendar Date Year", SUM(EUL5_SUM100750,"Profit SUM") FROM ADMINTUTORNF806.EUL5_SUM100750 EUL5_SUM100750 GROUP BY EUL5_SUM10075."Department", EUL5_SUM10075."REgion", EUL5_SUM10075."Calendar Date Year"; |
Discoverer automatically chooses the most appropriate summary table to process the query efficiently. This action is completely transparent to the Discoverer end user.
The next table below displays the SQL statement for the same Discoverer worksheet as above, except that the end user has now drilled down from Year to Month.
The SQL statement shows that Discoverer has rewritten the first part of the query to the summary table EUL5_SUM100750 (as above). However, Discoverer has rewritten the second part of the query (the drill down) to the summary table EUL5_SUM100774.
| A SQL statement that Discoverer Plus might display in the SQL Inspector dialog: SQL tab following a drill down |
|---|
SELECT EUL5_SUM100750,"Department", EUL5_SUM100750, "Region", EUL5_SUM100750,"Calendar Date Year", SUM(EUL5_SUM100750,"Profit SUM") FROM ADMINTUTORNF806.EUL5_SUM100750 EUL5_SUM100750 GROUP BY EUL5_SUM100750."Department", EUL5_SUM100750."Region", EUL5_SUM100750."Calendar Date Year";
SELECT EUL5_SUM100774,"Department", EUL5_SUM100774, "Region", EUL5_SUM100774,"Calendar Date Month", EUL5_SUM100774,"Calendar Date Year", SUM(EUL5_SUM100774,"Profit SUM") FROM ADMINTUTORNF806.EUL5_SUM100774 EUL5_SUM100774 WHERE (EUL5_SUM100774."Calendar Date Year" = TO_DATE('200001011000000','YYYYMMDDHH24MISS') GROUP BY EUL5_SUM100774."Department", EUL5_SUM100774."Region", EUL5_SUM100774,"Calendar Date Month", EUL5_SUM100774."Calendar Date Year";
|
This example consists of five tables, one of which has almost 70,000 records (for more information, see the figure below). The schema and data are taken from the tutorial data.
Consider a query requiring the following items:
Region - (from the STORE table)
Department - (from the PRODUCT table)
Fiscal Year - (from the FISCAL DATE table)
SUM (Dollar_Profit) - (from the SALES FACT table)
This would require a four-table join and an aggregation of all matching rows in SALES_FACT (the table with almost 70,000 rows). Producing results for the query could take several minutes depending on the capability of the server.
On the other hand, if the query could be rewritten to use a single table that already contains the data for Region, Department, Fiscal Year, and SUM (Profit) (see the Sample summary table figure), then the query would produce an almost instantaneous response.
The Sample summary table above stores the information needed by the query at the month level, and only has to be aggregated to the year level. Discoverer therefore uses a single table rather than aggregating from a four table join and performing a full table scan.
A number of characteristics differ between summary folders when using different database versions and are compared in the following table:
For more information about summary folders, see "About folders and summary folders in Discoverer" and Chapter 15, "Creating summary folders manually". The following table compares summary folders in Oracle Standard Edition databases, and Oracle Enterprise Edition databases:
| Question? | Oracle Standard Edition databases | Oracle Enterprise Edition databases |
|---|---|---|
| How are summary folders stored in the database? | Stored as summary tables | Stored as materialized views or summary tables |
| How are summary folders refreshed? | Full refresh only | Full or incremental refresh |
| What kind of refresh is available? | Refresh is On Demand only | Refresh can be On Demand/On Commit |
| How is refresh performed? | Discoverer performs the refresh | The server performs the refresh |
| What performs the summary rewrite? | Discoverer performs the summary rewrite | The server performs the query rewrite |
| What are the terms used to define summary folders? | Summary folders are defined in terms of items and folders | Summary folders are defined in terms of tables and columns |
| Can other applications take advantage of them? | No, only Discoverer | Yes, other applications can take advantage of materialized views |
Notes
Since materialized views are stored in the server, they are available for refresh by other client applications. For example, a materialized view created when using Discoverer can be refreshed through SQL*Plus using the supplied DBMS_MVIEW package.
Discoverer creates summary folders based on:
Discoverer summary tables or materialized views
external summary tables
The main differences between summary folders based on Discoverer summary tables/materialized views and summary folders based on external summary tables are outlined below.
| Question? | Summary folders based on Discoverer summary tables/materialized views | Summary folders based on external summary tables |
|---|---|---|
| How are they populated and maintained? | Automatically by Discoverer Administrator or the Oracle Enterprise Edition database. | Using another application (e.g. SQL*Plus). |
| How are they created? | Using Discoverer Administrator. | Using another application. |
| How are they refreshed? | Automatically at regular intervals (defined by the Discoverer manager in Discoverer Administrator). | Using another application. |
The figure below illustrates how Discoverer creates a summary folder that is based on a Materialized View. The Materialized View is supplied with data from an external summary, which is populated by an external application.
Figure 16-3 Discoverer using external summaries
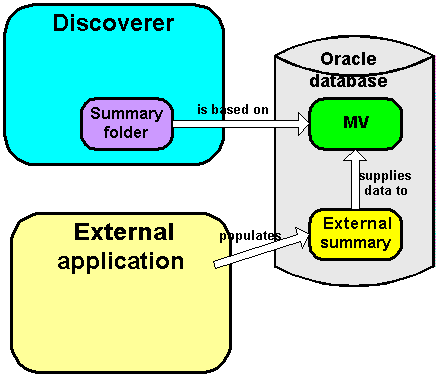
When you create a summary using Discoverer Administrator, you specify how the summary is refreshed, which is in one of the following ways:
by Discoverer - the Manage the refresh of this summary check box has been selected on the "Edit Summary dialog: Refresh tab"
by an external application - the Manage the refresh of this summary check box has been cleared on the "Edit Summary dialog: Refresh tab"
External summary tables are useful when:
you are working with existing warehouse applications that have already generated the summary tables using some other method and you want to maintain them externally
You can create summary folders in Discoverer Administrator by mapping external summary tables or views to EUL items, with Oracle Enterprise Edition databases. However, when you map a view to EUL items, materialized views are not created. This is a restriction imposed by Oracle Enterprise Edition databases. Where materialized views are not created, query rewrite to Discoverer summary tables is used instead. For more information about query rewrite, see "What is query rewrite?".
The differences in Mapping external summary tables or views to EUL items with Oracle Enterprise Edition databases are highlighted in the table below:
| Mapping a table | Mapping a view |
|---|---|
| Where an external summary table is mapped to EUL items, a materialized view definition is created.
In this case the materialized view definition is used for the OracleEnterprise Edition database's query rewrite. |
Where an external view is mapped to EUL items, a materialized view is not created.
In this case summary folders behave in the same manner as for Oracle Standard Edition databases where Discoverer rewrites queries to use Discoverer summary tables. |
When you register an external summary folder in Discoverer Administrator, a materialized view is created in the database (for more information, see "How to create summary folders based on external summary tables"). The name of the materialized view is always identical to the name of the external summary table. This restriction of the Create Materialized View DDL command (within the Database server) means that only one materialized view can be registered against a single table. When you attempt to register more than one external summary folder against the same table you will receive an error message informing you of this restriction.To register more than one external summary folder against a single summary table, you create a database view on top of the summary table and register the database view as an external summary within Discoverer Administrator. Under this scenario a materialized view is not created in the database, and the Discoverer summary management/query rewrite mechanism is used instead (for more information, see "What is query rewrite?"). For more information about creating database views, ask your database administrator.
Oracle Enterprise Edition databases support incremental refresh (when available) enabling you to work with large data warehouses/databases. Parallelism (for more information, see below) is also supported for the refresh operation.
For further information on the conditions required for incremental refresh, see Oracle Database Data Warehousing Guide.
Export from an Oracle Standard Edition database to an Oracle Enterprise Edition database
If you export a business area with summary folders from an Oracle Standard Edition database and then import it into an OracleEnterprise Edition database, materialized views need to be created for these summary folders. For the database server to create the materialized views, you must refresh the summary folders in Discoverer.
Export from an Oracle Enterprise Edition database to an Oracle Standard Edition database
If you export a business area with summary folders from an Oracle Enterprise Edition database and then import it into a Oracle Standard Edition database, Discoverer needs to create summary tables based on the summary folders. For Discoverer to do this, you must refresh the summary folders.